一:术语、定义、特点
1、树
树是一种数据结构,它是由n(n>=1)个有限结点组成一个具有层次关系的集合。
树结构中的术语
- 节点的度:节点拥有的子树的数目;
- 叶子节点:度为0的节点;
- 分支结点:度不为0的节点;
- 树的度:树中节点的最大的度;
- 层次:根结点的层次为1,其余节点的层次等于该结点的双亲节点的层次加1;
- 树的高度:树中节点的最大层次;
- 森林:0个或多个不相交的树组成。对森林加上一个根,森林即成为树;删去根,树即成为森林。
2、二叉树
二叉树也是树;
二叉树有五种基本形态,如下图:

二叉树结构特点
- 每个节点最多有两个子树(即二叉树的度不能大于2),并且二叉树的子树有左右之分,其次序不能颠倒;
- 没有父节点的节点称为根节点;
- 没有子节点的节点称为叶子节点;
- 每一个非根节点有且只有一个父节点;
- 除了根节点外,每个子节点可以分为多个不相交的子树;
- 树里面没有环路。
二叉树性质
性质1:在二叉树的第 i 层上最多有 2^(i – 1) 个节点; (i>=1)
性质2:深度为 k 的二叉树至多有 2^k – 1 个节点;(k>=1)
性质3:包含n个节点的二叉树的高度至少为(log2n)+1;
性质4:在任意一棵二叉树中,若终端节点的个数为n0,度为2的节点数为n2,则n0=n2+1;
考试时常考性质4的证明
性质4:在任意一棵二叉树中,若终端节点的个数为n0,度为2的节点数为n2,则n0=n2+1。
证明:因为二叉树中所有节点的度数均不大于2,不妨设n0表示度为0的节点个数,n1表示度为1的节点个数,n2表示度为2的节点个数。三类节点加起来为总结点个数,于是便可得到:n=n0+n1+n2 (式1)
由度之间的关系可得第二个等式:n=n00+n11+n2*2+1即n=n1+2n2+1 (式2)
合(式1)(式2),移项可得:n0=n2+1,证毕。
3、几种特殊形态的二叉树
3.1 满二叉树
深度为k 且有2^k -1 个节点的二叉树。

∴
已知某二叉树深度为k,则该树最多有2^k - 1个节点;
每层有2^k+1 个节点;
3.2 完全二叉树
深度为k,有n个节点的二叉树,其每一个节点都与深度为k 的满二叉树中编号从1 至n 的节点一一对应。
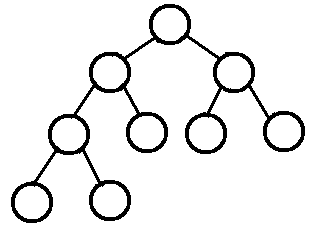
特点:叶子节点只能出现在最下层和次下层,且最下层的叶子节点集中在树的左部。显然,一棵满二叉树必定是一棵完全二叉树,而完全二叉树未必是满二叉树。
面试题:如果一个完全二叉树的节点总数为768个,求叶子节点的个数。
由二叉树的性质知:n0=n2+1,将之带入768=n0+n1+n2中得:768=n1+2n2+1,因为完全二叉树度为1的节点个数要么为0,要么为1,那么就把n1=0或者1都代入公式中,很容易发现n1=1才符合条件。所以算出来n2=383,所以叶子节点个数n0=n2+1=384。
总结:如果一棵完全二叉树的节点总数为n,那么叶子节点等于n/2(当n为偶数时)或者(n+1)/2(当n为奇数时)
3.3 平衡二叉树
当且仅当两个子树的高度差不超过1时,这个树是平衡二叉树。
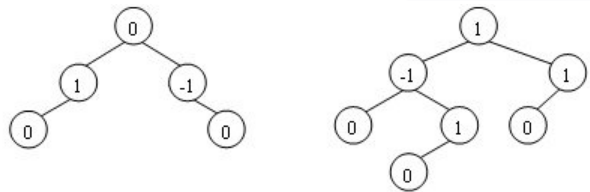
3.4 二叉搜索树
又称二叉查找树,设x为二叉查找树中的一个节点,x节点包含关键字key,节点x的key值计为key[x]。如果y是x的左子树中的一个节点,则key[y]<=key[x];如果y是x的右子树的一个节点,则key[y]>=key[x]。即满足:左子树<=根节点<=右子树。
(1)若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值。
(2)任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值。
(3)任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树。
二:二叉树的代码实现
typedef struct node{
type_t data;
struct node *left;
struct node *right;
}Node;
1、创建节点
Node *node_create(type_t data){
Node *p = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
p->data = data;
p->left = NULL;
p->right = NULL;
return p;
}
2、递归实现二叉树的三序遍历
2.1 前序遍历
void tree_pre_order(Node *tree){
if(tree == NULL)
return;
else{
printf("pre: %d
", tree->data);
tree_pre_order(tree->left);
tree_pre_order(tree->right);
}
}
2.2 中序遍历
void tree_in_order(Node *tree){
if(tree == NULL)
return;
else{
tree_in_order(tree->left);
printf("in: %d
", tree->data);
tree_in_order(tree->right);
}
}
2.3 后序遍历
void tree_post_order(Node *tree){
