1.IOS沙盒机制
IOS中的沙盒机制(SandBox)是一种安全体系,它规定了应用程序只能在为该应用创建的文件夹内读取文件,不可以访问其他地方的内容。所有的非代码文件都保存在这个地方,比如图片、声音、属性列表和文本文件等。
1.每个应用程序都在自己的沙盒内
2.不能随意跨越自己的沙盒去访问别的应用程序沙盒的内容
3.应用程序向外请求或接收数据都需要经过权限认证
2.查看模拟器沙盒文件夹
查看模拟器的沙盒文件夹在Mac电脑上的存储位置,文件都在个人用户名文件夹下的一个隐藏文件夹里,中文叫资源库,他的目录其实是Library。
首先,这个文件夹是被隐藏的,所以要先将这些文件显示出来,打开命令行:
显示Mac隐藏文件的命令:defaults write com.apple.finder AppleShowAllFiles -bool true
隐藏Mac隐藏文件的命令:defaults write com.apple.finder AppleShowAllFiles -bool false
然后重新启动Finder(点击屏幕左上角苹果标志——强制退出——选择Finder然后点击重新启动),这个时候在重新打开Finder就可以看到被隐藏的文件了。
然后按下图进入相应的文件夹,就可以到模拟器的沙盒文件目录了:

接着进入一个模拟器版本,我这里是5.1。
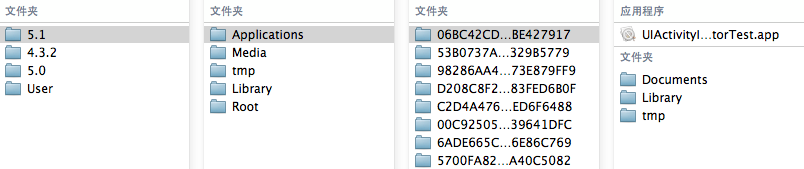
然后可以看到Applications下面存放的就是模拟器中所装的开发的应用程序,随便进入一个后可以看到,一个沙盒中包含了四个部分,如图所示:

分别是
.app文件,这个就是可运行的应用文件;
Documents,苹果建议将程序中创建的或在程序中浏览到的文件数据保存在该目录下,iTunes备份和恢复的时候会包括此目录;
Library,存储程序的默认设置或其它状态信息,Library下有两个子文件夹Caches和Preferences:
Library/Caches:保存应用运行时生成的需要持久化的数据(缓存文件),iTunes不会备份该目录,此目录下文件不会在应用退出删除;
Library/Preferences:应用程序的偏好设置文件,iTunes 同步设备时会备份该目录。您不应该直接创建偏好设置文件,而是应该使用NSUserDefaults类来取得和设置应用程序的偏好设置。
tmp,保存应用运行时所需的临时数据,使用完毕后再将相应地文件从该目录删除,应用没有运行时,系统也可能会清除该目录下得所有文件。iTunes 同步设备时不会备份该目录。
还有一种比较简单的办法就是直接点击Finder图标右键——前往文件夹——输入/Users/UserName/Library/Application Support/iPhone Simulator ,然后确认就可以了。UserName是你本机的用户名。
但xcode6上的一些路径都作了更改。
模拟器的路径更改为:/Users/UserName/ Library/Developer/CoreSimulator。

Devices文件夹下的每一个文件对应Xcode6下的一个模拟器,可以根据各个文件夹下的device.plist文件得到具体的是哪个模拟器:

Xcode6中沙盒的路径为:/Users/UserName/Library/Developer/CoreSimulator/Devices/模拟器UDID/data/Containers/Data/Application/对应应用程序文件夹
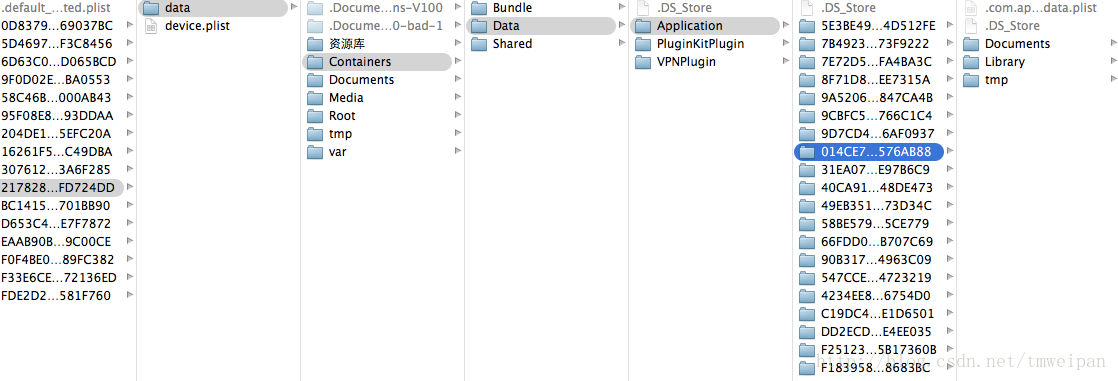 Xcode6中偏好设置目录的路径为:/Users/UserName/Library/Developer/CoreSimulator/Devices/模拟器UDID/data/Containers/Bundle/Applications/对应应用程序文件夹/Library/Preferences
Xcode6中偏好设置目录的路径为:/Users/UserName/Library/Developer/CoreSimulator/Devices/模拟器UDID/data/Containers/Bundle/Applications/对应应用程序文件夹/Library/Preferences


1 //获取根目录 2 NSString *homePath = NSHomeDirectory(); 3 NSLog(@"Home目录:%@",homePath); 4 5 //获取Documents文件夹目录,第一个参数是说明获取Doucments文件夹目录,第二个参数说明是在当前应用沙盒中获取,所有应用沙盒目录组成一个数组结构的数据存放 6 NSArray *docPath = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory,NSUserDomainMask, YES); 7 NSString *documentsPath = [docPath objectAtIndex:0]; 8 NSLog(@"Documents目录:%@",documentsPath); 9 10 //获取Cache目录 11 NSArray *cacPath = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSCachesDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES); 12 NSString *cachePath = [cacPath objectAtIndex:0]; 13 NSLog(@"Cache目录:%@",cachePath); 14 15 //Library目录 16 NSArray *libsPath = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSLibraryDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES); 17 NSString *libPath = [libsPath objectAtIndex:0]; 18 NSLog(@"Library目录:%@",libPath); 19 20 //temp目录 21 NSString *tempPath = NSTemporaryDirectory(); 22 NSLog(@"temp目录:%@",tempPath);
输出结果如下:
