$ color{#0066ff}{ 题目描述 }$
如果一个字符串可以被拆分为(AABB)的形式,其中 A和 B是任意非空字符串,则我们称该字符串的这种拆分是优秀的。
例如,对于字符串(aabaabaa),如果令 (A=aab),(B=a),我们就找到了这个字符串拆分成 (AABB)的一种方式。
一个字符串可能没有优秀的拆分,也可能存在不止一种优秀的拆分。比如我们令 (A=a),(B=baa),也可以用 (AABB)表示出上述字符串;但是,字符串 (abaabaa) 就没有优秀的拆分。
现在给出一个长度为 (n)的字符串(S),我们需要求出,在它所有子串的所有拆分方式中,优秀拆分的总个数。这里的子串是指字符串中连续的一段。
以下事项需要注意:
- 出现在不同位置的相同子串,我们认为是不同的子串,它们的优秀拆分均会被记入答案。
- 在一个拆分中,允许出现(A=B)。例如 (cccc) 存在拆分(A=B=c)。
- 字符串本身也是它的一个子串。
(color{#0066ff}{输入格式})
每个输入文件包含多组数据。
输入的第一行只有一个整数(T),表示数据的组数。保证 (1≤T≤10)。
接下来 (T)行,每行包含一个仅由英文小写字母构成的字符串(S),意义如题所述。
(color{#0066ff}{输出格式})
输出 (T)行,每行包含一个整数,表示字符串(S) 所有子串的所有拆分中,总共有多少个是优秀的拆分。
(color{#0066ff}{输入样例})
4
aabbbb
cccccc
aabaabaabaa
bbaabaababaaba
(color{#0066ff}{输出样例})
3
5
4
7
(color{#0066ff}{数据范围与提示})
我们用(S_{i,j})表示字符串 (S)第 (i)个字符到第(j)个字符的子串(从(1)开始计数)。
第一组数据中,共有 (3)个子串存在优秀的拆分:
(S_{1,4}=aabb),优秀的拆分为(A=a),(B=b);
(S_{3,6}=bbbb),优秀的拆分为 (A=b),(B=b);
(S_{1,6}=aabbbb),优秀的拆分为 (A=a),(B=bb)。
而剩下的子串不存在优秀的拆分,所以第一组数据的答案是 (3)。
第二组数据中,有两类,总共(4)个子串存在优秀的拆分:
对于子串 (S_{1,4}=S_{2,5}=S_{3,6}=cccc),它们优秀的拆分相同,均为(A=c),(B=c),但由于这些子串位置不同,因此要计算(3) 次;
对于子串 (S_{1,6}=cccccc),它优秀的拆分有 (2)种:(A=c),$B=cc $和 (A=cc),(B=c),它们是相同子串的不同拆分,也都要计入答案。
所以第二组数据的答案是(3+2=5)。
第三组数据中,(S_{1,8})和 (S_{4,11}) 各有 (2) 种优秀的拆分,其中(S_{1,8}) 是问题描述中的例子,所以答案是(2+2=4)。
第四组数据中,(S_{1,4},S_{6,11},S_{7,12},S_{2,11},S_{1,8}) 各有 (1)种优秀的拆分,(S_{3,14}) 有(2) 种优秀的拆分,所以答案是 (5+2=7)。
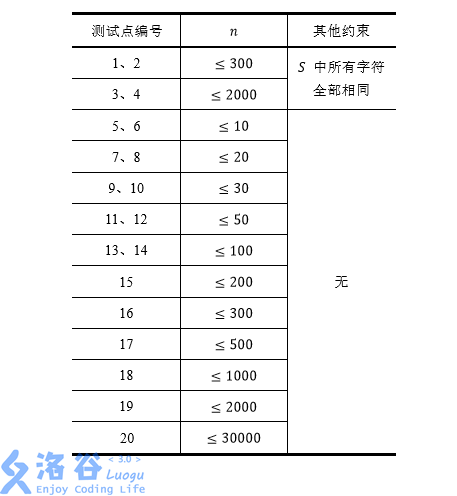
对于全部的测试点,保证(1≤T≤10)。以下对数据的限制均是对于单组输入数据而言的,也就是说同一个测试点下的(T)组数据均满足限制条件。
我们假定(n)为字符串(S)的长度,每个测试点的详细数据范围见下表:
(color{#0066ff}{题解})
AA和BB本质上是一样的,都是两个相同的串连接,我们考虑枚举AA和BB中间的那个分界线,那么,以那个分界线为末尾的AA和以那个分界线为开头的BB的方案乘一下就是当前位置对答案的贡献
我们可以发现, A和B的长度都不会超过(n/2)
我们考虑分段来维护这个东西
枚举段长从1到n的一半,枚举(1,len+1,2*len+1,3*len+1dots frac{n}{len}*len + 1)这些分界线
统计两个分界线之间的贡献
把字符串正反跑一遍SA,然后RMQ快速求出这两个分界线的向前LCPx和向后LCPy
如果(x + y> =len + 1)那么就说明这是一个合法的拆分,中间重合的部分,就是l和r变化的范围
在l和r的范围上差分一下就行了
// luogu-judger-enable-o2
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
LL in() {
char ch; LL x = 0, f = 1;
while(!isdigit(ch = getchar()))(ch == '-') && (f = -f);
for(x = ch ^ 48; isdigit(ch = getchar()); x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48));
return x * f;
}
const int maxn = 5e4 + 10;
int lg[maxn];
struct SA {
char s[maxn];
int rk[maxn], sa[maxn], c[maxn], x[maxn], y[maxn], h[maxn], n, m, st[maxn][20];
void init() {
memset(x, 0, sizeof x);
memset(y, 0, sizeof y);
memset(h, 0, sizeof h);
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
memset(sa, 0, sizeof sa);
memset(rk, 0, sizeof rk);
