对于任何程序设计语言而言,输入输出(I/O)系统都是比较复杂的而且还是比较核心的。在java.io.包中提供了相关的API.
java中流的概念划分
流的方向:
-
- 输入流:数据源到程序(inputStream,Reader读进来)
- 输出流:程序到目的地(OutPutStream,Writer写出去)
处理数据单元:
-
- 字节流:按照字节读取数据(InputStream,OutputStream)
- 字符流:按照字符读取数据(Reader,Writer)
功能不同
-
- 节点流:直接从数据源或目的地读写数据
- 处理流:不直接连接到数据源或目的地,是处理流的流,童工对其他流的处理提高程序的性能。
Jdk提供的流继承了四大类:InputStream(字节输入流),OutputStream(字节输出流),Reader(字符输入流),Writer(字符输出流)。
以下是java中io中常用的流。

InputStream
抽象类java.io.InputStream是所有字节输入流类型的父类,该类中定义了以字节为单位读取数据的基本方法,并在其子类中进行了分化和实现.
三个基本的read方法:
- int read()
- int read(byte[] buffer)
- int read(byte[] buffer,int offset,int length)
其他方法:
- void close()
- int available()
- skip(long n)
- boolean markSupported()
InputStream类层次

import java.io.File ; import java.io.InputStream ; import java.io.FileInputStream ; public class InputStreamDemo{ public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{ // 异常抛出,不处理 // 第1步、使用File类找到一个文件 File f= new File("d:" + File.separator + "test.txt") ; // 声明File对象 // 第2步、通过子类实例化父类对象 InputStream input = null ; // 准备好一个输入的对象 input = new FileInputStream(f) ; // 通过对象多态性,进行实例化 // 第3步、进行读操作 byte b[] = new byte[1024] ; // 数组大小由文件决定 int len = 0 ; int temp = 0 ; // 接收每一个读取进来的数据 while((temp=input.read())!=-1){ // 表示还有内容,文件没有读完 b[len] = (byte)temp ; len++ ; } // 第4步、关闭输出流 input.close() ; // 关闭输出流 System.out.println("内容为:" + new String(b,0,len)) ; // 把byte数组变为字符串输出 } };
OutputStream
java.io.OutputStream与java.io.InputStream对应,是所有字节输出流类型的抽象父类。
三个基本的write方法:
- void write(int c)
- void write(byte[] buffer)
- void write(byte[] buffer,int offset,int length)
其他方法:
- void close()
- void flush()
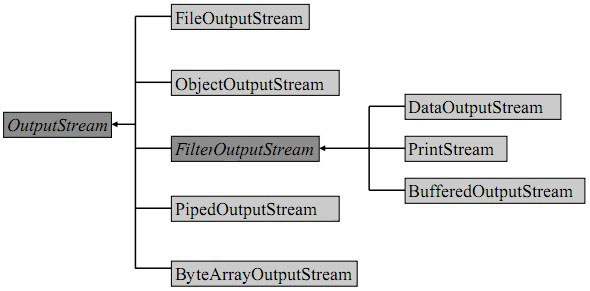
OutputStream类层次
import java.io.File ; import java.io.OutputStream ; import java.io.FileOutputStream ; public class OutputStreamDemo{ public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{ // 异常抛出,不处理 // 第1步、使用File类找到一个文件 File f= new File("d:" + File.separator + "test.txt") ; // 声明File对象 // 第2步、通过子类实例化父类对象 OutputStream out = null ; // 准备好一个输出的对象 out = new FileOutputStream(f) ; // 实例化 // 第3步、进行写操作 String str = "Hello World!!!" ; // 准备一个字符串 byte b[] = str.getBytes() ; // 只能输出byte数组,所以将字符串变为byte数组 out.write(b) ; // 写入数据 // 第4步、关闭输出流 // out.close() ; // 关闭输出流 } };
Reader
抽象类java.io.Reader是所有字符输入流类型的父类,其中声明了用于读取字符流的有关方法.
三个基本的read方法:
- int read()
- int read(char[] cbuf)
- int read(char[] cbuf,int offset,int length)
其他方法:
- void close()
- boolean ready()
- skip(long n)
- boolean markSupported()
- void mark(int readAheadLimit)
- void reset()
Reader类层次

