springmvc执行过程分析
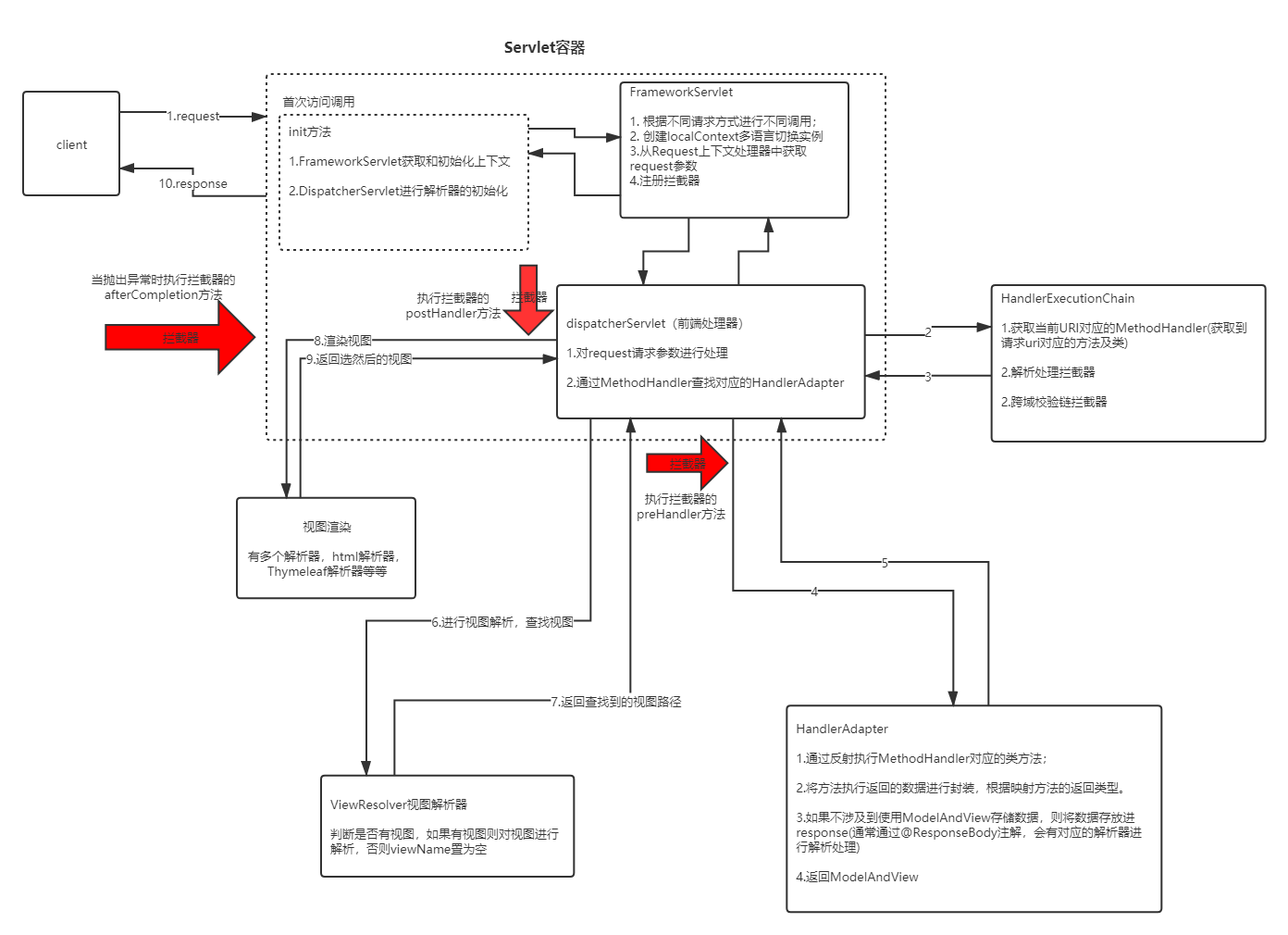
源码分析
前端解析器的UML图
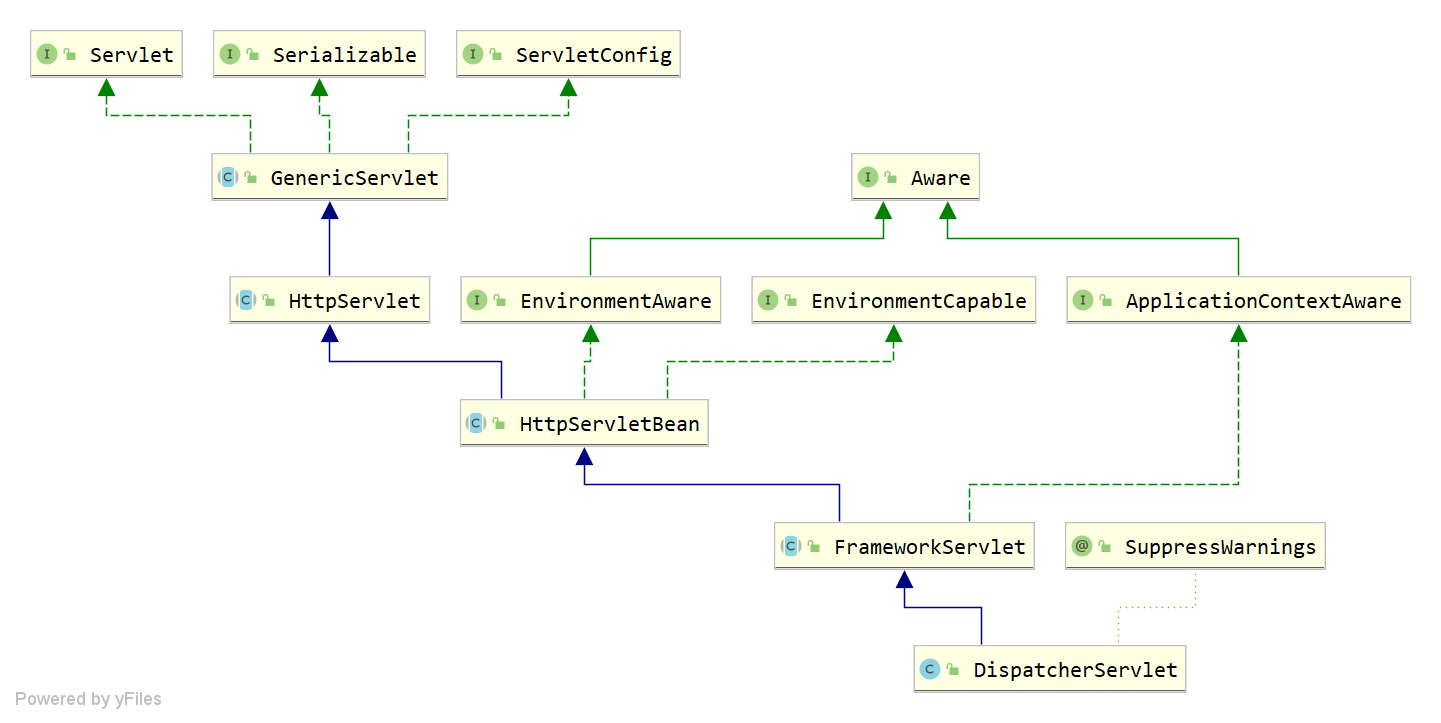
- 因为是对前端请求的URL进行处理,我们只需要看Servlet的继承类就可以了
初始化(主要工作:上下文初始化,和解析器初始化)
-
FrameworkServlet
- 初始化Servlet的上下文, 调用子类的onFresh方法 进行初始化;
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
//。。。。。。。
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
}
/**
* 初始化应用
*/
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//获取应用上下文
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// 上下文在构造时已经注入则直接使用
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
//如果还么有父上下文,则设置父上下文为根上下文
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
// 配置并刷新应用
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
// 如果不存在上下文,查找现有的上下文
if (wac == null) {
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
//需要创建一个Servlet的上下文,初始化上下文的设置
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
// 刷新上下文,这里的onRefresh方法在DispatcherServlet中进行实现
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
//获取Servlet上下文,设置上下文属性。
if (this.publishContext) {
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
-
DispatcherServlet
- 主要是解析器的初始化,总共有一下几种解析器
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
//进行初始化
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
initMultipartResolver(context);//初始化文件上传解析器
initLocaleResolver(context);//本地化解析器(多语言切换使用)
initThemeResolver(context);//当前主题解析
initHandlerMappings(context);//beanNameURL进行映射
initHandlerAdapters(context);//controller进行映射
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);//异常解析器
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);//请求URI转视图名称解析器
initViewResolvers(context);//视图解析器
initFlashMapManager(context);//FlashMap管理
}
接收发送来的请求
-
FrameworkServlet
-
提供了接收请求的实现方法,提供了入口;
-
提供了请求的大致流程,具体如下源码中进行了分析;
-
请求URL业务处理在DispatcherServlet中进行完成,后续代码中会进行分析。
-
@Override
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
/**
* 主要流程:
* 1.创建localContext多语言切换实例
* 2.从Request上下文处理器中获取request参数
* 3.注册拦截器
* 4.初始化上下文处理器,后续请求参数和多语言切换进行处理
* 5.doService处理的是核心的URL隐射业务,这块业务在DispatcherServlet实现
* 6.如果有异常则抛出异常
* 7.请求处理完,则将上下文重置;打印请求日志
* 8.异步执行应用的监听事件
*/
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
//获取本地语言上下文
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
// 获取request新传入的语言
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
//从Request上下文获取请求参数
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
//请求参数转换为ServletRequest的请求参数类型
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
//新建通过管理及注册回调拦截器
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
// 初始化上下文
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
doService(request, response);//子类进行实现
}catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}finally {
//重置上下文
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
//进行回调
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
//打印响应的结果
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
//异步执行应用监听事件
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
//request完成
public void requestCompleted() {
//执行Request回调
executeRequestDestructionCallbacks();
//更新session权限
updateAccessedSessionAttributes();
this.requestActive = false;
}
private void logResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable Throwable failureCause, WebAsyncManager asyncManager) {
if (!logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
return;
}
//转发类型
String dispatchType = request.getDispatcherType().name();
boolean initialDispatch = request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.REQUEST);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
logger.debug("Exiting but response remains open for further handling");
return;
}
// 下面都是日志打印,省略代码。。。。。。
}
-
DispatcherServlet(请求业务的核心处理部分)
- 核心在于,根据MethodHandler,生成ModelAndView 或存入response
/**
* 作用:1.格式化请求参数,派发请求任务到对应的方法处理
*/
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {//当请求有URI的时候,格式化请求参数
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// 设置请求参数
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
try { //进行转发,也是核心方法
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {//重置request的属性
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 这里的主要处理过程是这样的:
* 1.先判断是不是multipart 请求,如果是要进行标记,等处理完之后要进行清空
* 2.判断能否找到request对应的handler处理器(一般都是url请求都是RequestMappingHandlerMapping),如果查找不到直接返回404;
* 3.查找对应请求的处理适配器(一般的都是RequestMappingHandlerAdapter)
* 4.判断如果是GET请求方式,且最后次修改没有变化,直接返回
* 5.执行拦截器的pre方法,如果存在异常直接返回;
* 6.处理器适配器进行业务处理返回ModelAndView,如果ModelAndView非空,且没有View的情况下
* 7.处理拦截器的post方法
* 8.出现异常之后,处罚拦截器的complete方法
* 9.如果是multipart Request的话,进行清空请求数据
*/
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);//判断请求是否为上传文件,如果是文件则进行解析
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 查找当前请求的mappedHandler,下面有分析
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {//映射为空的时候,返回404 错误。
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
/**
* 查找对应的Handler适配器,一般有对应的controller解析,还有requestMapping解析等
*/
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 检测最后修改头,检查请求头是否存在问题,存在问题直接返回
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
//在这里执行拦截器(interceptor),如果执行错误则,返回
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
//执行映射的处理器,是核心部分。后面单独分析
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
//如果ModelAndView中没有View,则返回请求的url
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 拦截器执行postHandler方法