1 2012-08-03 11:10:24.325 SandBoxTest[12549:f803] Home目录:/Users/Ryan/Library/Application Support/iPhone Simulator/5.1/Applications/A6B99E5A-E2C7-46E9-867A-4E7619F0DA45 2 3 2012-08-03 11:10:24.325 SandBoxTest[12549:f803] Documents目录:/Users/Ryan/Library/Application Support/iPhone Simulator/5.1/Applications/A6B99E5A-E2C7-46E9-867A-4E7619F0DA45/Documents 4 5 2012-08-03 11:10:24.326 SandBoxTest[12549:f803] Cache目录:/Users/Ryan/Library/Application Support/iPhone Simulator/5.1/Applications/A6B99E5A-E2C7-46E9-867A-4E7619F0DA45/Library/Caches 6 7 2012-08-03 11:10:24.326 SandBoxTest[12549:f803] Library目录:/Users/Ryan/Library/Application Support/iPhone Simulator/5.1/Applications/A6B99E5A-E2C7-46E9-867A-4E7619F0DA45/Library 8 9 2012-08-03 11:10:24.326 SandBoxTest[12549:f803] temp目录:/var/folders/7z/1wj5h8zx7b59c02pxmpynd500000gn/T/
这些是模拟器上的目录。真机上的Home目录是/var/mobile/Applications/这个目录下的,和模拟器不一样。这个是Home目录,其他的子目录和模拟器一样。
4、NSString类路径的处理方法
文件路径的处理,例如:
NSString *path = @"/Uesrs/apple/testfile.txt"
常用方法如下:
获得组成此路径的各个组成部分,结果:("/","User","apple","testfile.txt")
- (NSArray *)pathComponents;
提取路径的最后一个组成部分,结果:testfile.txt
- (NSString *)lastPathComponent;
删除路径的最后一个组成部分,结果:/Users/apple
- (NSString *)stringByDeletingLastPathCpmponent;
将path添加到现有路径的末尾,结果:/Users/apple/testfile.txt/app.txt
- (NSString *)stringByAppendingPathConmponent:(NSString *)str;
取路径最后部分的扩展名,结果:text
- (NSString *)pathExtension;
删除路径最后部分的扩展名,结果:/Users/apple/testfile
- (NSString *)stringByDeletingPathExtension;
路径最后部分追加扩展名,结果:/User/apple/testfile.txt.jpg
- (NSString *)stringByAppendingPathExtension:(NSString *)str;
根据components中的元素来构建路径
+ (NSString *)pathWithComponents:(NSArray *)components。
5、NSData
NSData是用来包装数据的;NSData存储的是二进制数据,屏蔽了数据之间的差异,文本、音频、图像等数据都可用NSData来存储。
NSData的用法:
(1)NSString与NSData相互转换
NSData-> NSString
NSString *aString = [[NSString alloc] initWithData:adata encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSString->NSData
NSString *aString = @"1234abcd";
NSData *aData = [aString dataUsingEncoding: NSUTF8StringEncoding];
将data类型的数据,转成UTF8的数据
+(NSString *)dataToUTF8String:(NSData *)data
{
NSString *buf = [[NSString alloc] initWithData:data encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
return [buf autorelease];
}
将string转换为指定编码
+(NSString *)changeDataToEncodinString:(NSData *)data encoding:(NSStringEncoding )encoding
{
NSString *buf = [[[NSString alloc] initWithData:data encoding:encodin] autorelease];
return buf;
}
(2)NSData 与 UIImage
NSData->UIImage
UIImage *aimage = [UIImage imageWithData: imageData];
//例:从本地文件沙盒中取图片并转换为NSData
NSString *path = [[NSBundle mainBundle] bundlePath];
NSString *name = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"ceshi.png"];
NSString *finalPath = [path stringByAppendingPathComponent:name];
NSData *imageData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile: finalPath];
UIImage *aimage = [UIImage imageWithData: imageData];
(3)NSData与NSArray 、NSDictionary
+(NSString *)getLocalFilePath:(NSString *) fileName
{
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@/%@%@", NSHomeDirectory(),@“Documents”,fileName];
}
