本篇将介绍TypeScript的声明文件,并简单演示一下如何编写和使用声明文件。本篇也是这个系列的最后一篇。
一、声明文件简介
TypeScript作为JavaScript的超集,在开发过程中不可避免要引用其他第三方的JavaScript的库。虽然通过直接引用可以调用库的类和方法,但是却无法使用TypeScript诸如类型检查等特性功能。为了解决这个问题,需要将这些库里的函数和方法体去掉后只保留导出类型声明,而产生了一个描述JavaScript库和模块信息的声明文件。通过引用这个声明文件,就可以借用TypeScript的各种特性来使用库文件了。
二、常见库的结构
有以下几种:全局库、CommonJS、AMD、UMD
全局库:
早期版本的jQuery就是使用了全局库的使用方式:
1 (function( window, undefined ) { 2 var jQuery = function( selector, context ) { 3 return new jQuery.fn.init( selector, context, rootjQuery ); 4 } 5 6 // ...... 7 8 window.jQuery = window.$ = jQuery; 9 })(window);
通常会看到:
-
- 顶级的声明是 var 或者 function
- 有 window 或者 document 这些DOM对象存在
- 对象一般会赋值到 window 上
CommonJS
NodeJs模块化采用的规范,声明和使用方式如下:
1 // 模块定义文件 2 exports.module_name = {}; 3 4 // 模块调用文件 5 var module = require('模块定义文件名');
通常会看到:
-
- 赋值给 exports 或者 module.exports
- 无条件调用 require
AMD
前端框架普遍采用的模块化的规范,声明和使用方式如下:
1 // 定义模块 2 define('模块名', ['jquery', ...], function($){ 3 // ...... 4 }); 5 6 // 调用模块 7 require(['模块名'], function(module) { 8 // ...... 9 });
通常会看到:
-
- 无条件调用 define 或者 require
UMD
为了能同时支持上述所有风格的库声明方式,就有了通用模块规范(UMD)。一般会有下面这种声明方式:
1 // moment.js 2 (function (global, factory) { 3 typeof exports === 'object' && typeof module !== 'undefined' ? module.exports = factory() : 4 typeof define === 'function' && define.amd ? define(factory) : 5 global.moment = factory() 6 }(this, function() { 7 function hooks() { 8 // ...... 9 } 10 11 // ...... 12 return hooks; 13 }));
通常会看到:
-
- 在文件顶端会有一大串 typeof XXX 的判断
- 同时有 exports 、 define 这种关键词
通过识别库的结构,采用不用的声明方式来编写声明文件。
三、如何编写声明文件
linq.js实现了在JavaScript里使用Linq语法,在C#有的Linq方法,在它里面几乎都有。下面将在nodejs环境里演示如何编写和使用linq.js的一个简单的声明文件。
1. 创建一个nodejs工程,并通过 npm install linq --save 下载插件包。工程结构如下所示:


1 { 2 "name": "tstest", 3 "version": "1.0.0", 4 "description": "", 5 "main": "index.js", 6 "scripts": { 7 "test": "echo "Error: no test specified" && exit 1", 8 "start": "node dist\main.js" 9 }, 10 "author": "", 11 "license": "ISC", 12 "dependencies": { 13 "linq": "^3.0.5" 14 } 15 }