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
/**
* 这里的代码不详细分析,大概执行过程如下:
* 1.判断是否有异常,如果有异常,按照ModelAndViewDefiningException生成对应的ModelAndView
* 2.判断是否有View视图要render,如果有,根据自己配置的渲染方式html,或者thymeleaf进行对应的渲染
*/
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
//出现错误,进行处罚任务完成处理
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
//出现错误,进行处罚任务完成处理
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
//同步管理,判断当前的请求是同步启动则,进行响应的拦截器处理
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// 清空中 multipart request 中的文件信息
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
//获取mappedHandler的具体方法
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);//获取内部的handler
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// 如果处理器是字符串从工厂中招对应的bean
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// 获取执行链,也即MappedInteraptor相关操作
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
//如果有跨域的配置时,重新调整执行链
if (hasCorsConfigurationSource(handler)) {
CorsConfiguration config = (this.corsConfigurationSource != null ? this.corsConfigurationSource.getCorsConfiguration(request) : null);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
config = (config != null ? config.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
//获取对应的HandlerMethod
@Override
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//对Request中的请求url进行解析请求url
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
request.setAttribute(LOOKUP_PATH, lookupPath);
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try { //这里是重点:获取对应的handlerMethod (包含请求uri对应的类及方法)
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
HandlerAdapter进行映射(以RequestMappingHandlerAdapter为例)
- 这里是所有操作的核心所在,主要是,根据URI进行解析查找对应的方法,返回结果进行封装(代码细节太多没有解析)
# AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
}
// 作用:处理uri映射
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
//检查请求头是否允许
checkRequest(request);
//判断session是否要加锁,并执行映射处理方法
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
//省略一部分代码。。。。。。。。。。
}else {
//执行处理的方法
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
//判断请求头是否cache设置,设置response信息
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}
/**
* 作用:
* 1.查找bean对应的方法invocableMethod
* 2.通过反射执行方法;
* 3.将获取到的结果进行封装,并返回ModelAndView.
*/
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try { /**
* 将bean与对应的method进行绑定
* 将method设置参数解析器
*/
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
/**
* 1.获取bean类路径,查看是否有model请求中是否有,以bean类路径为key的访问,没有则初始化
* 2.model访问缓存中如果已经有了这个bean路径,则将对应的方法加入
* 3.新键一个ModelFactory
*/
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
//如过没有设置参数解析器和返回解析器的,增加解析器
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
//ModelView容器进行初始化
