作者|Vishal Mishra
编译|VK
来源|Towards Data Science
欢迎阅读Python教程。在本章中,我们将学习文件、异常处理和其他一些概念。我们开始吧。

__name__ == '__main__'是什么意思?
通常,在每个Python项目中,我们都会看到上面的语句。所以它到底是干什么的,我们在这里就要明白了。
简单地说,在Python中,__name__是一个特殊的变量,它告诉我们模块的名称。无论何时直接运行python文件,它都会在执行实际代码之前设置一些特殊变量。__name__是一个特殊变量。根据以下几点确定__name__变量的值-
-
如果直接运行python文件,
__name__会将该名称设置为main。 -
如果你将一个模块导入另一个文件中,
__name__会将该名称设置为模块名。
__name__
'__main__'
first_module.py. 直接运行

first_module.py从其他模块导入
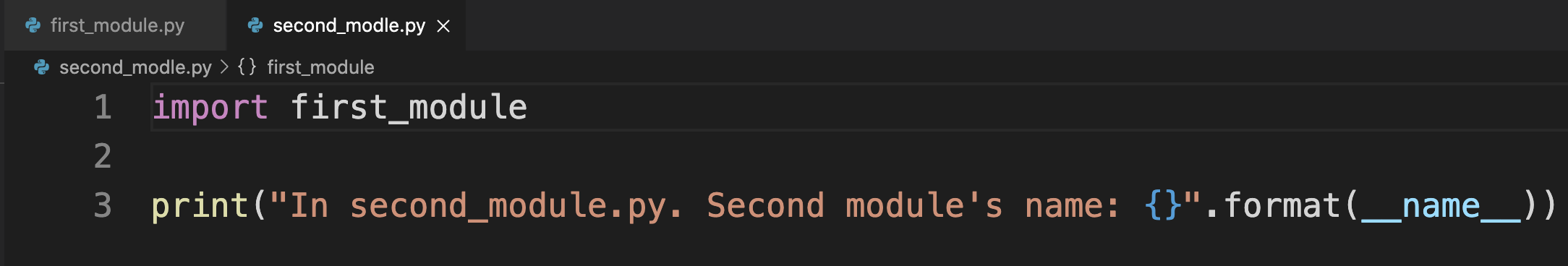
输出
In first_module.py, Running from Import
In second_module.py. Second module’s name: main
上面的示例中,你可以看到,当你在另一个python文件中导入第一个模块时,它将进入else条件,因为模块的名称不是main。但是,在second_module.py,名字仍然是main。
所以我们在下面的条件下使用了
-
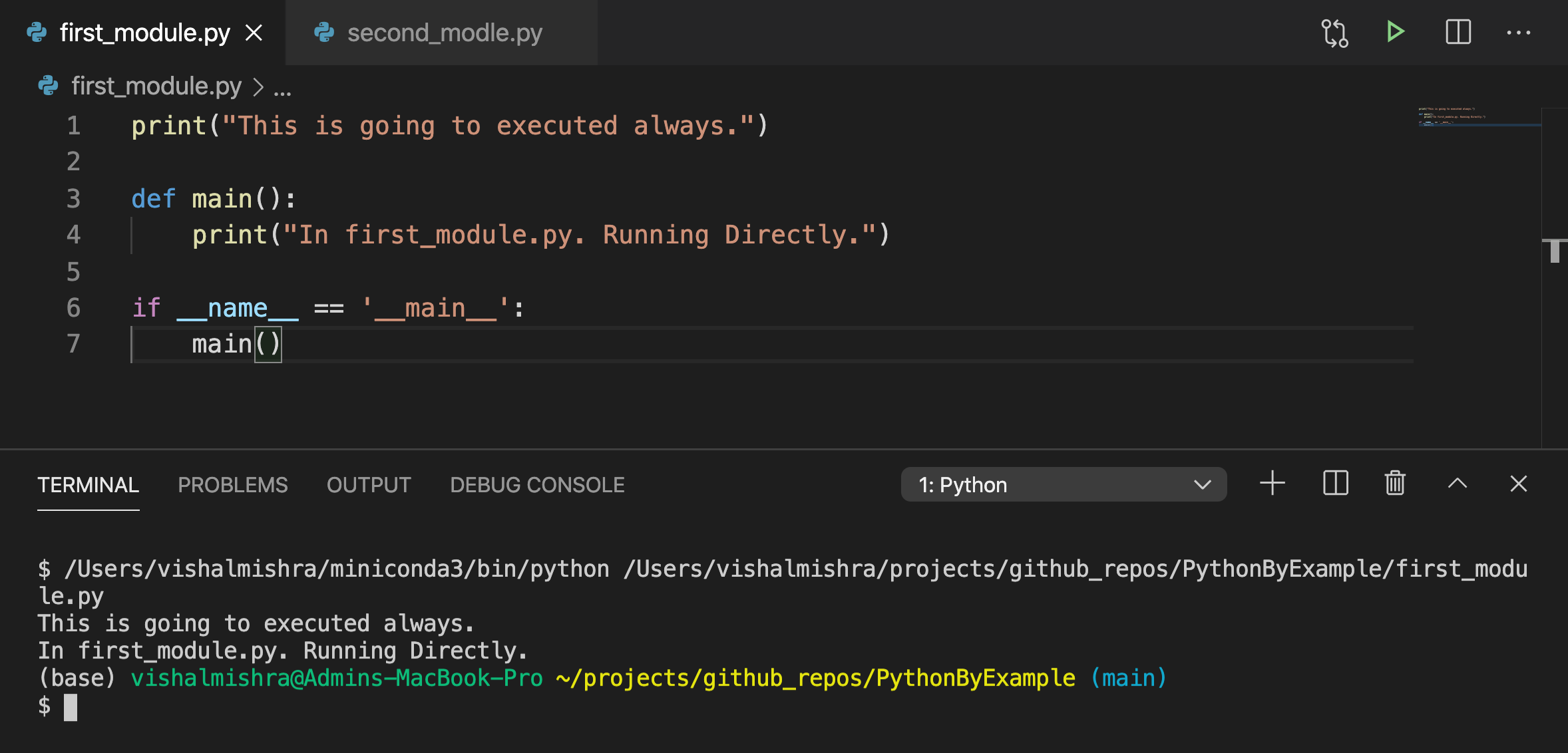
当我们想执行某些特定任务时,我们可以直接调用这个文件。
-
如果模块被导入到另一个模块中,而我们不想执行某些任务时。
最好是创建一个main方法,并在if __name__ == __main__内部调用。因此,如果需要,你仍然可以从另一个模块调用main方法。
