/** * Creates and returns a copy of this object. The precise meaning * of "copy" may depend on the class of the object. * 创建并返回此对象的副本,“复制”的确切含义可能取决于对象的类别 */ protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
自我理解:
clone()方法返回当前对象的副本对象。
测试一:
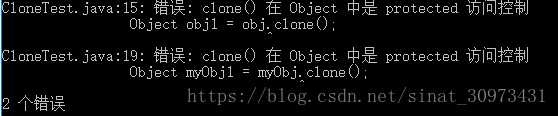
//内部类 class MyObject {} // 定义一个空类,Object类的子类 //公共类 public class CloneTest { // Object类的子类 public static void main(String[] args) { Object obj = new Object(); Object obj1 = obj.clone(); //错误:clone()在Object中是protected访问控制 MyObject myObj = new MyObject(); MyObject myObj1 = myObj.clone(); // 错误: 不兼容的类型: Object无法转换为MyObject // 错误:clone()在Object中是protected访问控制 CloneTest cloneTest = new CloneTest(); CloneTest cloneTest1 = cloneTest.clone(); //错误: 不兼容的类型: Object无法转换为MyObject System.out.println("obj: "+obj+" obj1: "+obj1); System.out.println("myObj: "+myObj+" myObj1: "+myObj1); System.out.println("cloneTet: "+cloneTest+" cloneTest1: "+cloneTest1); } }
修改最后两行代码
//内部类 class MyObject {} // 定义一个空类,Object类的子类 //公共类 public class CloneTest { // Object类的子类 public static void main(String[] args) { Object obj = new Object(); Object obj1 = obj.clone(); //错误:clone()在Object中是protected访问控制 MyObject myObj = new MyObject(); //MyObject myObj1 = myObj.clone(); // 错误: 不兼容的类型: Object无法转换为MyObject // 错误:clone()在Object中是protected访问控制 Object myObj1 = myObj.clone(); CloneTest cloneTest = new CloneTest(); //CloneTest cloneTest1 = cloneTest.clone(); //错误: 不兼容的类型: Object无法转换为MyObject Object cloneTest1 = cloneTest.clone(); System.out.println("obj: "+obj+" obj1: "+obj1); System.out.println("myObj: "+myObj+" myObj1: "+myObj1); System.out.println("cloneTet: "+cloneTest+" cloneTest1: "+cloneTest1); } }
后面的两个错误就没了
分析:
在上面的代码中,公共类CloneTest、内部类MyObject都是Object类的子类,都继承了Object的clone()方法
1. 测试一可以看出,obj.clone()、myObj.clone()受protected访问限制不可见,cloneTest.clone()只是类型转换错误,及cloneTest.clone()通过强制类型转换就可以访问。
说明:CloneTest的对象可以访问自己类型的clone()方法,不能访问父类Object和子类(内部类)MyObject的clone方法,即 不能在一个子类中访问另一个子类的对象的protected方法,尽管这两个子类继承自同一个父类;此外,子类不能访问父类的对象的protected方法,要通过自己类型的对象才能访问。可以看看protected关键字的访问限制。
只能通过自身实例(自身的引用)访问,不能通过父类实例(父类的引用)、其他子类实例(除非是该子类有重写clone()方法)
2、子类使用继承自父类的clone()方法时,返回的对象仍然是父类类型的对象。
测试二:
class MyObject { //重写父类Object的clone方法 protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } } public class CloneTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { MyObject myObj = new MyObject(); Object myObj1 = myObj.clone(); CloneTest cloneTest = new CloneTest(); Object cloneTest1 = cloneTest.clone(); System.out.println("myObj: "+myObj+" myObj1: "+myObj1); System.out.println("cloneTet: "+cloneTest+" cloneTest1: "+cloneTest1); } }
在MyObject类中重写clone()方法,覆盖掉继承自父类的clone()方法,则编译通过,不再有因为protected引起的不可见问题
这时,子类CloneTest可以访问另一个子类MyObject的一个对象的clone()方法。
这时因为,在MyObject类中覆盖clone()方法时,MyObject类和CloneTest类在同一个包下,所以此protected方法对CloneTest类可见。
注意:main方法、重写的clone方法需要throws CloneNotSupportedException,否则编译时会报错,Object类中的clone()没有实现Cloneable接口,运行时就会抛出CloneNotSupportedException异常。
测试三:
//实现Cloneable接口 class MyObject implements Cloneable { protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } } public class CloneTest implements Cloneable { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { MyObject myObj = new MyObject(); Object myObj1 = myObj.clone(); CloneTest cloneTest = new CloneTest(); Object cloneTest1 = cloneTest.clone(); System.out.println("myObj: "+myObj+" myObj1: "+myObj1); System.out.println("cloneTet: "+cloneTest+" cloneTest1: "+cloneTest1); } }
(1)调用clone()返回的对象是一个独立的副本,两个对象地址不同,属性相同。
(2)当我们直接输出两个对象时,尽管原对象的引用是子类类型、副本对象的引用是Object父类类型,输出结果显示对象是子类类型。也就是说,父类类型、子类类型的引用,都可以指向子类类型的对象。
(3)前面看到,clone()返回的对象依然是Object类型,因此,我们只需做强制转换,就可以转化成想要的类型了
文章转载至:https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_30973431/article/details/81872636