RSA

公钥加密


具有乘法同态性

程序实现
1、实现上述例子,有问题:只能是小数
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#define randomInt(a,b) (rand()%(b-a)+a)
//是否为素数
int prime(int n)
{
int i;
if (n < 2) {
return -1;
}
else {
for (i = 2; i < n; i++) {//判断n在2~n-1中有没有因数
if (n % i == 0)//如果用可以除尽的数,则非素数
break;
}
if (i < n) {//存在2~n-1之间有因数
return -1;
}
else
return 0;
}
return 0;
}
//素数生成
int creat_Prime(int a,int b)
{
int res,k;
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
do
{
res = randomInt(a, b);
k = prime(res);
} while (k == -1);
return res;
}
//求最大公约数,判断两个数是否互素
int gcd(int x, int y)
{
int t;
while (y) t = x, x = y, y = t % y;
return x;
}
//扩展欧几里得算法 (C++实现)
int exgcd(int a, int b, int& x, int& y)
{
if (b == 0)
{
x = 1, y = 0;
return a;
}
int ret = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
y -= a / b * x;
return ret;
}
//求逆元:基于费马定理
int reverse(int a, int mod)
{
int x, y;
int d = exgcd(a, mod, x, y);
return d == 1 ? (x % mod + mod) % mod : -1;
}
//求a的b次方带模mod
int power(int a, int b, int mod)
{
int tmp = a;
for (int i = 0; i < b; i++)
{
tmp = a * tmp % mod;
}
return tmp % mod;
}
int main()
{
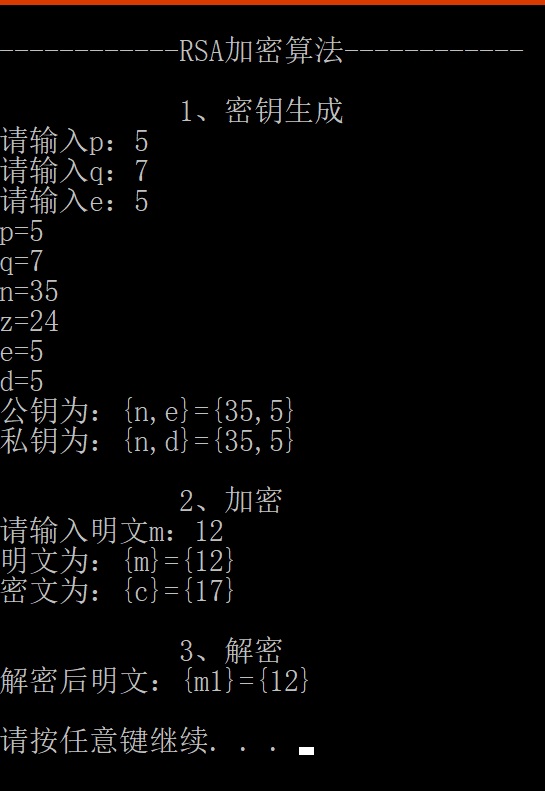
printf("
------------RSA加密算法------------
");
printf("
1、密钥生成
");
//p和q是大素数;n=pq;z=(p-1)(q-1);任取e,使满足gcd(e,z)=1;d是e的逆;m是明文;c是密文;m1是解密后明文
int p, q, n, z, e, d, m, c, m1;
//随机生成p和q
//p = creat_Prime(1, 5);
//q = creat_Prime(5, 10);
printf("请输入p:");
scanf("%d", &p);
printf("请输入q:");
scanf("%d", &q);
//求n和z
n = q * p;
z = (p - 1) * (q - 1);
//随机生成e:e和z互素,e < n
/*
do
{
e = creat_Prime(1, n);
} while (gcd(e, z) != 1);
*/
printf("请输入e:");
scanf("%d", &e);
//求d:d是e的逆元,mod z
d = reverse(e, z);
printf("p=%d
q=%d
n=%d
z=%d
e=%d
d=%d
", p,q,n,z,e,d);
//输出公私钥
printf("公钥为:{n,e}={%d,%d}
", n, e);
printf("私钥为:{n,d}={%d,%d}
", n, d);
printf("
2、加密
");
//明文生成输入
printf("请输入明文m:");
scanf("%d",&m);
//加密
c = (int)pow(m, e) % n;
printf("明文为:{m}={%d}
", m);
printf("密文为:{c}={%d}
", c);
printf("
3、解密
");
//解密
m1 = (int)pow(c, d) % n;
printf("解密后明文:{m1}={%d}
", m1);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2、不使用miracl库实现大数计算,可加解密数字和字母 ,来源
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string.h>
#define ACCURACY 5
#define SINGLE_MAX 10000
#define EXPONENT_MAX 1000
#define BUF_SIZE 1024
/**
* Computes a^b mod c
*/
int modpow(long long a, long long b, int c) {
int res = 1;
while (b > 0) {
/* Need long multiplication else this will overflow... */