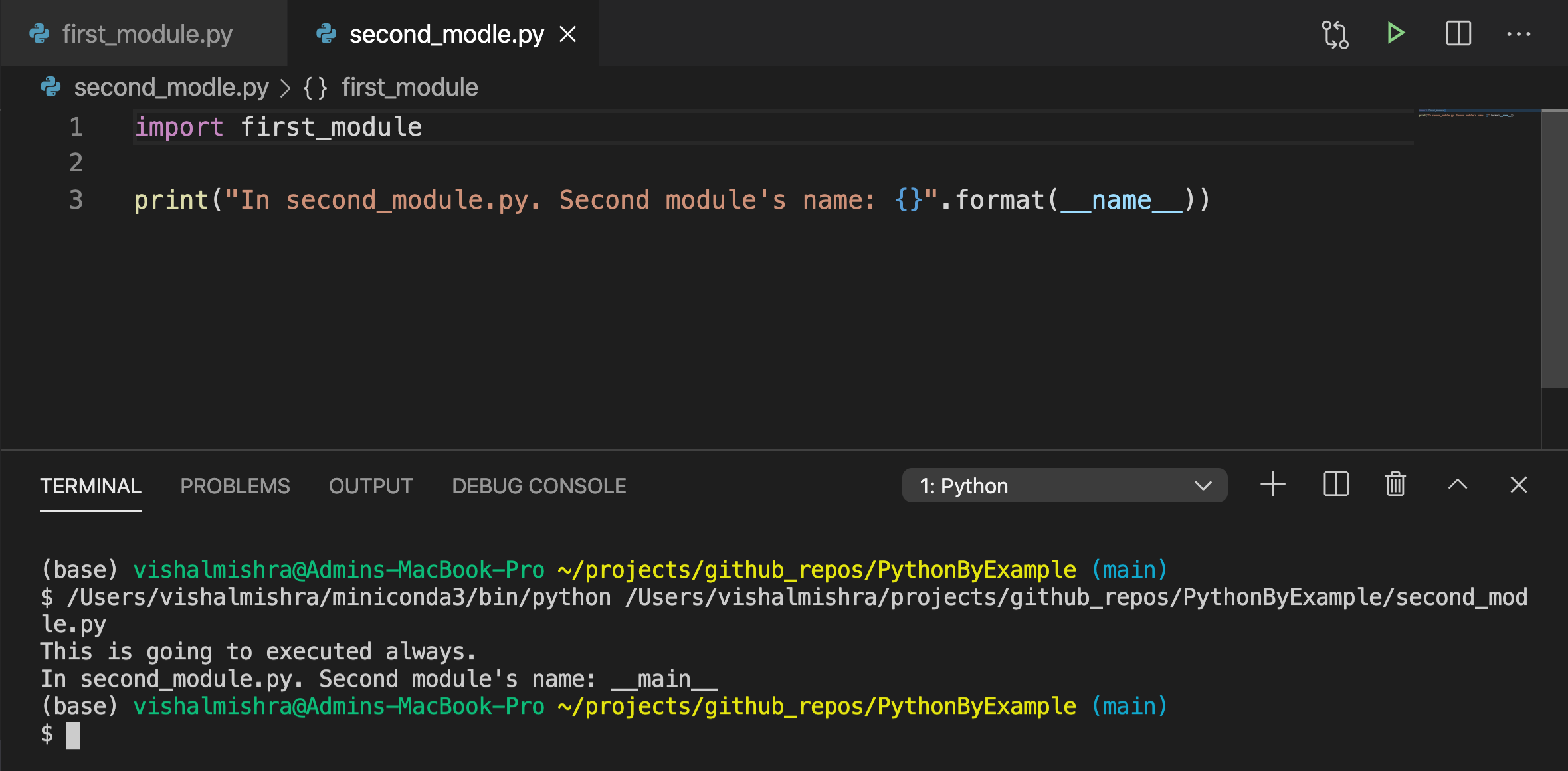
我们仍然可以通过显式调用main方法来调用另一个模块的main方法,因为main方法应该存在于第一个模块中。
出了问题怎么办
Python中的异常处理
当我们用任何编程语言编写任何程序时,有时即使语句或表达式在语法上是正确的,也会在执行过程中出错。在任何程序执行过程中检测到的错误称为异常。
Python中用于处理错误的基本术语和语法是try和except语句。可以导致异常发生的代码放在try块中,异常的处理在except块中实现。python中处理异常的语法如下-
try 和except
try:
做你的操作…
...
except ExceptionI:
如果有异常ExceptionI,执行这个块。
except ExceptionII:
如果有异常ExceptionII,执行这个块。
...