包括将NSData写进Documents目录、从Documents目录读取数据、在进行网络数据通信的时候,经常会遇到NSData类型的数据。在该数据是dictionary结构的情况下,系统没有提供现成的转换成NSDictionary的方法,为此可以通过Category对NSDictionary进行扩展,以支持从NSData到NSDictionary的转换。声明和实现如下:
+ (NSDictionary *)dictionaryWithContentsOfData:(NSData *)data {
CFPropertyListRef list = CFPropertyListCreateFromXMLData(kCFAllocatorDefault, (CFDataRef)data, kCFPropertyListImmutable, NULL);
if(list == nil) return nil;
if ([(id)list isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]]) {
return [(NSDictionary *)list autorelease];
} else {
CFRelease(list);
return nil;
}
}
6、写入文件与读取文件
1 NSArray *docPath = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory,NSUserDomainMask, YES); 2 NSString *documentsPath = [docPath objectAtIndex:0]; 3 //写入文件 4 if (!documentsPath) { 5 NSLog(@"目录未找到"); 6 }else { 7 NSString *filePath = [documentsPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"test.txt"]; 8 NSArray *array = [NSArray arrayWithObjects:@"Title",@"Contents", nil]; 9 [array writeToFile:filePath atomically:YES]; 10 }
创建成功后打开文件夹目录,可以看到test.txt文件:

接下来是把该文件中的内容读出来:
1 //读取文件 2 NSArray *docPath = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory,NSUserDomainMask, YES); 3 NSString *documentsPath = [docPath objectAtIndex:0]; 4 NSString *readPath = [documentsPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"test.txt"]; 5 NSArray *fileContent = [[NSArray alloc] initWithContentsOfFile:readPath]; 6 NSLog(@"文件内容:%@",fileContent);
输出结果如下:
1 2012-08-03 11:26:53.594 SandBoxTest[12642:f803] 文件内容:( 2 Title, 3 Contents 4 )
7、文件管理常用方法
NSFileManager
创建文件管理
NSFileManager *fileManager = [NSFileManager defaultManager];
创建一个文件并写入数据
- (BOOL)createFileAtPath:(NSString *)path contents:(NSData *)data attributes:(NSDictionary *)attr;
从一个文件中读取数据
- (NSData *)contentsAtPath:(NSString *)path;
scrPath路径上的文件移动到dstPath路径上,注意这里的路径是文件路径而不是目录
- (BOOL)moveItemAtPath:(NSString *)srcPath toPath:(NSString *)dstPath error:(NSError **) error;
scrPath路径上的文件复制到dstPath路径上
- (BOOL)copyItemAtPath:(NSString *)scrPath toPath:(NSString *)dstPath error:(NSError **) error;
比较两个文件的内容是否一样
- (BOOL)contentsEqualAtPath:(NSString *)path1 andPath:(NSString *)path2;
文件是否存在
- (BOOL)fileExistsAtPath:(NSString *)path;
移除文件
- (BOOL)removeItemAtPath:(NSString *)path error:(NSError **) error;
部分方法应用实例:
(1)在Documents里创建目录
创建一个叫test的目录:
1 NSArray *paths = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES); 2 NSString *documentsDirectory = [paths objectAtIndex:0]; 3 NSLog(@"documentsDirectory%@",documentsDirectory); 4 NSFileManager *fileManager = [NSFileManager defaultManager]; 5 NSString *testDirectory = [documentsDirectory stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"test"]; 6 // 创建目录 7 [fileManager createDirectoryAtPath:testDirectory withIntermediateDirectories:YES attributes:nil error:nil];
启动程序,这时候目录就创建了:

创建文件怎么办呢?接着上面的代码 testPath 要用stringByAppendingPathComponent拼接上你要生成的文件名,比如test00.txt。这样才能在test下写入文件。
