接上一篇《spring基础——DI(三)》
3.5 引用其他bean
上一篇已经介绍了注入常量、集合等基本数据类型和集合数据类型,承接上文继续介绍注入依赖bean及注入内部bean。引用其他bean的步骤与注入常量的步骤一样,可以通过构造器注入及setter注入引用其他bean。
- 构造器方式注入:通过constructor-arg标签ref属性来引用其他bean,这是最简化的配置:或者通过constructor-arg标签的子ref标签来引用其他bean。

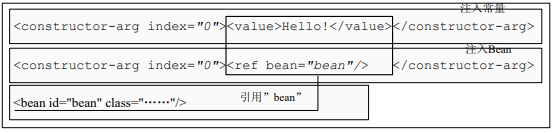
- setter方式注入:通过property标签的ref属性来引用其他bean,或者通过property标签的子ref标签来引用其他bean。
1 <!-- 定义依赖Bean --> 2 <bean id="helloApi" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter2.helloworld.HelloImpl"/> 3 <!-- 通过构造器注入 --> 4 <bean id="bean1" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.HelloApiDecorator"> 5 <constructor-arg index="0" ref="helloApi"/> 6 </bean> 7 <!-- 通过构造器注入 --> 8 <bean id="bean2" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.HelloApiDecorator"> 9 <property name="helloApi"><ref bean=" helloApi"/></property> 10 </bean>
1 package cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean; 2 import cn.javass.spring.chapter2.helloworld.HelloApi; 3 public class HelloApiDecorator implements HelloApi { 4 private HelloApi helloApi; 5 //空参构造器 6 public HelloApiDecorator() { 7 } 8 //有参构造器 9 public HelloApiDecorator(HelloApi helloApi) { 10 this.helloApi = helloApi; 11 } 12 public void setHelloApi(HelloApi helloApi) { 13 this.helloApi = helloApi; 14 } 15 @Override 16 public void sayHello() { 17 System.out.println("==========装饰一下==========="); 18 helloApi.sayHello(); 19 System.out.println("==========装饰一下==========="); 20 } 21 }
1 @Test 2 public void testBeanInject() { 3 BeanFactory beanFactory = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("chapter3/beanInject.xml"); 4 //通过构造器方式注入 5 HelloApi bean1 = beanFactory.getBean("bean1", HelloApi.class); 6 bean1.sayHello(); 7 //通过setter方式注入 8 HelloApi bean2 = beanFactory.getBean("bean2", HelloApi.class); 9 bean2.sayHello(); 10 }
- 其他引用方式:除了基本配置除外,spring还提供了两种更高级的配置方式:<ref local="">、<ref parent="">。<ref local="">用于引用通过id属性指定的bean,它能利用xml解析器的验证功能在读取配置文件时来验证引用的bean是否存在。
<ref parent="">用于引用父容器的bean,不引用当前容器的bean。
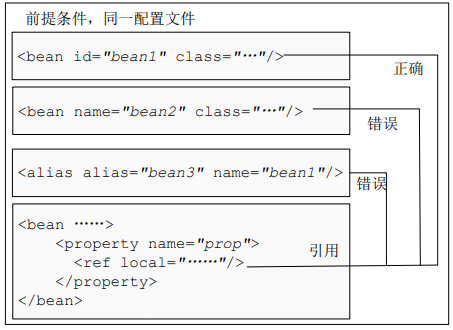
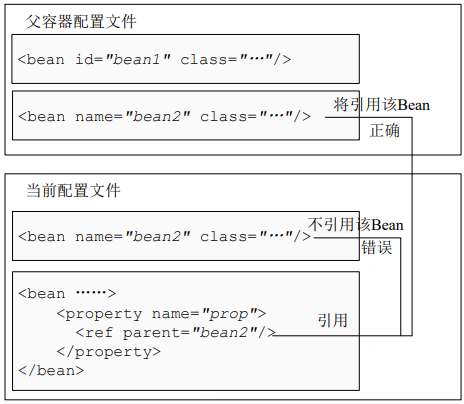
注:关于父子容器相关概念参照《Spring-SpringMVC父子容器&AOP使用总结(转)》。
3.6 内部bean定义:
内部bean就是在property或constructor-arg内部通过bean标签定义bean。该bean不管是否指定id或name,该bean都会有唯一的匿名标识符,而且不能指定别名,该内部bean对其他bean都不可见。
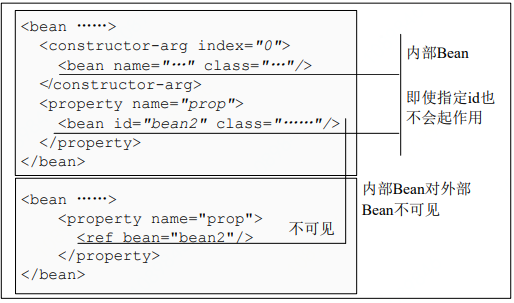
1 <bean id="bean" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.HelloApiDecorator"> 2 <property name="helloApi"> 3 <bean id="helloApi" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter2.helloworld.HelloImpl"/> 4 </property> 5 </bean>
1 @Test 2 public void testInnerBeanInject() { 3 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("chapter3/innerBeanInject.xml"); 4 HelloApi bean = context.getBean("bean", HelloApi.class); 5 bean.sayHello(); 6 }
3.7 注入null
spring通过value标签或value属性注入常量值,所有注入的数据都是字符串,那如何注入null值?spring提供了null标签。
1 <bean class="...HelloImpl4"> 2 <property name="message"><null/></property> 3 <property name="index" value="1"/> 4 </bean>
3.8 简写配置
接下来总结以下依赖注入配置及简写形式:
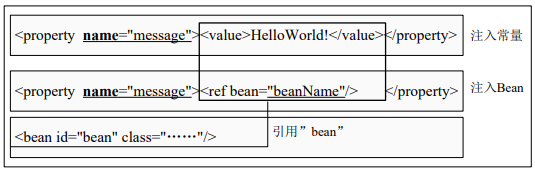
- 构造器注入:
1)常量值:
1 <!--简写--> 2 <constructor-arg index="0" value="常量"/> 3 <!--全写--> 4 <constructor-arg index="0"><value>常量</value></constructor-arg>
2)引用:
1 <!--简写--> 2 <constructor-arg index="0" ref="引用"/> 3 <!--全写--> 4 <constructor-arg index="0"><ref bean="引用"/></constructor-arg>
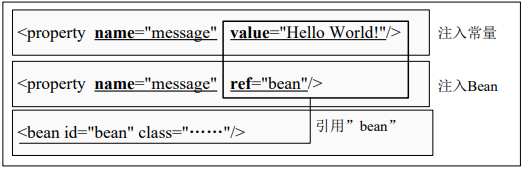
- setter注入:
1)常量值:
1 <!--简写--> 2 <property name="message" value="常量"/> 3 <!--全写--> 4 <property name="message"><value>常量</value></ property>