else:
如果没有异常,则执行此块。
finally:
无论是否有异常,此块都将始终执行
让我们用一个例子来理解这一点。在下面的示例中,我将创建一个计算数字平方的函数,以便计算平方,该函数应始终接受一个数字(本例中为整数)。但是用户不知道他/她需要提供什么样的输入。当用户输入一个数字时,它工作得很好,但是如果用户提供的是字符串而不是数字,会发生什么情况呢。
def acceptInput():
num = int(input("Please enter an integer: "))
print("Sqaure of the the number {} is {}".format(num, num*num))
acceptInput()
Please enter an integer: 5
Sqaure of the the number 5 is 25

它抛出一个异常,程序突然结束。因此,为了优雅地执行程序,我们需要处理异常。让我们看看下面的例子-
def acceptInput():
try:
num = int(input("Please enter an integer: "))
except ValueError:
print("Looks like you did not enter an integer!")
num = int(input("Try again-Please enter an integer: "))
finally:
print("Finally, I executed!")
print("Sqaure of the the number {} is {}".format(num, num*num))
acceptInput()
Please enter an integer: five
Looks like you did not enter an integer!
Try again-Please enter an integer: 4
Finally, I executed!
Sqaure of the the number 4 is 16
这样,我们就可以提供逻辑并处理异常。但在同一个例子中,如果用户再次输入字符串值。那会发生什么?
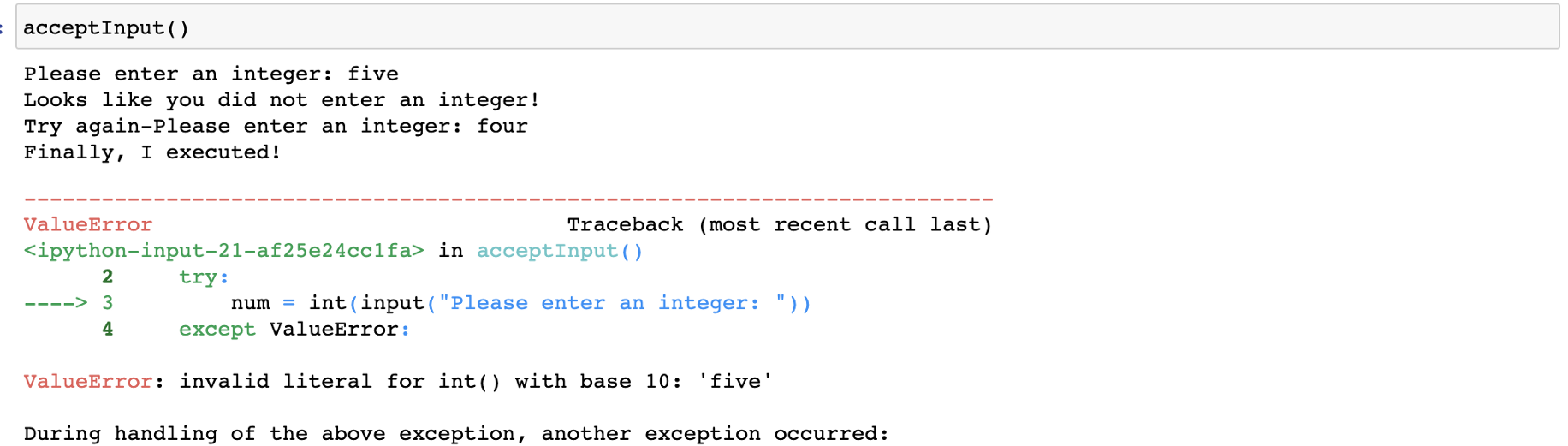
所以在这种情况下,最好在循环中输入,直到用户输入一个数字。
def acceptInput():
while True:
try:
num = int(input("Please enter an integer: "))
except ValueError:
print("Looks like you did not enter an integer!")
continue
else:
print("Yepie...you enterted integer finally so breaking out of the loop")
break
print("Sqaure of the the number {} is {}".format(num, num*num))
acceptInput()
Please enter an integer: six
Looks like you did not enter an integer!
Please enter an integer: five
Looks like you did not enter an integer!
Please enter an integer: four
Looks like you did not enter an integer!