if (b & 1) {
res = (res * a) % c;
}
b = b >> 1;
a = (a * a) % c; /* Same deal here */
}
return res;
}
/**
* Computes the Jacobi symbol, (a, n)
*/
int jacobi(int a, int n) {
int twos, temp;
int mult = 1;
while (a > 1 && a != n) {
a = a % n;
if (a <= 1 || a == n) break;
twos = 0;
while (a % 2 == 0 && ++twos) a /= 2; /* Factor out multiples of 2 */
if (twos > 0 && twos % 2 == 1) mult *= (n % 8 == 1 || n % 8 == 7) * 2 - 1;
if (a <= 1 || a == n) break;
if (n % 4 != 1 && a % 4 != 1) mult *= -1; /* Coefficient for flipping */
temp = a;
a = n;
n = temp;
}
if (a == 0) return 0;
else if (a == 1) return mult;
else return 0; /* a == n => gcd(a, n) != 1 */
}
/**
* Check whether a is a Euler witness for n
*/
int solovayPrime(int a, int n) {
int x = jacobi(a, n);
if (x == -1) x = n - 1;
return x != 0 && modpow(a, (n - 1) / 2, n) == x;
}
/**
* Test if n is probably prime, using accuracy of k (k solovay tests)
*/
int probablePrime(int n, int k) {
if (n == 2) return 1;
else if (n % 2 == 0 || n == 1) return 0;
while (k-- > 0) {
if (!solovayPrime(rand() % (n - 2) + 2, n)) return 0;
}
return 1;
}
/**
* Find a random (probable) prime between 3 and n - 1, this distribution is
* nowhere near uniform, see prime gaps
*/
int randPrime(int n) {
int prime = rand() % n;
n += n % 2; /* n needs to be even so modulo wrapping preserves oddness */
prime += 1 - prime % 2;
while (1) {
if (probablePrime(prime, ACCURACY)) return prime;
prime = (prime + 2) % n;
}
}
/**
* Compute gcd(a, b)
*/
int gcd(int a, int b) {
int temp;
while (b != 0) {
temp = b;
b = a % b;
a = temp;
}
return a;
}
/**
* Find a random exponent x between 3 and n - 1 such that gcd(x, phi) = 1,
* this distribution is similarly nowhere near uniform
*/
int randExponent(int phi, int n) {
int e = rand() % n;
while (1) {
if (gcd(e, phi) == 1) return e;
e = (e + 1) % n;
if (e <= 2) e = 3;
}
}
/**
* Compute n^-1 mod m by extended euclidian method
*/
int inverse(int n, int modulus) {
int a = n, b = modulus;
int x = 0, y = 1, x0 = 1, y0 = 0, q, temp;
while (b != 0) {
q = a / b;
temp = a % b;
a = b;
b = temp;
temp = x; x = x0 - q * x; x0 = temp;
temp = y; y = y0 - q * y; y0 = temp;
}
if (x0 < 0) x0 += modulus;
return x0;
}
/**
* Read the file fd into an array of bytes ready for encryption.
* The array will be padded with zeros until it divides the number of
* bytes encrypted per block. Returns the number of bytes read.