if(tree == NULL)
return;
else{
tree_post_order(tree->left);
tree_post_order(tree->right);
printf("next: %d
", tree->data);
}
}
3、层序遍历
思路:相当于广度优先搜索,使用队列实现。队列初始化,将根节点压入队列。当队列不为空,进行如下操作:弹出一个节点,访问,若左子节点或右子节点不为空,将其压入队列。
void LevelTraverse(BinaryTreeNode * pRoot){
if(pRoot == NULL)
return;
queue<BinaryTreeNode *> q;
q.push(pRoot);
while(!q.empty()){
BinaryTreeNode * pNode = q.front();
q.pop();
Visit(pNode); // 访问节点
if(pNode->m_pLeft != NULL)
q.push(pNode->m_pLeft);
if(pNode->m_pRight != NULL)
q.push(pNode->m_pRight);
}
return;
}
4、求二叉树中的节点数
递归思路:
(1)如果二叉树为空,节点个数为0;
(2)如果二叉树不为空,二叉树节点个数 = 左子树节点个数 + 右子树节点个数 + 1;
int GetNodeNum(BinaryTreeNode * pRoot){
// 递归出口
if(pRoot == NULL)
return 0;
return GetNodeNum(pRoot->m_pLeft) + GetNodeNum(pRoot->m_pRight) + 1;
}
5、求二叉树的深度
递归思路:
(1)如果二叉树为空,二叉树的深度为0;
(2)如果二叉树不为空,二叉树的深度 = max(左子树深度, 右子树深度) + 1;
int GetDepth(BinaryTreeNode * pRoot){
// 递归出口
if(pRoot == NULL)
return 0;
int depthLeft = GetDepth(pRoot->m_pLeft);
int depthRight = GetDepth(pRoot->m_pRight);
return depthLeft > depthRight ? (depthLeft + 1) : (depthRight + 1);
}
python版:
def treeDepth(self,root):
if not root:
return 0
depthLeft = self.treeDepth(root.left)
depthRight = self.treeDepth(root.right)
return depthLeft+1 if depthLeft > depthRight else depthRight+1
6、判断二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
递归思路:
(1)如果二叉树为空,返回真;
(2)如果二叉树不为空,如果左子树和右子树都是AVL树并且左子树和右子树高度相差不大于1,返回真,其他返回假;
bool IsAVL(BinaryTreeNode * pRoot, int & height){
// 空树,返回真
if(pRoot == NULL) {
height = 0;
return true;
}
int heightLeft;
bool resultLeft = IsAVL(pRoot->m_pLeft, heightLeft);
int heightRight;
bool resultRight = IsAVL(pRoot->m_pRight, heightRight);
// 左子树和右子树都是AVL,并且高度相差不大于1,返回真
if(resultLeft && resultRight && abs(heightLeft - heightRight) <= 1) {
height = max(heightLeft, heightRight) + 1;
return true;
}
else{
height = max(heightLeft, heightRight) + 1;
return false;
}
}
python版:
# 判断平衡二叉树
def isBalanced(self,root):
"""
:typeroot:TreeNode
:rtype:bool
"""
if not root:
return True
resultLeft = self.isBalanced(root.left)
heightLeft = self.treeDepth(root.left)
resultRight = self.isBalanced(root.right)
heightRight = self.treeDepth(root.right)
#左子树和右子树都是AVL,并且高度相差不大于1,返回真
if resultLeft and resultRight and abs(heightLeft-heightRight) <= 1:
return True
else:
return False
#求二叉树的深度
def treeDepth(self,root):
if not root:
return 0
