Description
When seeing his Citizens, Panagola always waves his hands. He may get tired and need a break. So please never make Panagola travel in a same west-east road for more than k minutes. If it takes p minutes to pass a love-hate zone, we say the length of that love-hate zone is p. Of course you know every love-hate zone’s length.
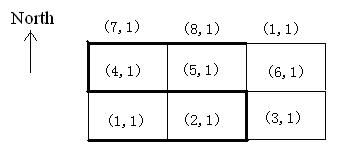
The figure below illustrates the case in sample input. In this figure, a best route is marked by thicker lines.
Input
The first line contains three integers: n, m and k.(0<n<=100,0<m<=10000, 0<=k<=3000000)
The next n+1 lines stands for n + 1 west-east roads in north to south order. Each line contains m integers showing the welcome values of the road’s m love-hate zones, in west to east order.
The last n+1 lines also stands for n + 1 west-east roads in north to south order. Each line contains m integers showing the lengths (in minutes) of the road's m love-hate zones, in west to east order.
Output
题目大意:有一个n*m的矩阵,只能沿着边走,只能往左、往右或往上走,在同一行只能沿一个方向走(走了左边就不能返回走右边了)。打横的边都有一个权值(可能为负数)和一个长度,每行走过的长度不能超过k,打竖的边没有权值和长度。先要从最下面的任意一个点开始,走到最上面的任意一个点,问最大权值和为多少(答案不超过$2^{31}-1$,虽然题目不是这么说的)。
思路:一看就是动态规划,每一行只和上一行的状态有关。因为习惯从小到大循环我们从上往下走,反正都一样。设dp[i][j]为走到第 i 行第 j 个点的最大权值(已往左往右走完),那么dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][x] + sum(welcome[i][y])),distance(x, y) ≤ k,y in [x, i]。其中distance和sum(welcome[i][y])可以预处理出来(如sum[i]代表1~i的和,distance(i, j) = sum[j] - sum[i],i ≤ j),平均到处理每个dp[i][j]身上时间复杂度为O(1)。但是这样计算dp数组,时间复杂度高达$O(nm^2)$。
现假设我们从左到右走,那么dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][x] - sum_welcome[x] + sum_welcome[y]) = dp[i][j] = max(dp[i - 1][x] - sum_welcome[x]) + sum_welcome[y],那么对每一个j,所用的dp[i - 1][x] - sum_welcome[x]都是一样的,这里很容易能想到单调队列优化(如果你知道单调队列的话)。每次把队列末尾小于dp[i - 1][j] - sum_welcome[j]弹出,把队头distance(i, x) > k的弹出,队头就是最佳的dp[i - 1][x] - sum_welcome[x]。优化完时间复杂度为$O(nm)$,已经是读入数据的复杂度了。(这里不介绍单调队列)
PS:可恶这题居然不让人在线非要我把整个矩阵一起读进来……
代码(1078MS,可恶啊C++又比G++快一倍):

1 #include <cstdio> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 const int MAXN = 110; 8 const int MAXM = 10010; 9 10 int wel[MAXN][MAXM], len[MAXN][MAXM]; 11 int sum_w[MAXM], sum_l[MAXM]; 12 int a[MAXM], b[MAXM], head, tail; 13 int dp[2][MAXM]; 14 int n, m, k, cur; 15 16 inline void insert(int x, int y) { 17 while(head != tail && a[tail - 1] < x) --tail; 18 a[tail] = x; b[tail] = y; ++tail; 19 } 20 21 void solve() { 22 memset(dp, 0, sizeof(dp)); 23 cur = 0; 24 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 25 cur ^= 1; 26 memset(dp[cur], 0, sizeof(dp[cur])); 27 28 sum_w[0] = sum_l[0] = 0; 29 for(int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) sum_w[j] = sum_w[j - 1] + wel[i][j]; 30 for(int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) sum_l[j] = sum_l[j - 1] + len[i][j]; 31 head = tail = 0; 32 for(int j = 0; j <= m; ++j) { 33 insert(dp[cur ^ 1][j] - sum_w[j], sum_l[j]); 34 while(k < sum_l[j] - b[head]) ++head; 35 dp[cur][j] = max(dp[cur][j], a[head] + sum_w[j]); 36 } 37 38 sum_w[m] = sum_l[m] = 0; 39 for(int j = m; j > 0; --j) sum_w[j - 1] = sum_w[j] + wel[i][j]; 40 for(int j = m; j > 0; --j) sum_l[j - 1] = sum_l[j] + len[i][j]; 41 head = tail = 0; 42 for(int j = m; j >= 0; --j) { 43 insert(dp[cur ^ 1][j] - sum_w[j], sum_l[j]); 44 while(k < sum_l[j] - b[head]) ++head; 45 dp[cur][j] = max(dp[cur][j], a[head] + sum_w[j]); 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 50 int main() { 51 while(scanf("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &k) != EOF) { 52 if(n == 0 && m == 0 && k == 0) break; 53 ++n; 54 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) 55 for(int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) scanf("%d", &wel[i][j]); 56 for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i) 57 for(int j = 1; j <= m; ++j) scanf("%d", &len[i][j]); 58 solve(); 59 int ans = 0; 60 for(int i = 0; i <= m; ++i) ans = max(ans, dp[cur][i]); 61 printf("%d ", ans); 62 } 63 }