*/
int readFile(FILE* fd, char** buffer, int bytes) {
int len = 0, cap = BUF_SIZE, r;
char buf[BUF_SIZE];
*buffer = (char*)malloc(BUF_SIZE * sizeof(char));
while ((r = fread(buf, sizeof(char), BUF_SIZE, fd)) > 0) {
if (len + r >= cap) {
cap *= 2;
*buffer = (char*)realloc(*buffer, cap);
}
memcpy(&(*buffer)[len], buf, r);
len += r;
}
/* Pad the last block with zeros to signal end of cryptogram. An additional block is added if there is no room */
if (len + bytes - len % bytes > cap) *buffer = (char*)realloc(*buffer, len + bytes - len % bytes);
do {
(*buffer)[len] = '�';
len++;
} while (len % bytes != 0);
return len;
}
/**
* Encode the message m using public exponent and modulus, c = m^e mod n
*/
int encode(int m, int e, int n) {
return modpow(m, e, n);
}
/**
* Decode cryptogram c using private exponent and public modulus, m = c^d mod n
*/
int decode(int c, int d, int n) {
return modpow(c, d, n);
}
/**
* Encode the message of given length, using the public key (exponent, modulus)
* The resulting array will be of size len/bytes, each index being the encryption
* of "bytes" consecutive characters, given by m = (m1 + m2*128 + m3*128^2 + ..),
* encoded = m^exponent mod modulus
*/
int* encodeMessage(int len, int bytes, char* message, int exponent, int modulus) {
int* encoded = (int*)malloc((len / bytes) * sizeof(int));
int x, i, j;
for (i = 0; i < len; i += bytes) {
x = 0;
for (j = 0; j < bytes; j++)
x += message[i + j] * (1 << (7 * j));
encoded[i / bytes] = encode(x, exponent, modulus);
#ifndef MEASURE
printf("%d ", encoded[i / bytes]);
#endif
}
return encoded;
}
/**
* Decode the cryptogram of given length, using the private key (exponent, modulus)
* Each encrypted packet should represent "bytes" characters as per encodeMessage.
* The returned message will be of size len * bytes.
*/
int* decodeMessage(int len, int bytes, int* cryptogram, int exponent, int modulus) {
int* decoded = (int*)malloc(len * bytes * sizeof(int));
int x, i, j;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
x = decode(cryptogram[i], exponent, modulus);
for (j = 0; j < bytes; j++) {
decoded[i * bytes + j] = (x >> (7 * j)) % 128;
#ifndef MEASURE
if (decoded[i * bytes + j] != '�') printf("%c", decoded[i * bytes + j]);
#endif
}
}
return decoded;
}
/**
* Main method to demostrate the system. Sets up primes p, q, and proceeds to encode and
* decode the message given in "text.txt"
*/
int main(void) {
int p, q, n, phi, e, d, bytes, len;
int* encoded, * decoded;
char* buffer;
FILE* f;
char str[600];
srand(time(NULL));
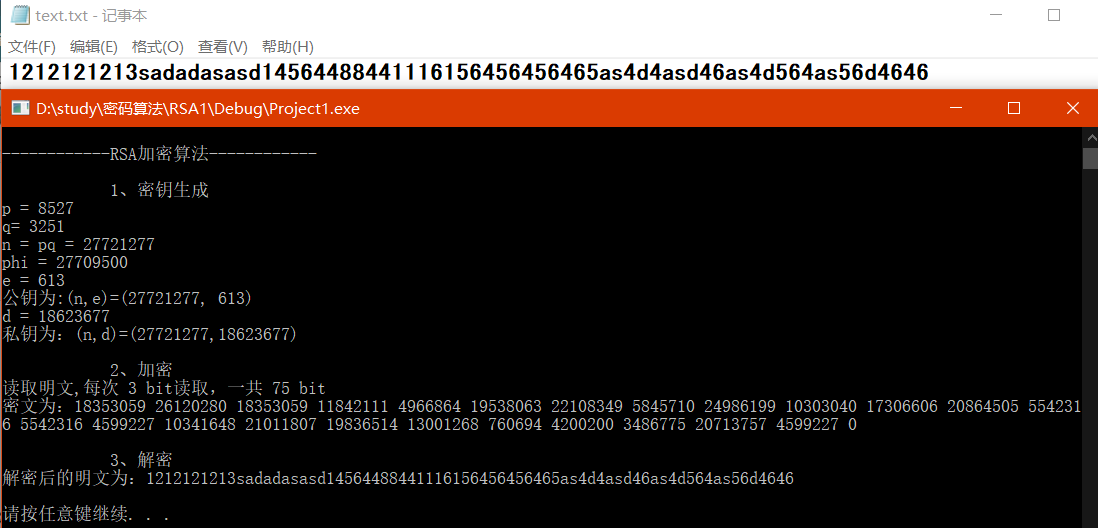
printf("
------------RSA加密算法------------
");
printf("
1、密钥生成
");
while (1) {
p = randPrime(SINGLE_MAX);
printf("p = %d
", p);
q = randPrime(SINGLE_MAX);
printf("q= %d
", q);
n = p * q;
printf("n = pq = %d
", n);
if (n < 128) {
printf("模数小于128,无法编码单个字节,再试一次
");
}
else break;
}
if (n >> 21) bytes = 3;
else if (n >> 14) bytes = 2;
else bytes = 1;
phi = (p - 1) * (q - 1);
printf("phi = %d
", phi);
e = randExponent(phi, EXPONENT_MAX);
printf("e = %d
公钥为:(n,e)=(%d, %d)
", e, n, e);
d = inverse(e, phi);
printf("d = %d
私钥为:(n,d)=(%d,%d)", d, n, d);
printf("
2、加密
");
printf("读取明文,");
f = fopen("text.txt", "r");
if (f == NULL) {
printf("打开文件失败!是否存在?
