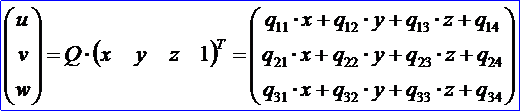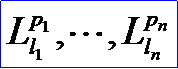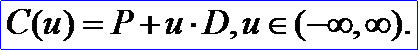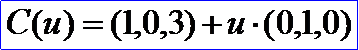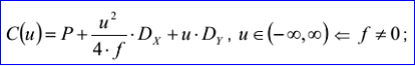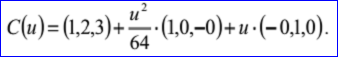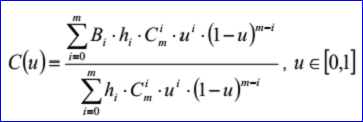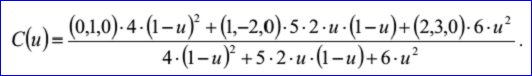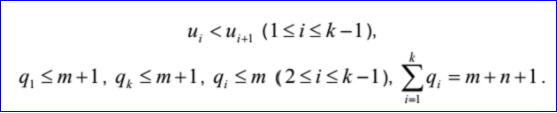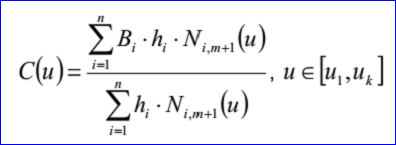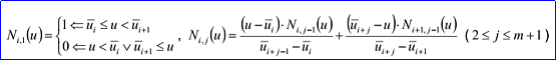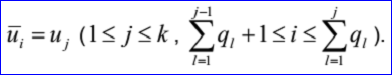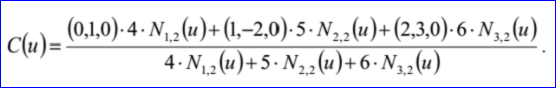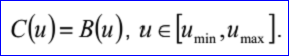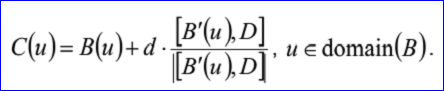OpenCascade BRep Format Description
摘要Abstract:本文结合OpenCascade的BRep格式描述文档和源程序,对BRep格式进行分析,详细说明BRep的数据组织形式。结合源程序,可以对OpenCascade中Modeling Data模块中的模型数据结构进行理解。
关键字Key Words:OpenCascade, BRep Format, ModelingData
一、引言 Introduction
OpenCascade中的BRep格式主要用来存储3D模型,也可用来存储由下列元素组成的模型:vertices, edges, wires, faces, shells, solids, compsolids, compounds, edge triangulations, face triangulations, polylines on triangulations, space location and orientation.