Please enter an integer: 7
Yepie...you enterted integer finally so breaking out of the loop
Sqaure of the the number 7 is 49
如何处理多个异常
可以在同一个try except块中处理多个异常。你可以有两种方法-
-
在同一行中提供不同的异常。示例:ZeroDivisionError,NameError :
-
提供多个异常块。当你希望为每个异常提供单独的异常消息时,这很有用。示例:
except ZeroDivisionError as e:
print(“Divide by zero exception occurred!, e)
except NameError as e:
print(“NameError occurred!, e)
在末尾包含except Exception:block总是很好的,可以捕捉到你不知道的任何不需要的异常。这是一个通用的异常捕捉命令,它将在代码中出现任何类型的异常。
# 处理多个异常
def calcdiv():
x = input("Enter first number: ")
y = input("Enter second number: ")
try:
result = int(x) / int(y)
print("Result: ", result)
except ZeroDivisionError as e:
print("Divide by zero exception occured! Try Again!", e)
except ValueError as e:
print("Invalid values provided! Try Again!", e)
except Exception as e:
print("Something went wrong! Try Again!", e)
finally:
print("Program ended.")
calcdiv()
Enter first number: 5
Enter second number: 0
Divide by zero exception occured! Try Again! division by zero
Program ended.

如何创建自定义异常
有可能创建自己的异常。你可以用raise关键字来做。

创建自定义异常的最佳方法是创建一个继承默认异常类的类。
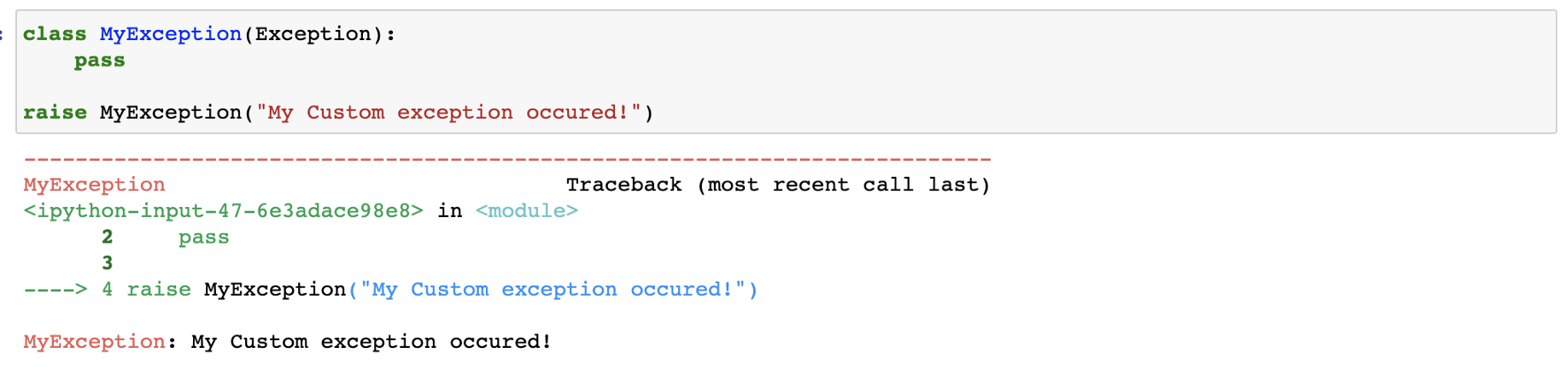
这就是Python中的异常处理。你可以在这里查看内置异常的完整列表:https://docs.python.org/3.7/library/exceptions.html
如何处理文件
Python中的文件处理
Python使用文件对象与计算机上的外部文件进行交互。这些文件对象可以是你计算机上的任何文件格式,即可以是音频文件、图像、文本文件、电子邮件、Excel文档。你可能需要不同的库来处理不同的文件格式。
让我们使用ipython命令创建一个简单的文本文件,我们将了解如何在Python中读取该文件。
%%writefile demo_text_file.txt
hello world
i love ipython
jupyter notebook
fourth line
fifth line
six line
This is the last line in the file
Writing demo_text_file.txt
打开文件
你可以用两种方式打开文件
-
定义一个包含file对象的变量。在处理完一个文件之后,我们必须使用file对象方法close再次关闭它:
f = open("demo_text_file.txt", "r") --- f.close() -
使用with关键字。不需要显式关闭文件。
with open(“demo_text_file.txt”, “r”): ##读取文件
在open方法中,我们必须传递定义文件访问模式的第二个参数。“r”是用来读文件的。类似地,“w”表示写入,“a”表示附加到文件。在下表中,你可以看到更常用的文件访问模式。

读取文件
在python中,有多种方法可以读取一个文件-
-
fileObj.read()=>将把整个文件读入字符串。
-
fileObj.readline() =>将逐行读取文件。
-
fileObj.readlines()=>将读取整个文件并返回一个列表。小心使用此方法,因为这将读取整个文件,因此文件大小不应太大。
# 读取整个文件
print("------- reading entire file --------")
with open("demo_text_file.txt", "r") as f:
print(f.read())
# 逐行读取文件
print("------- reading file line by line --------")