");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
len = readFile(f, &buffer, bytes); /* len will be a multiple of bytes, to send whole chunks */
fclose(f);
printf("每次 %d bit读取,一共 %d bit
密文为:",bytes,len);
encoded = encodeMessage(len, bytes, buffer, e, n);
printf("
3、解密
解密后的明文为:");
decoded = decodeMessage(len / bytes, bytes, encoded, d, n);
printf("
");
free(encoded);
free(decoded);
free(buffer);
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
3、使用大数库miracl,加密1000次
#include <stdio.h>
#include "miracl.h"
#include <time.h>
//char *primetext="155315526351482395991155996351231807220169644828378937433223838972232518351958838087073321845624756550146945246003790108045940383194773439496051917019892370102341378990113959561895891019716873290512815434724157588460613638202017020672756091067223336194394910765309830876066246480156617492164140095427773547319";
char *text="";
time_t begin, end;
int main()
{
/*
加解密
*/
big a,b,p,q,n,p1,q1,phi,pa,pb,key,e,d,dp,dq,t,m,c;
big primes[2],pm[2];
big_chinese ch;
long l=12;
long cum=0;
miracl *mip;
char input[256];
#ifndef MR_NOFULLWIDTH
mip=mirsys(100,0);
#else
mip=mirsys(100,MAXBASE);
#endif
a=mirvar(0);
b=mirvar(0);
p=mirvar(0);
q=mirvar(0);
n=mirvar(0);
p1=mirvar(0);
q1=mirvar(0);
phi=mirvar(0);
pa=mirvar(0);
pb=mirvar(0);
e=mirvar(0);
d=mirvar(0);
dp=mirvar(0);
dq=mirvar(0);
t=mirvar(0);
m=mirvar(0);
c=mirvar(0);
pm[0]=mirvar(0);
pm[1]=mirvar(0);
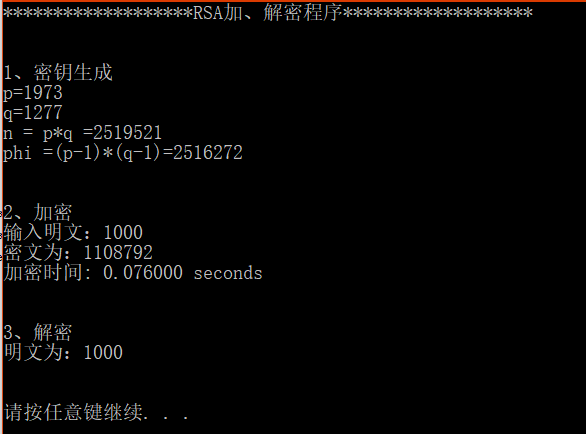