本格式的目的就是为了便于理解,也使用了类似BNF的定义方式。以下章节都是按下面的格式组织的:
l 该部分的示例;
l 该部分的类BNF定义;
l 该部分的详细说明;
l 该部分的源程序片段。
二、通用结构 Format Common Structure
BRep格式文件的读写采用了ASCII的编码方式,该格式的数据都是文本形式存储。
BRep格式使用了下面的BNF术语:
1) < >:换行;
2) <_ >:
3) <_>:空格;
4) <flag>:标志位:0和1;
5) <int>:整数,范围-231到231-1;
6) <real>:实数,范围-1.7976931348623159X10308到1.7976931348623158X10308;
7) <2D point>:二维点,两个实数;
8) <3D point>:三维点,三个实数;
9) <2D direction>:二维方向矢量,两个实数,平方和为1,即为单位方向矢量;
10) <3D direction>:三维方向矢量,三个实数,平方和为1,即为单位方向矢量;
11) <+>
BRep格式包含以下部分:
1) <content type>
2) <version>
3) <locations>
4) <geometry>
5) <shapes>
<content type>部分:
<content type>也可以有其它的值。
<version>部分:
不同版本之间的区别将会在本文档中说明。
三、<locations>部分 Section <locations>
示例:
BNF 定义:
详细说明:
<location data 1>定义了3X4的矩阵Q,描述了三维空间的线性变换,并满足如下约定:
矩阵Q是线性变换矩阵,它可以通过矩阵乘法将一个点(x, y, z)变换成另外一点(u, v, w):
Q也可能是以下基本变换矩阵的组合:
1) 平移变换矩阵:
2) 绕任意轴旋转的变换矩阵,轴的方向为D(Dx, Dy, Dz),旋转角度ψ:
3) 缩放变换矩阵:
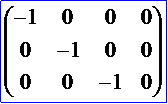
4) 中心对称变换矩阵:
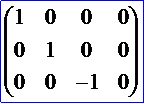
5) 轴对称变换矩阵:
6) 平面对称变换矩阵:
<location data 2>解释为组合变换的幂。<location data 2>是整数对li, pi的序列。这个序列将被解释为:
Lli是<location record>部分的变换矩阵。
读取<locations>部分的类为TopTools_LocationSet,程序代码如下所示:
1 //======================================================================= 2 //function : Read 3 //purpose : 4 //======================================================================= 5 void TopTools_LocationSet::Read(Standard_IStream& IS) 6 { 7 myMap.Clear(); 8 9 char buffer[255]; 10 Standard_Integer l1,p; 11 12 IS >> buffer; 13 if (strcmp(buffer,"Locations")) { 14 cout << "Not a location table "<<endl; 15 return; 16 } 17 18 Standard_Integer i, nbLoc; 19 IS >> nbLoc; 20 21 TopLoc_Location L; 22 gp_Trsf T; 23 24 //OCC19559 25 Message_ProgressSentry PS(GetProgress(), "Locations", 0, nbLoc, 1); 26 for (i = 1; i <= nbLoc&& PS.More(); i++, PS.Next()) { 27 if ( !GetProgress().IsNull() ) 28 GetProgress()->Show(); 29 30 Standard_Integer typLoc; 31 IS >> typLoc; 32 33 if (typLoc == 1) { 34 ReadTrsf(T,IS); 35 L = T; 36 } 37 38 else if (typLoc == 2) { 39 L = TopLoc_Location(); 40 IS >> l1; 41 while (l1 != 0) { 42 IS >> p; 43 TopLoc_Location L1 = myMap(l1); 44 L = L1.Powered(p) *L; 45 IS >> l1; 46 } 47 } 48 49 if (!L.IsIdentity()) myMap.Add(L); 50 } 51 }
虽然代码风格不好,缩进、括号什么的都不工整,看起来很吃力,但是结合源程序,对上面的详细说明的理解还是很有帮助的。
其中变量nbLoc是<location record count>的值,成员变量myMap是TopLoc_Location的一个map。当是<location record 1>时把<location data 1>都放到TopLoc_Location的map中。当是<location record 2>时将li的变换矩阵TopLoc_Location乘pi次方。<flag>0表示<location data 2>的结束。
四、<geometry>部分
<geometry>包含以下子部分:
1.<2D curves>
2.<3D curves>
3.<3D polygons>