往test文件夹里写入三个文件,test00.txt ,test22.txt,text.33.txt。内容都是写入内容,write String。
实现代码如下:
1 NSString *testPath = [testDirectory stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"test00.txt"]; 2 NSString *testPath2 = [testDirectory stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"test22.txt"]; 3 NSString *testPath3 = [testDirectory stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"test33.txt"]; 4 5 6 NSString *string = @"写入内容,write String"; 7 [fileManager createFileAtPath:testPath contents:[string dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding] attributes:nil]; 8 [fileManager createFileAtPath:testPath2 contents:[string dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding] attributes:nil]; 9 [fileManager createFileAtPath:testPath3 contents:[string dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding] attributes:nil];
结果如下:
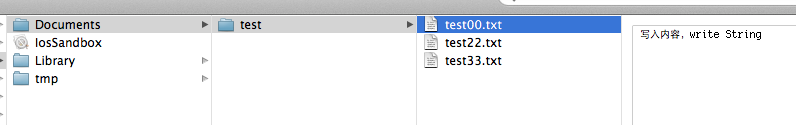
如果要在在Documents目录下创建文件,直接更改文件路径就可以了。
(2)获取目录列里所有文件名
两种方法获取:subpathsOfDirectoryAtPath 和 subpathsAtPath
1 NSArray *paths = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES); 2 NSString *documentsDirectory = [paths objectAtIndex:0]; 3 NSLog(@"documentsDirectory%@",documentsDirectory); 4 NSFileManager *fileManage = [NSFileManager defaultManager]; 5 NSString *myDirectory = [documentsDirectory stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"test"]; 6 NSArray *file = [fileManage subpathsOfDirectoryAtPath: myDirectory error:nil]; 7 NSLog(@"%@",file); 8 NSArray *files = [fileManage subpathsAtPath: myDirectory ]; 9 NSLog(@"%@",files);
获取上面刚才test文件夹里的文件名,打印结果:
2012-06-17 23:23:19.684 IosSandbox[947:f803] fileList:(
".DS_Store",
"test00.txt",
"test22.txt",
"test33.txt"
)
2012-06-17 23:23:19.686 IosSandbox[947:f803] fileLit(
".DS_Store",
"test00.txt",
"test22.txt",
"test33.txt"
)
两种方法都可以,隐藏的文件也打印出来了。还有另外一种方法,大家也可以试试:
1 NSArray *paths = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES); 2 NSString *documentsDirectory = [paths objectAtIndex:0]; 3 NSLog(@"documentsDirectory%@",documentsDirectory); 4 NSFileManager *fileManager = [NSFileManager defaultManager]; 5 NSString *enuPath = [documentsDirectory stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Test"]; 6 NSDictionaryEnumerator *dirEnum = [fileManager enumeratorAtPath:enuPath]; 7 NSString *file = nil; 8 while ((file = [dirEnum nextObject]} != nil) 9 { 10 NSLog(@"%@",file); 11 }
(3)判断文件是否存在、删除文件
1 if([fileManager fileExistsAtPath:filePath]) 2 { 3 [fileManager removeItemAtPath:fileName error:nil]; 4 }
(4)混合数据的读写
用NSMutableData创建混合数据,然后写到文件里。并按数据的类型把数据读出来。写入数据:
1 NSString * fileName = @"testFileNSFileManager.txt"; 2 NSArray *paths = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES); 3 NSString *documentsDirectory = [paths objectAtIndex:0]; 4 //获取文件路径 5 NSString *path = [documentsDirectory stringByAppendingPathComponent:fileName]; 6 //待写入的数据 7 NSString *temp = @"nihao 世界"; 8 int dataInt = 1234; 9 float dataFloat = 3.14f; 10 //创建数据缓冲 11 NSMutableData *writer = [[NSMutableData alloc] init]; 12 //将字符串添加到缓冲中 13 [writer appendData:[temp dataUsingEncoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]]; 14 //将其他数据添加到缓冲中 15 [writer appendBytes:&dataInt length:sizeof(dataInt)]; 16 [writer appendBytes:&dataFloat length:sizeof(dataFloat)]; 17 //将缓冲的数据写入到文件中 18 [writer writeToFile:path atomically:YES];