printf("*******************RSA加、解密程序*******************
");
printf("
1、密钥生成
");
do
{
bigbits(l,p);
if (subdivisible(p,2)) incr(p,1,p);
while (!isprime(p)) incr(p,2,p);
bigbits(l,q);
if (subdivisible(q,2)) incr(q,1,q);
while (!isprime(q)) incr(q,2,q);
multiply(p,q,n); /* n=p.q */
lgconv(65537L,e);
decr(p,1,p1);
decr(q,1,q1);
multiply(p1,q1,phi); /* phi =(p-1)*(q-1) */
} while (xgcd(e,phi,d,d,t)!=1);
printf("p=");
cotnum(p,stdout);
printf("q=");
cotnum(q,stdout);
printf("n = p*q =");
cotnum(n,stdout);
printf("phi =(p-1)*(q-1)=");
cotnum(phi,stdout);
/* set up for chinese remainder thereom */
primes[0]=p;
primes[1]=q;
crt_init(&ch,2,primes);
copy(d,dp);
copy(d,dq);
divide(dp,p1,p1); /* dp=d mod p-1 */
divide(dq,q1,q1); /* dq=d mod q-1 */
printf("
2、加密
");
printf("输入明文:");
scanf("%s",input);
text=input;
mip->IOBASE=l;
cinstr(m,text);
mip->IOBASE=10;
begin = clock();
while(cum<10000)
{
powmod(m,e,n,c);
cum++;
}
printf("密文为:");
cotnum(c,stdout);
end = clock();
printf("加密时间: %f seconds
", (double)(end - begin) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
zero(m);
printf("
3、解密
");
powmod(c,dp,p,pm[0]); /* get result mod p */
powmod(c,dq,q,pm[1]); /* get result mod q */
crt(&ch,pm,m); /* combine them using CRT */
printf("明文为:");
mip->IOBASE=l;
cotnum(m,stdout);
crt_end(&ch);
printf("
");
system("pause");
return 0;
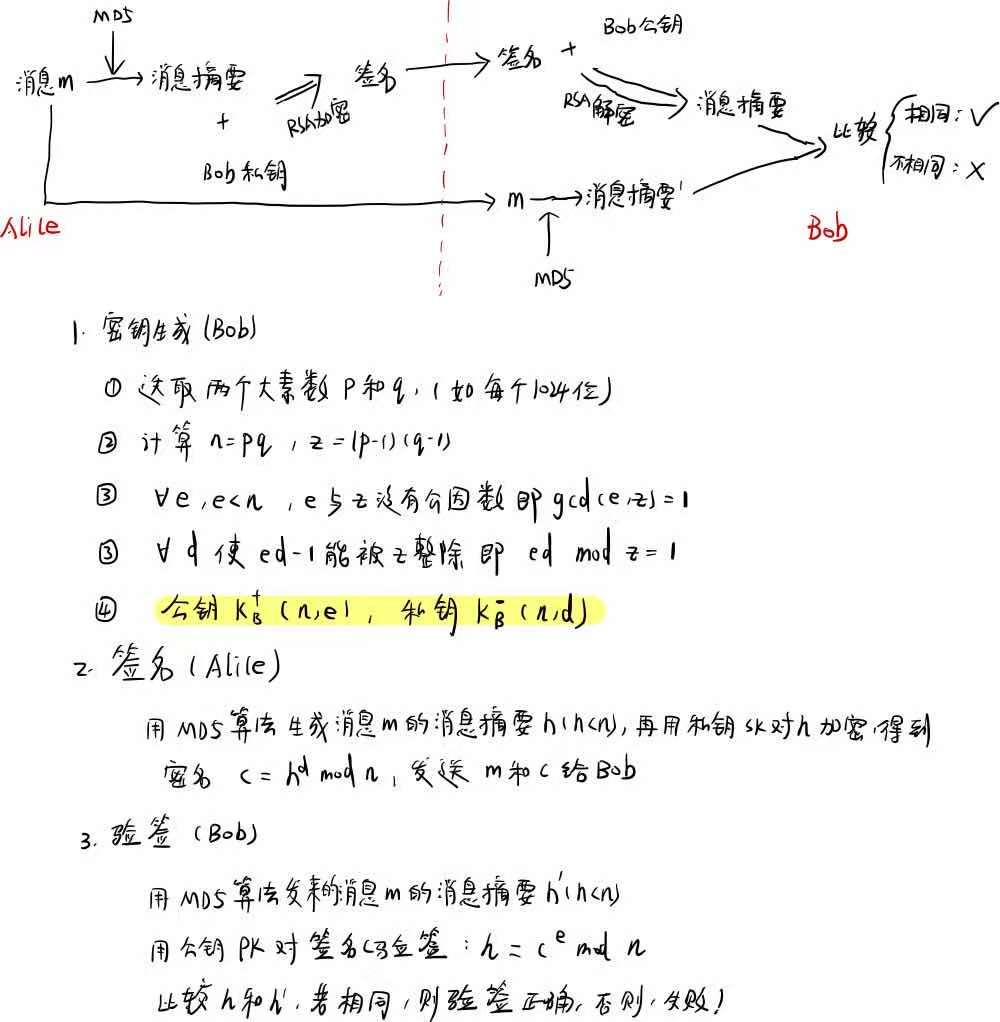
数字签名

参考
2、密码基础
3、基于同态加密的金融数据安全共享方案研究及实现-王婧琳