4.<polygons on triangulations>
5.<surfaces>
6.<triangulations>
读取<geometry>部分的类为BRepTools_ShapeSet,程序代码如下所示:
1 //======================================================================= 2 //function : ReadGeometry 3 //purpose : 4 //======================================================================= 5 void BRepTools_ShapeSet::ReadGeometry(Standard_IStream& IS) 6 { 7 //OCC19559 8 myCurves2d.SetProgress(GetProgress()); 9 myCurves.SetProgress(GetProgress()); 10 mySurfaces.SetProgress(GetProgress()); 11 12 if ( !GetProgress().IsNull()) { 13 if( GetProgress()->UserBreak() ) return; 14 GetProgress()->NewScope ( 15, "2D Curves" ); 15 } 16 myCurves2d.Read(IS); 17 18 if ( !GetProgress().IsNull()) { 19 if( GetProgress()->UserBreak() ) return; 20 GetProgress()->EndScope(); 21 GetProgress()->Show(); 22 23 GetProgress()->NewScope ( 15, "3D Curves" ); 24 } 25 myCurves.Read(IS); 26 27 if ( !GetProgress().IsNull()) { 28 if( GetProgress()->UserBreak() ) return; 29 GetProgress()->EndScope(); 30 GetProgress()->Show(); 31 32 GetProgress()->NewScope ( 10, "3D Polygons" ); 33 } 34 ReadPolygon3D(IS); 35 if ( !GetProgress().IsNull() ) { 36 if( GetProgress()->UserBreak() ) return; 37 GetProgress()->EndScope(); 38 GetProgress()->Show(); 39 40 GetProgress()->NewScope ( 10, "Polygons On Triangulation" ); 41 } 42 ReadPolygonOnTriangulation(IS); 43 if ( !GetProgress().IsNull()) { 44 if( GetProgress()->UserBreak() ) return; 45 GetProgress()->EndScope(); 46 GetProgress()->Show(); 47 48 GetProgress()->NewScope ( 10, "Surfaces" ); 49 } 50 mySurfaces.Read(IS); 51 if ( !GetProgress().IsNull() ) { 52 if( GetProgress()->UserBreak() ) return; 53 GetProgress()->EndScope(); 54 GetProgress()->Show(); 55 56 GetProgress()->NewScope ( 15, "Triangulations" ); 57 } 58 ReadTriangulation(IS); 59 if ( !GetProgress().IsNull()) { 60 if( GetProgress()->UserBreak() ) return; 61 GetProgress()->EndScope(); 62 GetProgress()->Show(); 63 } 64 }
4.1 子部分<3D curves>
示例:
BNF定义:
详细说明:
由Curves开始,后面是曲线的数量,再下面是每条曲线的具体数据。
读取<curves>部分的类为GeomTools_CurveSet,程序代码如下所示:
1 #define LINE 1 2 #define CIRCLE 2 3 #define ELLIPSE 3 4 #define PARABOLA 4 5 #define HYPERBOLA 5 6 #define BEZIER 6 7 #define BSPLINE 7 8 #define TRIMMED 8 9 #define OFFSET 9 10 //======================================================================= 11 //function : ReadCurve 12 //purpose : 13 //======================================================================= 14 Standard_IStream& GeomTools_CurveSet::ReadCurve(Standard_IStream& IS, 15 Handle(Geom_Curve)& C) 16 { 17 Standard_Integer ctype; 18 19 try { 