面向对象的三大特性
1 继承
2 封装
3 多态
绑定方法与非绑定方法
异常处理
上次复习:
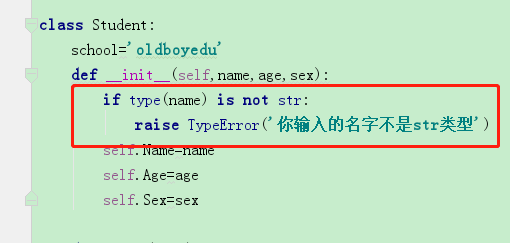
定义类的时候 建议首字母大写
名称空间以字典形式显示
__init__ 这个函数不能有返回值
内部可以有一些其他逻辑,比如判断
举例:
绑定方法在调用的时候 谁调用绑定方法就会把谁传进去
1 继承
2 封装
3 多态
继承 封装 多态 会体现面向对象的可扩展性
1 继承
什么是继承
是一种新建类的方式,新建的类是子类,子类会遗传父类的属性
作用:减少代码的冗余
在Python当中,子类可以继承1个或多个父类
python支持多继承
子类称之为派生类 父类可以被称为基类 派生类
在Python2当中类分为两种 1 经典类 2 新式类
继承的写法:

1 #定义2个父类 2 class Parent1: 3 pass 4 5 class Parent2: 6 pass 7 8 #定义2个子类 9 #子类的单继承 10 class sub1(Parent1): 11 pass 12 #子类的多继承 13 class sub2(Parent1,Parent2): 14 pass 15 #查看子类继承了哪些父类__bases__ 16 # print(sub1.__bases__) #(<class '__main__.Parent1'>,) 17 # print(sub2.__bases__) #(<class '__main__.Parent1'>, <class '__main__.Parent2'>) 18 # 19 # 20 # print(Parent1.__base__)#<class 'object'>
在Python2当中类分为两种
1 经典类 2 新式类:
1 经典类 指的是没有继承object类的类,以及该类的子类
2 新式类 指的是继承object类的类,以及该类的子类
在Python3当中,统一为新式类,默认都继承object
先抽象再继承
1一系列对象得到一种类
2总结类之间相似部分就可以得到父类
3 子类是父类的关系
减少代码的冗余
示例代码:

1 #原来的书写方式 这样写有代码冗余 2 3 #1 student类 4 class Student: 5 school='oldboyedu' 6 def __init__(self,name,age,sex): 7 self.Name=name 8 self.Age=age 9 self.Sex=sex 10 11 def learn(self): 12 print('%s is learning'%self.Name) 13 14 15 class Teacher: 16 school = 'oldboyedu' 17 18 def __init__(self, name, age, sex): 19 self.Name = name 20 self.Age = age 21 self.Sex = sex 22 23 def teach(self): 24 print('%s is teach python'%self.Name) 25 26 #通过继承的方式减少冗余 27 28 class OldboyPerson: 29 school='oldboyedu' 30 def __init__(self,name,age,sex): 31 self.Name=name 32 self.Age=age 33 self.Sex=sex 34 def tell_info(self): 35 print('info:%s-%s-%s'%(self.Name,self.Age,self.Sex)) 36 class Student(OldboyPerson): 37 def learn(self): 38 print('%s is learning'%self.Name) 39 40 def tell_info(self): 41 print('infostuent:%s-%s-%s'%(self.Name,self.Age,self.Sex)) 42 class Teacher(OldboyPerson): 43 def teach(self): 44 print('%s is teach python'%self.Name) 45 def tell_info(self): 46 print('infoteacher:%s-%s-%s'%(self.Name,self.Age,self.Sex)) 47 48 49 #派生的概念 参照对象的属性查找顺序: 50 #对象的名称空间-->对象所在类的数据属性函数属性-->如果没有的话查找继承的父类的数据属性和函数属性 51 52 53 stu1=Student('nod','25','M') 54 tea1=Teacher('luna','26','F') 55 stu1.tell_info() 56 tea1.tell_info()
如果对象的类有继承的话,对象属性的查找顺序是先从对象本身查找,再查找对象的类,
最后再查找对象继承的类
03 子类重用父类的功能,方法
先来一段示例:

1 class Foo: 2 def f1(self): 3 print('foo.f1') 4 def f2(self): 5 print('foo.f2') 6 self.f1() #obj.f1() 7 8 class Bar(Foo): 9 def f1(self): 10 print('bar.f1') 11 12 obj=Bar() 13 14 obj.f2() 15 #以上代码的执行效果 16 #foo.f2 17 #bar.f1
说明:找的顺序始终跟之前一样
如果子类派生出新的属性是以自己的为准
子类派生出新方法要重用父类的功能时 不依赖于继承 重用父类的方法
OldboyPeople.tellinfo(self)
示例代码