depthLeft = self.treeDepth(root.left)
depthRight = self.treeDepth(root.right)
return depthLeft + 1 if depthLeft > depthRight else depthRight + 1
7、判断两棵二叉树结构是否相同
不考虑数据内容。结构相同意味着对应的左子树和对应的右子树都结构相同。
递归思路:
(1)如果两棵二叉树都为空,返回真;
(2)如果两棵二叉树一棵为空,另一棵不为空,返回假;
(3)如果两棵二叉树都不为空,如果对应的左子树和右子树都同构返回真,其他返回假;
bool StructureCmp(BinaryTreeNode * pRoot1, BinaryTreeNode * pRoot2){
// 都为空,返回真
if(pRoot1 == NULL && pRoot2 == NULL)
return true;
// 有一个为空,一个不为空,返回假
else if(pRoot1 == NULL || pRoot2 == NULL)
return false;
// 比较对应左子树
bool resultLeft = StructureCmp(pRoot1->m_pLeft, pRoot2->m_pLeft);
bool resultRight = StructureCmp(pRoot1->m_pRight, pRoot2->m_pRight); // 比较对应右子树
return (resultLeft && resultRight);
}
8、求二叉树第k层节点个数
递归思路:
(1)如果二叉树为空或者k<1返回0;
(2)如果二叉树不为空并且k==1,返回1;
(3)如果二叉树不为空且k>1,返回左子树中k-1层的节点个数与右子树k-1层节点个数之和;
int GetNodeNumKthLevel(BinaryTreeNode * pRoot, int k){
if(pRoot == NULL || k < 1)
return 0;
if(k == 1)
return 1;
// 左子树中k-1层的节点个数
int numLeft = GetNodeNumKthLevel(pRoot->m_pLeft, k-1);
// 右子树中k-1层的节点个数
int numRight = GetNodeNumKthLevel(pRoot->m_pRight, k-1);
return (numLeft + numRight);
}
9、求二叉树的叶子节点个数
递归思路:
(1)如果二叉树为空,返回0;
(2)如果二叉树不为空且左右子树为空,返回1;
(3)如果二叉树不为空,且左右子树不同时为空,返回左子树中叶子节点个数加上右子树中叶子节点个数;
int GetLeafNodeNum(BinaryTreeNode * pRoot){
if(pRoot == NULL)
return 0;
if(pRoot->m_pLeft == NULL && pRoot->m_pRight == NULL)
return 1;
int numLeft = GetLeafNodeNum(pRoot->m_pLeft); // 左子树中叶节点的个数
int numRight = GetLeafNodeNum(pRoot->m_pRight); // 右子树中叶节点的个数
return (numLeft + numRight);
}
10、求二叉树的镜像
递归思路:
(1)如果二叉树为空,返回空;
(2)如果二叉树不为空,求左子树和右子树的镜像,然后交换左子树和右子树;
BinaryTreeNode * Mirror(BinaryTreeNode * pRoot){
if(pRoot == NULL) // 返回NULL
return NULL;
BinaryTreeNode * pLeft = Mirror(pRoot->m_pLeft); // 求左子树镜像
BinaryTreeNode * pRight = Mirror(pRoot->m_pRight); // 求右子树镜像
// 交换左子树和右子树
pRoot->m_pLeft = pRight;
pRoot->m_pRight = pLeft;
return pRoot;
}
11、求二叉树中两个节点的最近公共祖先节点
递归思路
(1)如果两个节点分别在根节点的左子树和右子树,则返回根节点;
(2)如果两个节点都在左子树,则递归处理左子树;如果两个节点都在右子树,则递归处理右子树;
bool FindNode(BinaryTreeNode * pRoot, BinaryTreeNode * pNode){
if(pRoot == NULL || pNode == NULL)
return false;
if(pRoot == pNode)
return true;
bool found = FindNode(pRoot->m_pLeft, pNode);
if(!found)
found = FindNode(pRoot->m_pRight, pNode);
return found;
}
BinaryTreeNode * GetLastCommonParent(BinaryTreeNode * pRoot, BinaryTreeNode * pNode1, BinaryTreeNode * pNode2){
if(FindNode(pRoot->m_pLeft, pNode1)){