20 OCC_CATCH_SIGNALS 21 IS >> ctype; 22 switch (ctype) { 23 24 case LINE : 25 { 26 Handle(Geom_Line) CC; 27 IS >> CC; 28 C = CC; 29 } 30 break; 31 32 case CIRCLE : 33 { 34 Handle(Geom_Circle) CC; 35 IS >> CC; 36 C = CC; 37 } 38 break; 39 40 case ELLIPSE : 41 { 42 Handle(Geom_Ellipse) CC; 43 IS >> CC; 44 C = CC; 45 } 46 break; 47 48 case PARABOLA : 49 { 50 Handle(Geom_Parabola) CC; 51 IS >> CC; 52 C = CC; 53 } 54 break; 55 56 case HYPERBOLA : 57 { 58 Handle(Geom_Hyperbola) CC; 59 IS >> CC; 60 C = CC; 61 } 62 break; 63 64 case BEZIER : 65 { 66 Handle(Geom_BezierCurve) CC; 67 IS >> CC; 68 C = CC; 69 } 70 break; 71 72 case BSPLINE : 73 { 74 Handle(Geom_BSplineCurve) CC; 75 IS >> CC; 76 C = CC; 77 } 78 break; 79 80 case TRIMMED : 81 { 82 Handle(Geom_TrimmedCurve) CC; 83 IS >> CC; 84 C = CC; 85 } 86 break; 87 88 case OFFSET : 89 { 90 Handle(Geom_OffsetCurve) CC; 91 IS >> CC; 92 C = CC; 93 } 94 break; 95 96 default: 97 { 98 Handle(Geom_Curve) CC; 99 GeomTools::GetUndefinedTypeHandler()->ReadCurve(ctype,IS,CC); 100 C = CC; 101 } 102 } 103 } 104 catch(Standard_Failure) { 105 #ifdef DEB 106 Handle(Standard_Failure) anExc = Standard_Failure::Caught(); 107 cout <<"EXCEPTION in GeomTools_CurveSet::ReadCurve(..)!!!" << endl; 108 cout << anExc << endl; 109 #endif 110 C = NULL; 111 } 112 return IS; 113 }
因为重载了操作符>>,使不同的类调用了不同的处理函数。
因为读取点和方向用得很频繁,所以将读取点和方向的函数程序先列出如下所示:
1 //======================================================================= 2 //function : ReadPnt 3 //purpose : 4 //======================================================================= 5 static Standard_IStream& operator>>(Standard_IStream& IS, gp_Pnt& P) 6 { 7 Standard_Real X=0.,Y=0.,Z=0.; 8 IS >> X >> Y >> Z; 9 P.SetCoord(X,Y,Z); 10 return IS; 11 } 12 13 //======================================================================= 14 //function : ReadDir 15 //purpose : 16 //======================================================================= 17 static Standard_IStream& operator>>(Standard_IStream& IS, gp_Dir& D) 18 { 19 Standard_Real X=0.,Y=0.,Z=0.; 20 IS >> X >> Y >> Z; 21 D.SetCoord(X,Y,Z); 22 return IS; 23 }
4.1.1 <3D curve record 1>-Line
示例:
BNF定义:
详细说明:
<3D curve record 1>定义了直线。直线数据由一个三维点P和一个三维方向矢量D组成。通过点P且方向为D的直线由下面的参数方程来定义:
示例数据表示的直线为通过点P(1,0,3),方向D(0,1,0),得到的参数方程为:
读取直线部分的程序代码如下所示:
1 //======================================================================= 2 //function : ReadCurve 3 //purpose : 4 //======================================================================= 5 static Standard_IStream& operator>>(Standard_IStream& IS, 6 Handle(Geom_Line)& L) 7 { 8 gp_Pnt P(0.,0.,0.); 9 gp_Dir AX(1.,0.,0.); 10 IS >> P >> AX; 11 L = new Geom_Line(P,AX); 12 return IS; 13 }