我们看看数据怎么样了:

我们看到后面的是乱码,那是中文被转成了NSData后,还有int float的二进制。
读取刚才写入的数据:
1 //读取数据: 2 int intData; 3 float floatData = 0.0; 4 NSString *stringData; 5 6 NSData *reader = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:path]; 7 stringData = [[NSString alloc] initWithData:[reader subdataWithRange:NSMakeRange(0, [temp length])] 8 encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding]; 9 [reader getBytes:&intData range:NSMakeRange([temp length], sizeof(intData))]; 10 [reader getBytes:&floatData range:NSMakeRange([temp length] + sizeof(intData), sizeof(floatData))]; 11 NSLog(@"stringData:%@ intData:%d floatData:%f", stringData, intData, floatData);
打印出来的结果:
2012-06-17 23:51:14.723 IosSandbox[1285:f803] stringData:nihao hello! intData:1234332 floatData:3.140000
这里把写入的汉字改成了 hello。因为[temp length]算长度时,把中文算成一位了,出来的结果有误。
(5)获取文件大小
1 NSFileManager *fileManager = [NSFileManager defaultManager]; 2 NSDictionary *attrDic = [fileManager attributesOfItemAtpath:sourcePath error:nil]; //获得文件的属性字典 3 NSNumber *fileSize = [attrDic objectForKey:NSFileSize];
(6)移动、复制文件
移动文件(重命名)
1 NSString *toPath = [NSHomeDirectory( ) stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"hellogod/NewTestament.txt"]; 2 NSString *path = [toPath stringByDeletingLastPathComponent]; 3 [fileManager createDirectoryAtPath:path withIntermediateDirectories:YES attributes:nil error:nil]; 4 NSError *error; 5 BOOL isSuccess = [fileManager moveItemAtPath:filePath toPath:toPath error:&error];
复制文件(重命名)
1 NSString *copyPath = [NSHomeDirectory( ) stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"备份/OldTestament.txt"]; 2 [fileManager createDirectoryAtPath:[toPath stringByDeletingLastPathComponent] withIntermediateDirectories:YES attributes:nil error:nil]; 3 BOOL success = [fileManager copyItemAtPath:toPath toPath:toPath error:nil];
(7)读取内容
1 //读取内容 2 NSData *fileData = [fileManager contentsAtPath:filePath]; 3 NSString *content = [[NSString alloc] initWithData:fileData dataUsingEncoding: NSUTF8StringEncoding]; 4 5 //NSData 6 NSString *filePath = [path stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"holyBible.txt"]; 7 NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentOfFile:filePath]; 8 9 //NSString 10 NSString *filePath = [path stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"holyBible.txt"]; 11 NSString *content = [[NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:filePath encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];
参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/taintain1984/archive/2013/03/19/2969201.html
http://blog.csdn.net/totogo2010/article/details/7671144