2)引用:
1 <!--简写--> 2 <property name="message" ref="引用"/> 3 <!--全写--> 4 <property name="message"><ref bean="引用"/></ property>
3)数组:<array>没有简写形式
4)列表:<list>没有简写形式
5)集合:<set>没有简写形式
6)字典:
1 <!--简写--> 2 <map> 3 <entry key="键常量" value="值常量"/> 4 <entry key-ref="键引用" value-ref="值引用"/> 5 </map> 6 <!--全写--> 7 <map> 8 <entry><key><value>键常量</value></key><value>值常量</value></entry> 9 <entry><key><ref bean="键引用"/></key><ref bean="值引用"/></entry> 10 </map>
7)Properties:没有简写形式
- 使用p命名空间简化setter注入:
使用p命名空间来简化setter配置如下
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" 5 xsi:schemaLocation=" 6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 7 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"> 8 <bean id="bean1" class="java.lang.String"> 9 <constructor-arg index="0" value="test"/> 10 </bean> 11 <bean id="idrefBean1" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.IdRefTestBean" p:id="value"/> 12 <bean id="idrefBean2" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.IdRefTestBean" p:id-ref="bean1"/> 13 </beans>
。xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p": 首先指定命名空间;
。<bean id="" class="" p:id=""/>:常量setter注入方式,等价于<property name="" value=""/>。
。<bean id="" class="" p:id-ref=""/>:引用setter注入方式,等价于<property name="" ref=""/>。
3.9 循环依赖
循环依赖就是循环引用,就是两个或多个bean之间相互持有对方,比如CircleA引用CircleB,CircleB引用CircleC,CircleC又引用CircleA,则他们始终反应为一个环。
构造器循环依赖:表示通过构造器注入构成的循环依赖,此依赖是无法解决的,只能抛出BeanCurrentlyInCreateException。
1 <bean id="circleA" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.CircleA"> 2 <constructor-arg index="0" ref="circleB"/> 3 </bean> 4 <bean id="circleB" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.CircleB"> 5 <constructor-arg index="0" ref="circleC"/> 6 </bean> 7 <bean id="circleC" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.CircleC"> 8 <constructor-arg index="0" ref="circleA"/> 9 </bean>
1 @Test(expected = BeanCurrentlyInCreationException.class) 2 public void testCircleByConstructor() throws Throwable { 3 try { 4 new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("chapter3/circleInjectByConstructor.xml"); 5 } 6 catch (Exception e) { 7 //因为要在创建circle3时抛出; 8 Throwable e1 = e.getCause().getCause().getCause(); 9 throw e1; 10 } 11 }
setter循环依赖:表示通过setter注入方式构成的循环依赖,对于setter注入构成的循环依赖是通过spring容器提供的通过提前暴露刚完成构造器注入但还未完成其他步骤(如setter注入)的bean来完成的,而且只能解决单例作用域的bean的循环依赖。
1 <!-- 定义 Bean 配置文件,注意 scope 都是“prototype”--> 2 <bean id="circleA" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.CircleA" scope="prototype"> 3 <property name="circleB" ref="circleB"/> 4 </bean> 5 <bean id="circleB" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.CircleB" scope="prototype"> 6 <property name="circleC" ref="circleC"/> 7 </bean> 8 <bean id="circleC" class="cn.javass.spring.chapter3.bean.CircleC" scope="prototype"> 9 <property name="circleA" ref="circleA"/> 10 </bean>
1 //测试代码cn.javass.spring.chapter3.CircleTest 2 @Test(expected = BeanCurrentlyInCreationException.class) 3 public void testCircleBySetterAndPrototype () throws Throwable { 4 try { 5 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( 6 "chapter3/circleInjectBySetterAndPrototype.xml"); 7 System.out.println(ctx.getBean("circleA")); 8 } 9 catch (Exception e) { 10 Throwable e1 = e.getCause().getCause().getCause(); 11 throw e1; 12 } 13 }
对于prototype作用域bean,spring容器无法完成依赖注入,因为prototype作用域的bean,spring容器不进行缓存,因此无法提前暴露一个创建中的bean。对于singleton作用域的bean可以禁用循环引用 。