4.1.2 <3D curve record 2>-Circle
示例:
BNF定义:
详细说明:
<3D curve record 2>定义了圆。圆的数据包含一个三维点P,一个正交坐标系的三个轴的方向N,Dx,Dy,还有一个非负的实数r。其中点P为圆心坐标,圆位于平面的法向量为N的平面上,圆的半径为r。圆的参数方程如下所示:
示例数据表示的圆为:圆心P(1,2,3),位于平面的法向量N(0,0,1),圆的方向Dx=(1,0,-0),Dy=(-0,1,0),半径r=4,其参数方向为:
读取圆部分的程序代码如下所示:
1 //======================================================================= 2 //function : ReadCurve 3 //purpose : 4 //======================================================================= 5 static Standard_IStream& operator>>(Standard_IStream& IS, 6 Handle(Geom_Circle)& C) 7 { 8 gp_Pnt P(0.,0.,0.); 9 gp_Dir A(1.,0.,0.),AX(1.,0.,0.),AY(1.,0.,0.); 10 Standard_Real R=0.; 11 IS >> P >> A >> AX >> AY >> R; 12 C = new Geom_Circle(gp_Ax2(P,A,AX),R); 13 return IS; 14 }
4.1.3 <3D curve record 3>-Ellipse
示例:
BNF定义:
详细说明:
<3D curve record 3>定义了椭圆。椭圆的数据包含三维点P,三维正交坐标系N、Dmaj、Dmin和两个非负实数rmaj和rmin,且rmin<=rmaj。椭圆位于中心点P,法向量为N的平面上,且长轴、短轴的方向分别为Dmaj, Dmin,长轴、短轴上的半径分别为rmaj, rmin。椭圆的参数方程定义如下所示:
示例数据表示的椭圆的中心点P=(1,2,3),平面的法向量N=(0,0,1),长轴方向Dmaj=(1,0,-0),短轴方向Dmin=(-0,1,0),长轴半径为5,短轴半径为4,
读取椭圆部分的程序代码如下所示:
1 //======================================================================= 2 //function : ReadCurve 3 //purpose : 4 //======================================================================= 5 static Standard_IStream& operator>>(Standard_IStream& IS, 6 Handle(Geom_Ellipse)& E) 7 { 8 gp_Pnt P(0.,0.,0.); 9 gp_Dir A(1.,0.,0.),AX(1.,0.,0.),AY(1.,0.,0.); 10 Standard_Real R1=0.,R2=0.; 11 IS >> P >> A >> AX >> AY >> R1 >> R2; 12 E = new Geom_Ellipse(gp_Ax2(P,A,AX),R1,R2); 13 return IS; 14 }
4.1.4 <3D curve record 4>-Parabola
示例:
BNF定义:
详细说明:
<3D curve record 4>定义了抛物线。抛物线数据包含三维点P,三维正交坐标系坐标轴方向N,Dx,Dy和一个非负的实数f。抛物线通过点P,且位于法向量为N的平面上,焦点长度为f,其参数方程如下所示:
示例数据表示的抛物线过点P=(1,2,3),位于平面的法向N=(0,0,1),抛物线的另两个轴方向Dx=(1,0,-0),Dy=(-0,1,0),焦点长度f=16。参数方程为:
读取抛物线部分的程序代码如下所示:
1 //======================================================================= 2 //function : ReadCurve 3 //purpose : 4 //======================================================================= 5 static Standard_IStream& operator>>(Standard_IStream& IS, 6 Handle(Geom_Parabola)& C) 7 { 8 gp_Pnt P(0.,0.,0.); 9 gp_Dir A(1.,0.,0.),AX(1.,0.,0.),AY(1.,0.,0.); 10 Standard_Real R1=0.; 11 IS >> P >> A >> AX >> AY >> R1; 12 C = new Geom_Parabola(gp_Ax2(P,A,AX),R1); 13 return IS; 14 }
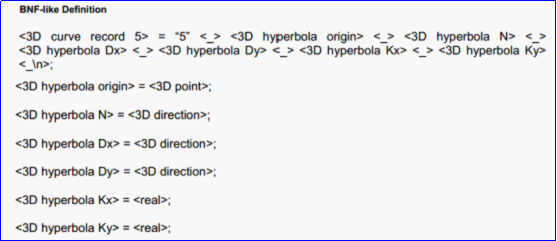
4.1.5 <3D curve record 5>-Hyperbola
示例:
BNF定义:
详细说明:
<3D curve record 5>定义了双曲线。双曲线定义数据有三维点P,三维正交坐标系坐标轴方向为N,Dx,Dy和两个非负实数Kx,Ky。双曲线过P点且法向量为N的平面上,其参数方程如下所示:
示例数据表示的双曲线过点P=(1,2,3)且位于的平面的法向N=(0,0,1),其它的数据Dx=(1,0,-0),Dy=(-0,1,0),Kx=5和Ky=4。其参数方程为:
读取双曲线部分的程序代码如下所示:
1 //======================================================================= 2 //function : ReadCurve 3 //purpose : 4 //======================================================================= 5 static Standard_IStream& operator>>(Standard_IStream& IS, 6 Handle(Geom_Hyperbola)& H) 7 { 8 gp_Pnt P(0.,0.,0.); 9 gp_Dir A(1.,0.,0.),AX(1.,0.,0.),AY(1.,0.,0.); 10 Standard_Real R1=0.,R2=0.; 11 IS >> P >> A >> AX >> AY >> R1 >> R2; 12 H = new Geom_Hyperbola(gp_Ax2(P,A,AX),R1,R2); 13 return IS; 14 }
4.1.6 <3D curve record 6>-Bezier Curve
示例:
BNF定义:
详细说明:
<3D curve record 6>定义了Bezier曲线。Bezier曲线数据包含有理标志r,曲线的次数m(degree m <= 25查看源代码可知OpenCascade可处理的B样条次数不超过25)和带权的控制点(weight poles)。当有理标志位r=0时,weight poles就是m+1个三维点:B0,B1...Bn;当有理标志位r=1时,weight poles就是带权的控制点B0 h0... Bm hm。Bi是三维点,hi是[0,m]正实数,即权因子。当有理标志位r=0时,即不是有理Bezier曲线时,hi=1。Bezier曲线参数方程如下所示:
示例数据表示的Bezier曲线是有理Bezier曲线,因其有理标志位r=1,次数m=2,带权控制点及权因子分别为:B0=(0,1,0),h0=4,B1=(1,-2,0),h1=5,B2=(2,3,0),h2=6。Bezier曲线的参数方程如下所示:
读取Bezier曲线部分的程序代码如下所示:
1 //======================================================================= 2 //function : ReadCurve 3 //purpose : 4 //======================================================================= 5 static Standard_IStream& operator>>(Standard_IStream& IS, 6 Handle(Geom_BezierCurve)& B) 7 { 8 Standard_Boolean rational=Standard_False; 9 IS >> rational; 10 11 // poles and weights 12 Standard_Integer i=0,degree=0; 13 IS >> degree; 14 15 TColgp_Array1OfPnt poles(1,degree+1); 16 TColStd_Array1OfReal weights(1,degree+1); 17 18 for (i = 1; i <= degree+1; i++) { 19 IS >> poles(i); 20 if (rational) 21 IS >> weights(i); 22 } 23 24 if (rational) 25 B = new Geom_BezierCurve(poles,weights); 26 else 27 B = new Geom_BezierCurve(poles); 28 29 return IS; 30 }
4.1.7 <3D curve record 7>-B-Spline curve
示例:
BNF定义:
详细说明:
<3D curve record 7>定义了B-Spline曲线。B-Spline曲线包含了有理标志位r,曲线次数m<=25,控制点数n>=2,重节点数k,带权控制点wieght poles和重节点multiplicity knots。
当有理标志位r=0时,是非有理B样条曲线,weight poles有n个三维点B1,...,Bn;当有理标志位r=1时,是有理B样条曲线,weight poles是n个带权控制点对:B1, h1, .... Bn, hn。这里Bi表示一个三维点,hi表示一个[0,1]正实数。当有理标志位r=0时,hi=1。
重节点有k对u1, q1, ... uk, qk。这里ui是重复度为qi>=1的节点。
B-Spline曲线的参数方程如下所示:
其中Ni,j有如下的递归定义:
示例数据表示的B样条曲线为:有理标志位r=1,次数m=1,控制点数n=3,重节点数k=5,带权控制点:B1=(0,1,0),h1=4,B2=(1,-2,0),h2=5,B3=(2,3,0),h3=6;重节点u1=0,q1=1,u2=0.25,q2=1,u3=0.5,q3=1,u4=0.75,q4=1,u5=1,q5=1。B-Spline曲线的参数方程如下所示:
读取B-Spline曲线部分的程序代码如下所示:
1 //======================================================================= 2 //function : ReadCurve 3 //purpose : 4 //======================================================================= 5 static Standard_IStream& operator>>(Standard_IStream& IS, 6 Handle(Geom_BSplineCurve)& B) 7 { 8 9 Standard_Boolean rational=Standard_False,periodic=Standard_False; 10 IS >> rational >> periodic; 11 12 // poles and weights 13 Standard_Integer i=0,degree=0,nbpoles=0,nbknots=0; 14 IS >> degree >> nbpoles >> nbknots; 15 16 TColgp_Array1OfPnt poles(1,nbpoles); 17 TColStd_Array1OfReal weights(1,nbpoles); 18 19 for (i = 1; i <= nbpoles; i++) { 20 IS >> poles(i); 21 if (rational) 22 IS >> weights(i); 23 } 24 25 TColStd_Array1OfReal knots(1,nbknots); 26 TColStd_Array1OfInteger mults(1,nbknots); 27 28 for (i = 1; i <= nbknots; i++) { 29 IS >> knots(i) >> mults(i); 30 } 31 32 if (rational) 33 B = new Geom_BSplineCurve(poles,weights,knots,mults,degree,periodic); 34 else 35 B = new Geom_BSplineCurve(poles,knots,mults,degree,periodic); 36 37 return IS; 38 }
4.1.8 <3D curve record 8>-Trimmed Curve
示例:
BNF定义:
详细说明:
<3D curve record 8>定义了裁剪曲线(trimmed curve)。裁剪曲线数据包含:两个实数umin,umax和<3D curve record>,且umin<umax。裁剪曲线是将<3D curve record>描述的曲线B限制在[umin,umax]。裁剪曲线的参数方程如下所示:
示例数据表示的裁剪曲线为:umin=-4,umax=5,曲线B(u)=(1,2,3)+u(1,0,0)。裁剪曲线的参数方程如下所示:
读取裁剪曲线部分的程序代码如下所示:
1 //======================================================================= 2 //function : ReadCurve 3 //purpose : 4 //======================================================================= 5 6 static Standard_IStream& operator>>(Standard_IStream& IS, 7 Handle(Geom_TrimmedCurve)& C) 8 { 9 Standard_Real p1=0.,p2=0.; 10 IS >> p1 >> p2; 11 Handle(Geom_Curve) BC; 12 GeomTools_CurveSet::ReadCurve(IS,BC); 13 C = new Geom_TrimmedCurve(BC,p1,p2); 14 return IS; 15 }
4.1.9 <3D curve record 9>-Offset Curve
示例:
BNF定义:
详细说明:
<3D curve record 9>定义了偏移曲线(offset curve)。偏移曲线的数据包含偏移距离d,偏移方向D和曲线数据<3D curve record>。偏移曲线是将<3D curve record>描述的曲线沿矢量![]() 偏移距离d后的结果。偏移曲线的参数方程如下所示:
偏移距离d后的结果。偏移曲线的参数方程如下所示:
示例数据表示的偏移曲线为偏移距离d=2,方向D=(0,1,0),基曲线B(u)=(1,2,3)+u(1,0,0),其参数方程如下所示:
读取偏移曲线部分程序代码如下所示:
1 //======================================================================= 2 //function : ReadCurve 3 //purpose : 4 //======================================================================= 5 static Standard_IStream& operator>>(Standard_IStream& IS, 6 Handle(Geom_OffsetCurve)& C) 7 { 8 Standard_Real p=0.; 9 IS >> p; 10 gp_Dir D(1.,0.,0.); 11 IS >> D; 12 Handle(Geom_Curve) BC; 13 GeomTools_CurveSet::ReadCurve(IS,BC); 14 C = new Geom_OffsetCurve(BC,p,D); 15 return IS; 16 }
未完,待续……