memset(c, 0, sizeof c);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) x[i] = y[i] = h[i] = st[i][0] = sa[i] = rk[i] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) c[i] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) c[x[i] = s[i]]++;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) c[i] += c[i - 1];
for(int i = n; i >= 1; i--) sa[c[x[i]]--] = i;
for(int k = 1; k <= n; k <<= 1) {
int num = 0;
for(int i = n - k + 1; i <= n; i++) y[++num] = i;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if(sa[i] > k) y[++num] = sa[i] - k;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) c[i] = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) c[x[i]]++;
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++) c[i] += c[i - 1];
for(int i = n; i >= 1; i--) sa[c[x[y[i]]]--] = y[i], y[i] = 0;
std::swap(x, y);
x[sa[1]] = 1, num = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) x[sa[i]] = (y[sa[i]] == y[sa[i - 1]] && y[sa[i] + k] == y[sa[i - 1] + k])? num : ++num;
if(num == n) break;
m = num;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) rk[i] = x[i];
int H = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(rk[i] == 1) continue;
if(H) H--;
int j = sa[rk[i] - 1];
while(i + H <= n && j + H <= n && s[i + H] == s[j + H]) H++;
h[rk[i]] = H;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) st[i][0] = h[i];
for(int j = 1; j <= 18; j++)
for(int i = 1; i + (1 << j) - 1 <= n; i++)
st[i][j] = std::min(st[i][j - 1], st[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1]);
}
int LCP(int x, int y) {
x = rk[x], y = rk[y];
if(x > y) std::swap(x, y);
x++;
int l = lg[y - x + 1];
return std::min(st[x][l], st[y - (1 << l) + 1][l]);
}
void ins(char *s, int len) {
n = len, m = 122;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) this->s[i] = s[i];
}
}A, B;
LL pre[maxn], nxt[maxn];
char s[maxn];
int main() {
lg[0] = -1;
for(int i = 1; i < maxn; i++) lg[i] = lg[i >> 1] + 1;
for(int T = in(); T --> 0;) {
scanf("%s", s + 1);
int n = strlen(s + 1);
A.ins(s, n);
std::reverse(s + 1, s + n + 1);
B.ins(s, n);
A.init(), B.init();
memset(pre, 0, sizeof pre), memset(nxt, 0, sizeof nxt);
for(int L = 1; L <= n >> 1; L++)
for(int i = 1; i + L <= n; i += L) {
int j = i + L;
int xx = A.LCP(i, j), yy = B.LCP(n - i + 1, n - j + 1);
xx = std::min(xx, L), yy = std::min(yy, L);
if(xx + yy < L + 1) continue;
int nowlen = xx + yy - L - 1;
nxt[i - yy + 1]++, nxt[i - yy + nowlen + 2]--;
pre[j + xx - nowlen - 1]++, pre[j + xx]--;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) pre[i] += pre[i - 1], nxt[i] += nxt[i - 1];
LL ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) ans += pre[i] * nxt[i + 1];
printf("%lld
", ans);
}
return 0;
}