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);
asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);
//执行映射,这里执行对应方法的映射,下面有分析
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
//这一步就是设置Model和View,如果Redirect则进行重定向
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
finally {
//request进行销毁
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}
//执行url映射,这里是核心的方法。
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
//这里就是执行任务并且返回结果
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
//设置响应的状态码
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
//判断返回值,如果没数据,或者response有返回原因,则设置请求跳转为true,否则设置为false
if (returnValue == null) {
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
disableContentCachingIfNecessary(webRequest);
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
}
else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");
//将返回数据进行格式化
try {
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatErrorForReturnValue(returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
//执行方法的具体过程
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
//获取请求的参数
Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args));
}
/**
* 这里不具体分析里面的过程,其实就是通过反射调用方法,获取方法执行结果
* 再将执行的结果进行封装,有不同的封装解析器
* RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor这个类提供了将返回的数据进行格式化ServletServerHttpResponse的方法
* 如果不需要ViewAndModel变量,会将requestHandled参数设置为true,表示程序已经处理,不需要视图。
*/
return doInvoke(args);
}
拦截器的执行过程
-
上面源码分析的过程中,已经分析了拦截器的执行过程,这些主要分析一下拦截器pre方法的执行逻辑;
- 拦截器的任一pre前置方法返回false,则触发拦截器的afterCompletion方法
boolean applyPreHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for (int i = 0; i < interceptors.length; i++) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
//执行拦截器前置操作,返回true则继续,false的话进入方法里面
if (!interceptor.preHandle(request, response, this.handler)) {
triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
return false;
}
this.interceptorIndex = i;
}
}
return true;
}
//触发完成后拦截器操作
void triggerAfterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Exception ex)
throws Exception {
HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) {
for (int i = this.interceptorIndex; i >= 0; i--) {
HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i];
try {
//执行完成后操作
interceptor.afterCompletion(request, response, this.handler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex2) {
logger.error("HandlerInterceptor.afterCompletion threw exception", ex2);
}
}
}
}
总结
1. springmvc的重要组件有哪些?都有什么作用?
这个问题,其实在我们前面解析源码的时候就已经看到了。DispatcherServlet初始化的时候,初始化的几个解析器都是常使用的组件。
其中使用频率比较多的就是:
1.HandlerMapping解析器,处理请求URI和对应方法的映射关系的处理器;
2.HandlerAdapter解析器,根据HandleMapping进行对应方法调用处理的解析器;
3.ViewResolver视图解析器,因为现在前后端分离其实很少使用了。