1 #子类重用父类的方法示例 2 class OldboyPerson: 3 school='oldboyedu' 4 def __init__(self,name,age,sex): 5 self.Name=name 6 self.Age=age 7 self.Sex=sex 8 def tellinfo(self): #此处的self是1个object 有名称空间 9 print('info is %s-%s-%s'%(self.Name,self.Age,self.Sex)) 10 class Teacher(OldboyPerson): 11 def teach(self): 12 print('%s is teach'%self.Name) 13 #需要重用父类的方法 父类当中本身有tellinfo方法 但是子类当中的tellinfo新增了部分功能 14 def tellinfo(self): 15 print('Teacher info') 16 OldboyPerson.tellinfo(self) 17 class Student(OldboyPerson): 18 def learn(self): 19 print('%s is learning'%self.Name) 20 def tellinfo(self): 21 print('student info') 22 OldboyPerson.tellinfo(self) #重用父类的方法 23 24 stu1=Student('nod','25','M') 25 stu1.tellinfo() 26 tea1=Teacher('luna','26','F') 27 tea1.tellinfo() 28 29 30 #子类重用父类的属性 自己还要新增部分属性示例 31 #不依赖于继承 重用父类的方法 32 33 34 class OldboyPerson: 35 school='oldboyedu' 36 def __init__(self,name,age,sex): 37 self.Name=name 38 self.Age=age 39 self.Sex=sex 40 def tellinfo(self): 41 print('info is %s-%s-%s'%(self.Name,self.Age,self.Sex)) 42 43 class Student(OldboyPerson): 44 def __init__(self,name,age,sex,course,id): 45 OldboyPerson.__init__(self,name,age,sex) 46 self.Course=course 47 self.Id=id 48 def tellinfo(self): 49 print('student info ',end='') 50 OldboyPerson.tellinfo(self) #不依赖于继承 重用父类的方法 51 print('%s-%s'%(self.Course,self.Id)) 52 print(self.__dict__) 53 54 stu2=Student('nod','25','F','linux','51') 55 stu2.tellinfo()
OldboyPerson.__init__是1个函数<function OldboyPerson.__init__ at 0x006C5468>
04 组合
有时候继承不能表达的关系 比如学生与日期 日期是学生的生日
学生有生日 学生有一些自己的属性
学生怎么实现学生有生日的这层关系
将日期的功能集中
让student类可以用到date类的功能
不是继承
采用的是让student类产生的对象新增1个属性 来指向date类的对象的方法
这种思路就是将个类整合到一起
组合区别于继承 指的是什么区别于什么
组合实现代码的重用方式
举例:1--老男孩的老师和老男孩的学生 可以归档为老男孩的人 满足什么是什么 因而可以用继承
实现代码冗余,减少代码的重用
2--用组合的方式实现代码的冗余
示例:
1 class OldboyPerson: 2 def __init__(self, name, age, sex): 3 self.Name = name 4 self.Age = age 5 self.Sex = sex 6 7 def tellinfo(self): 8 print('info is %s-%s-%s' % (self.Name, self.Age, self.Sex)) 9 10 11 class Student(OldboyPerson): 12 def __init__(self, name, age, sex, course, stu_id): 13 OldboyPerson.__init__(self, name, age, sex) 14 self.Course = course 15 self.Stu_id = stu_id 16 17 def tellinfo(self): 18 print('student info ', end='') 19 OldboyPerson.tellinfo(self) 20 21 22 class Teacher(OldboyPerson): 23 def __init__(self, name, age, sex, level, salary): 24 OldboyPerson.