if(FindNode(pRoot->m_pRight, pNode2))
return pRoot;
else
return GetLastCommonParent(pRoot->m_pLeft, pNode1, pNode2);
}
else{
if(FindNode(pRoot->m_pLeft, pNode2))
return pRoot;
else
return GetLastCommonParent(pRoot->m_pRight, pNode1, pNode2);
}
}
非递归思路
先求从根节点到两个节点的路径,然后再比较对应路径的节点就行,最后一个相同的节点也就是他们在二叉树中的最低公共祖先节点。
bool GetNodePath(BinaryTreeNode * pRoot, BinaryTreeNode * pNode,
list<BinaryTreeNode *> & path){
if(pRoot == NULL)
return false;
if(pRoot == pNode){
path.push_back(pRoot);
return true;
}
path.push_back(pRoot);
bool found = false;
found = GetNodePath(pRoot->m_pLeft, pNode, path);
if(!found)
found = GetNodePath(pRoot->m_pRight, pNode, path);
if(!found)
path.pop_back();
return found;
}
BinaryTreeNode * GetLastCommonParent(BinaryTreeNode * pRoot, BinaryTreeNode * pNode1, BinaryTreeNode * pNode2){
if(pRoot == NULL || pNode1 == NULL || pNode2 == NULL)
return NULL;
list<BinaryTreeNode*> path1;
bool bResult1 = GetNodePath(pRoot, pNode1, path1);
list<BinaryTreeNode*> path2;
bool bResult2 = GetNodePath(pRoot, pNode2, path2);
if(!bResult1 || !bResult2)
return NULL;
BinaryTreeNode * pLast = NULL;
list<BinaryTreeNode*>::const_iterator iter1 = path1.begin();
list<BinaryTreeNode*>::const_iterator iter2 = path2.begin();
while(iter1 != path1.end() && iter2 != path2.end()){
if(*iter1 == *iter2)
pLast = *iter1;
else
break;
iter1++;
iter2++;
}
return pLast;
}
12、判断二叉树是否为完全二叉树
首先考虑完全二叉树的特点:若设二叉树的深度为h,除第 h 层外,其它各层 (1~h-1) 的结点数都达到最大个数,第 h 层所有的结点都连续集中在最左边,这就是完全二叉树。
可得思路:按层次(从上到下,从左到右)遍历二叉树,当遇到一个节点的左子树为空时,则该节点右子树必须为空,且后面遍历的节点左右子树都必须为空,否则不是完全二叉树。
bool IsCompleteBinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode * pRoot){
if(pRoot == NULL)
return false;
queue<BinaryTreeNode *> q;
q.push(pRoot);
bool mustHaveNoChild = false;
bool result = true;
while(!q.empty()){
BinaryTreeNode * pNode = q.front();
q.pop();
// 已经出现了有空子树的节点了,后面出现的必须为叶节点(左右子树都为空)
if(mustHaveNoChild){
if(pNode->m_pLeft != NULL || pNode->m_pRight != NULL){
result = false;
break;
}
}
else{
if(pNode->m_pLeft != NULL && pNode->m_pRight != NULL){
q.push(pNode->m_pLeft);
q.push(pNode->m_pRight);
}
else if(pNode->m_pLeft != NULL && pNode->m_pRight == NULL){
mustHaveNoChild = true;
q.push(pNode->m_pLeft);
}
else if(pNode->m_pLeft == NULL && pNode->m_pRight != NULL){
result = false;
break;
}
else{
mustHaveNoChild = true;
}
}
}
return result;
}