import java.io.File ; import java.io.Reader ; import java.io.FileReader ; public class ReaderDemo{ public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{ // 异常抛出,不处理 // 第1步、使用File类找到一个文件 File f= new File("d:" + File.separator + "test.txt") ; // 声明File对象 // 第2步、通过子类实例化父类对象 Reader input = null ; // 准备好一个输入的对象 input = new FileReader(f) ; // 通过对象多态性,进行实例化 // 第3步、进行读操作 char c[] = new char[1024] ; // 所有的内容都读到此数组之中 int temp = 0 ; // 接收每一个内容 int len = 0 ; // 读取内容 while((temp=input.read())!=-1){ // 如果不是-1就表示还有内容,可以继续读取 c[len] = (char)temp ; len++ ; } // 第4步、关闭输出流 input.close() ; // 关闭输出流 System.out.println("内容为:" + new String(c,0,len)) ; // 把字符数组变为字符串输出 } };
Writer
java.io.Writer与java.io.Reader类对应,是所有字符输出流类型的共同父类.
五个基本的write方法:
- void write(int c)
- void write(char[] cbuf)
- void write(char[] cbuf,int offset,int leng)
- void write(String string)
- void write(String string,int offset,int length)
其它方法:
- void close()
- void flush()
Writer类层次

import java.io.File ; import java.io.Writer ; import java.io.FileWriter ; public class WriterDemo{ public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{ // 异常抛出,不处理 // 第1步、使用File类找到一个文件 File f= new File("d:" + File.separator + "test.txt") ; // 声明File对象 // 第2步、通过子类实例化父类对象 Writer out = null ; // 准备好一个输出的对象 out = new FileWriter(f) ; // 通过对象多态性,进行实例化 // 第3步、进行写操作 String str = "Hello World!!!" ; // 准备一个字符串 out.write(str) ; // 将内容输出,保存文件 // 第4步、关闭输出流 out.flush() ; // 强制性清空缓冲区中的内容 // out.close() ; // 此时,没有关闭 } };
拷贝实例:
import java.io.* ; public class Copy{ public static void main(String args[]){ if(args.length!=2){ // 判断是否是两个参数 System.out.println("输入的参数不正确。") ; System.out.println("例:java Copy 源文件路径 目标文件路径") ; System.exit(1) ; // 系统退出 } File f1 = new File(args[0]) ; // 源文件的File对象 File f2 = new File(args[1]) ; // 目标文件的File对象 if(!f1.exists()){ System.out.println("源文件不存在!") ; System.exit(1) ; } InputStream input = null ; // 准备好输入流对象,读取源文件 OutputStream out = null ; // 准备好输出流对象,写入目标文件 try{ input = new FileInputStream(f1) ; }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace() ; } try{ out = new FileOutputStream(f2) ; }catch(FileNotFoundException e){ e.printStackTrace() ; } if(input!=null && out!=null){ // 判断输入或输出是否准备好 int temp = 0 ; try{ while((temp=input.read())!=-1){ // 开始拷贝 out.write(temp) ; // 边读边写 } System.out.println("拷贝完成!") ; }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace() ; System.out.println("拷贝失败!") ; } try{ input.close() ; // 关闭 out.close() ; // 关闭 }catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace() ; } } } }
*** 在一般操作输入输出内容就需要使用字节或字符流,但是有些时候需要将字符流变成字节流的形式,或着将字节流变成字符流的形式,所以就需要另外一组转换流操作类
-
- OutputStreamWriter:是Writer的子类,将输出的字符流变成字节流。
- InputStreamReader:是Reader的子类,将输入的字节流变成字符流。
转换步骤:
如果以文件操作为例,则在内存总的字符数据需要通过OutputStreamWriter变成字节流保存在文件中,读取的时候需要将读入的字节流通过InputStreamReader变成字符流

例如,将字节的文件输出流以字符的形式输出
import java.io.* ; public class OutputStreamWriterDemo{ public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception { // 所有异常抛出 File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "test.txt") ; Writer out = null ; // 字符输出流 out = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(f)) ; // 字节流变为字符流 out.write("hello world!!") ; // 使用字符流输出 out.close() ; } };
读的时候亦可以使用字符流的形式读取字节流的文件
import java.io.* ; public class InputStreamReaderDemo01{ public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception{ File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "test.txt") ; Reader reader = null ; reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(f)) ; // 将字节流变为字符流 char c[] = new char[1024] ; int len = reader.read(c) ; // 读取 reader.close() ; // 关闭 System.out.println(new String(c,0,len)) ; } };