__init__(self, name, age, sex) 25 self.Level = level 26 self.Salary = salary 27 28 def tellinfo(self): 29 print('teacher info ', end='') 30 OldboyPerson.tellinfo(self) 31 32 33 class Date: 34 def __init__(self, year, mon, day): 35 self.Year = year 36 self.Mon = mon 37 self.Day = day 38 39 def tell_birth(self): 40 print('birth is %s-%s-%s' % (self.Year, self.Mon, self.Day)) 41 42 43 stu1 = Student('nod', '25', 'F', 'linyx', '51') 44 birth1 = Date('1993', '04', '28') 45 birth1.tell_birth() 46 stu1.birth = birth1 # 将stu1的birth与birth': <__main__.Date object at 0x00820670>绑定 47 print(stu1.__dict__) 48 stu1.birth.tell_birth() 49 tea1 = Teacher('luna', '26', 'M', 10, 50000) 50 51 stu1.tellinfo() 52 tea1.tellinfo()
组合的示例2
class OldboyPerson: def __init__(self, name, age, sex,date_obj): self.Name = name self.Age = age self.Sex = sex self.Date_obj=date_obj def tellinfo(self): print('info is %s-%s-%s' % (self.Name, self.Age, self.Sex)) class Student(OldboyPerson): def __init__(self, name, age, sex, course, stu_id,date_obj): OldboyPerson.__init__(self, name, age, sex,date_obj) self.Course = course self.Stu_id = stu_id def tellinfo(self): print('student info ', end='') OldboyPerson.tellinfo(self) class Teacher(OldboyPerson): def __init__(self, name, age, sex, level, salary,date_obj): OldboyPerson.__init__(self, name, age, sex,date_obj) self.Level = level self.Salary = salary def tellinfo(self): print('teacher info ', end='') OldboyPerson.tellinfo(self) class Date: def __init__(self, year, mon, day): self.Year = year self.Mon = mon self.Day = day def tell_birth(self): print('birth is %s-%s-%s' % (self.Year, self.Mon, self.Day)) date_obj1=Date('1993','04','28') stu1=Student('nod','25','M','linux','51',date_obj1) stu1.Date_obj.tell_birth()
组合的示例3
此处的含义要再推敲推敲
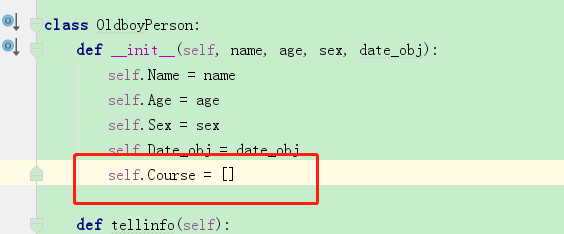

1 """ 2 Description: 3 Author:Nod 4 Date: 5 Record: 6 #---------------------------------v1-----------------------------------# 7 """ 8 9 10 class OldboyPerson: 11 def __init__(self, name, age, sex, date_obj): 12 self.Name = name 13 self.Age = age 14 self.Sex = sex 15 self.Date_obj = date_obj 16 self.Course = [] 17 18 def tellinfo(self): 19 print('info is %s-%s-%s' % (self.Name, self.Age, self.Sex)) 20 21 22 class Student(OldboyPerson): 23 def __init__(self, name, age, sex, stu_id, date_obj): 24 OldboyPerson.__init__(self, name, age, sex, date_obj) 25 26 self.Stu_id = stu_id 27 28 def tell_info(self): 29 print('student info', end='') 30 OldboyPerson.tellinfo(self) 31 32 33 class Teacher(OldboyPerson): 34 def __init__(self, name, age, sex, level, salary, date_obj): 35 OldboyPerson.