print("printing only first 2 lines")
with open("demo_text_file.txt", "r") as f:
print(f.readline())
print(f.readline())
# 读取文件并以列表形式返回
print("------- reading entire file as a list --------")
with open("demo_text_file.txt", "r") as f:
print(f.readlines())
# 使用for循环读取文件
print("
------- reading file with a for loop --------")
with open("demo_text_file.txt", "r") as f:
for lines in f:
print(lines)
------- reading entire file --------
hello world
i love ipython
jupyter notebook
fourth line
fifth line
six line
This is the last line in the file
------- reading file line by line --------
printing only first 2 lines
hello world
i love ipython
------- reading entire file as a list --------
['hello world
', 'i love ipython
', 'jupyter notebook
', 'fourth line
', 'fifth line
', 'six line
', 'This is the last line in the file
']
------- reading file with a for loop --------
hello world
i love ipython
jupyter notebook
fourth line
fifth line
six line
This is the last line in the file
写文件
与read类似,python提供了以下2种写入文件的方法。
-
fileObj.write()
-
fileObj.writelines()
with open("demo_text_file.txt","r") as f_in:
with open("demo_text_file_copy.txt", "w") as f_out:
f_out.write(f_in.read())
读写二进制文件
你可以使用二进制模式来读写任何图像文件。二进制包含字节格式的数据,这是处理图像的推荐方法。记住使用二进制模式,以“rb”或“wb”模式打开文件。
with open("cat.jpg","rb") as f_in:
with open("cat_copy.jpg", "wb") as f_out:
f_out.write(f_in.read())
print("File copied...")
File copied...
有时当文件太大时,建议使用块进行读取(每次读取固定字节),这样就不会出现内存不足异常。可以为块大小提供任何值。在下面的示例中,你将看到如何读取块中的文件并写入另一个文件。
### 用块复制图像
with open("cat.jpg", "rb") as img_in:
with open("cat_copy_2.jpg", "wb") as img_out:
chunk_size = 4096
img_chunk = img_in.read(chunk_size)
while len(img_chunk) > 0:
img_out.write(img_chunk)
img_chunk = img_in.read(chunk_size)
print("File copied with chunks")
File copied with chunks
结论
现在你知道了如何进行异常处理以及如何使用Python中的文件。
下面是Jupyter Notebook的链接:https://github.com/vishal2505/PythonByExample/blob/main/Python_Essentials_Part_3.ipynb
原文链接:https://towardsdatascience.com/python-essentials-part-3-5b61c1c25b9d
欢迎关注磐创AI博客站:
http://panchuang.net/
sklearn机器学习中文官方文档:
http://sklearn123.com/
欢迎关注磐创博客资源汇总站:
http://docs.panchuang.net/