1 { 2 "compilerOptions": { 3 "target": "es5", 4 "noImplicitAny": false, 5 "module": "commonjs", 6 "removeComments": true, 7 "sourceMap": false, 8 "outDir": "dist" 9 } 10 }
2. 在src目录下新建文件linq.d.ts
1 interface IEnumerator { 2 current: () => any; 3 moveNext: () => void; 4 dispose: () => void; 5 } 6 7 interface Enumerable { 8 getEnumerator: () => IEnumerator; 9 from: (obj: any) => Enumerable; 10 where: (predicate: string | ((x: any) => boolean)) => Enumerable; 11 toArray: () => Array<any>; 12 } 13 14 declare let linq: Enumerable; 15 16 declare module 'linq' { 17 export = linq; 18 }
3. 还是在src目录下新建文件main.ts
1 /// <reference path="linq.d.ts" /> 2 3 import * as Enumerable from 'linq'; 4 5 let result1 = Enumerable.from([1, 2, 3]).where('$>1').toArray(); 6 console.log(`result1 is ${result1}`); 7 8 let result2 = Enumerable.from([1, 2, 3]).where(x => { return x > 2; }).toArray(); 9 console.log(`result2 is ${result2}`);
4. 按下快捷键 Ctrl+Shift+B 编译main.ts文件到dist目录,生成main.js文件
1 "use strict"; 2 var Enumerable = require('linq'); 3 var result1 = Enumerable.from([1, 2, 3]).where('$>1').toArray(); 4 console.log("result1 is " + result1); 5 var result2 = Enumerable.from([1, 2, 3]).where(function (x) { return x > 2; }).toArray(); 6 console.log("result2 is " + result2);
在控制台执行命令 npm run start ,查看输出结果
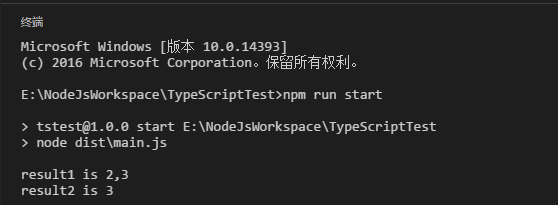
从这个例子里可以看出,声明文件linq.d.ts里只定义了linq的类型和方法名称,在这里我称之为“骨架”。在引用了声明文件后,即可以通过智能感知和强类型检查等特性使用linq模块。编译时会根据配置文件指定的模块标准( "module": "commonjs" )生成对应的文件。因为这个例子的运行环境是nodejs,所以采用commonjs标准。
如果是在前端使用,则要采用AMD标准。下面是采用这个标准后编译生成的文件:
1 define(["require", "exports", 'linq'], function (require, exports, Enumerable) { 2 "use strict"; 3 var result1 = Enumerable.from([1, 2, 3]).where('$>1').toArray(); 4 console.log("result1 is " + result1); 5 var result2 = Enumerable.from([1, 2, 3]).where(function (x) { return x > 2; }).toArray(); 6 console.log("result2 is " + result2); 7 });
linq模块也支持全局库的引用方式。通过修改linq.d.ts,支持全局库引用
1 interface IEnumerator { 2 current: () => any; 3 moveNext: () => void; 4 dispose: () => void; 5 } 6 7 interface Enumerable { 8 getEnumerator: () => IEnumerator; 9 from: (obj: any) => Enumerable; 10 where: (predicate: string | ((x: any) => boolean)) => Enumerable; 11 toArray: () => Array<any>; 12 } 13 14 declare let linq: Enumerable; 15 16 // 全局库引用 17 export as namespace Enumerable; 18 export = linq;
main.ts调用方式也要修改
1 /// <reference path="linq.d.ts" /> 2 3 let result1 = Enumerable.from([1, 2, 3]).where('$>1').toArray(); 4 console.log(`result1 is ${result1}`); 5 6 let result2 = Enumerable.from([1, 2, 3]).where(x => { return x > 2; }).toArray(); 7 console.log(`result2 is ${result2}`);
编译生成的main.js
1 var result1 = Enumerable.from([1, 2, 3]).where('$>1').toArray(); 2 console.log("result1 is " + result1); 3 var result2 = Enumerable.from([1, 2, 3]).where(function (x) { return x > 2; }).toArray(); 4 console.log("result2 is " + result2);
四、声明文件下载
TypeScript2.0支持通过npm下载常用的模块的声明文件,下面借用async模块简单演示一下如何引用和使用常用模块的声明文件。
1. 通过 npm install async --save 下载async模块
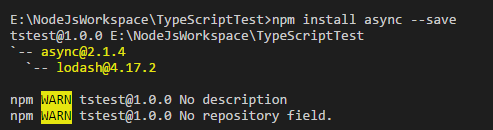
2. 使用 npm install @types/async --save-dev 下载async模块的声明文件。下载完成后会在工程的node_modules文件夹下生成存放声明文件的文件夹

3. main.ts引用声明文件
1 /// <reference types="async" /> 2 import * as async from 'async'; 3 4 // 并行执行方法 5 async.parallel([ 6 cb => { cb(null, 1); }, 7 cb => { cb(null, 2); }, 8 cb => { cb(null, 3); }, 9 ], (err, results) => { 10 console.log(`results is ${results}`); 11 });
这里的引用方式和上面的例子略有不同。上面的例子是用ref注释将文件名引用进来,通过npm下载的声明文件则是引用类型名称( /// <reference types="async" /> )
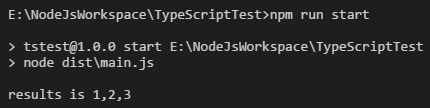
4. 编译之后生成main.js,控制台执行查看结果

1 "use strict"; 2 var async = require('async'); 3 async.parallel([ 4 function (cb) { cb(null, 1); }, 5 function (cb) { cb(null, 2); }, 6 function (cb) { cb(null, 3); }, 7 ], function (err, results) { 8 console.log("results is " + results); 9 });
更多声明文件可以去 http://microsoft.github.io/TypeSearch/ 查找。也许有些模块现在暂时没有声明文件,我们也可以自己编写声明文件后上传到 https://github.com/DefinitelyTyped/DefinitelyTyped,一起共建TypeScript的声明文件仓库。