__init__(self, name, age, sex, date_obj) 36 self.Level = level 37 self.Salary = salary 38 39 def tellinfo(self): 40 print('teacher info', end='') 41 OldboyPerson.tellinfo(self) 42 43 44 class Date: 45 def __init__(self, year, mon, day): 46 self.Year = year 47 self.Mon = mon 48 self.Day = day 49 50 def tell_birth(self): 51 print('birth is %s-%s-%s' % (self.Year, self.Mon, self.Day)) 52 53 54 class Course: 55 def __init__(self, name, price, perioid): 56 self.Name = name 57 self.Price = price 58 self.Perioid = perioid 59 60 def tell_course(self): 61 print('course info is %s-%s-%s' % (self.Name, self.Price, self.Perioid)) 62 63 64 date_obj = Date('1993', '04', '28') 65 date_obj.tell_birth() 66 stu1 = Student('nod', '25', 'F', '51', date_obj) 67 stu1.tellinfo() 68 69 stu1.Date_obj.tell_birth() 70 71 Python = Course('Python', '19000', '115') 72 Linux = Course('Linux', '15000', '100') 73 Python.tell_course() 74 stu1.Course.append(Python) 75 # stu1.Course.tell_course() 76 print(stu1.Course) 77 print('======================1') 78 print(Python) 79 # stu1.Course.append(Linux) 80 # stu1.Course.tell_course() 81 print('======================2') 82 Linux.tell_course() 83 Python.tell_course() 84 # print(stu1.Course) 85 # for course in stu1.Course: 86 # course.tell_course() 87 88 print('测试分割') 89 for item in stu1.Course: 90 item.tell_course()
05 抽象类
主要的作用就是归一化 :归一化的好处就是 成本降低 定义一套标准就可以
假定学车,学的只是开车,而不是各种车型;学会开车这个通用技能;因而其他车
也能开;
因此定义一套标准给子类继承 子类必须按照父类定义的方法去做
类似于java当中的接口
接口
在java中有interface
定义1个父类统一子类的方法
使用成本降低
一切皆文件:
读写

1 """ 2 Description: 3 Author:Nod 4 Date: 18-05-06 5 Record: 6 #---------------------------------v1-----------------------------------# 7 """ 8 9 10 import abc 11 12 class Animal(metaclass=abc.ABCMeta): 13 @abc.abstractmethod 14 def eat(self): 15 print(' is eatting') 16 17 @abc.abstractmethod 18 def run(self): 19 print('is running') 20 21 class People(Animal): 22 def eat(self): 23 print(' is eatting') 24 25 def run(self): 26 print(' is running') 27 28 class Pig(Animal): 29 def eat(self): 30 print('is eatting') 31 32 def run1(self): 33 #如果此处不为run 34 # 就或产生该报错TypeError: Can't instantiate abstract class Pig with abstract methods run 35 print('is running') 36 #当Animal类当中定义了metaclass=abc.ABCMeta 37 #@abc.abstractmethod 就说明继承animal类的子类的方法中必须要继承父类的方法名称 不能修改方法 38 #名称 但是方法名称内的代码是可以修改的 39 40 peo1=People() 41 pig1=Pig() 42 43 44 45 46 #模仿Linux系统 47 48 49 import abc 50 class File(metaclass=abc.ABCMeta): 51 @abc.abstractmethod 52 def write(self): 53 print(' is writing') 54 55 @abc.abstractmethod 56 def read(self): 57 print('is reading') 58 59 60 class Disk(File): 61 def write(self): 62 print(' is writing') 63 64 def read(self): 65 print('is reading') 66 67 class Process(File): 68 def write(self): 69 print(' is writing') 70 71 def read(self): 72 print('is reading')
