import sys def readfile(filename): f=open(filename) while True: line=f.readline() if len(line)==0: break print("wrong! EOF") print(line) if len(sys.argv) < 2: print ('No action specified.') sys.exit() if sys.argv[1].startswith('--'): option = sys.argv[1][2:] # fetch sys.argv[1] but without the first two characters if option == 'version': print ('Version 1.2') elif option == 'help': print (''' This program prints files to the standard output. Any number of files can be specified. Options include: --version : Prints the version number --help : Display this help''') else: print ('Unknown option.') sys.exit() else: for filename in sys.argv[1:]: readfile(filename)
以上是简明python基础上摘取下来的
都好理解。
用命令行执行你的python程序:如 python my.py --version -y
那么 sys.argv[0]指的是 my.py
sys.argv[1]指的是--version
sys.argv[2]指的是-y
sys.argv[1]("--version")表示的是一个字符串。
所以sys.argv[1][2:]就是 字符串下标为2开始的后面的字符串 就是 “version”了.
备注: my.py 后面要改参数. 即用my.py --version -y
==================================
应用:
把字幕文件 *.VTT 批量转为 *.srt
查看了vtt和srt的区别,使用记事本打开vtt和srt,发现主要有两个
- 首行多了 WEBVTT 标识符
- 标点格式区别,vtt内部的"."在srt中为","
流程图:
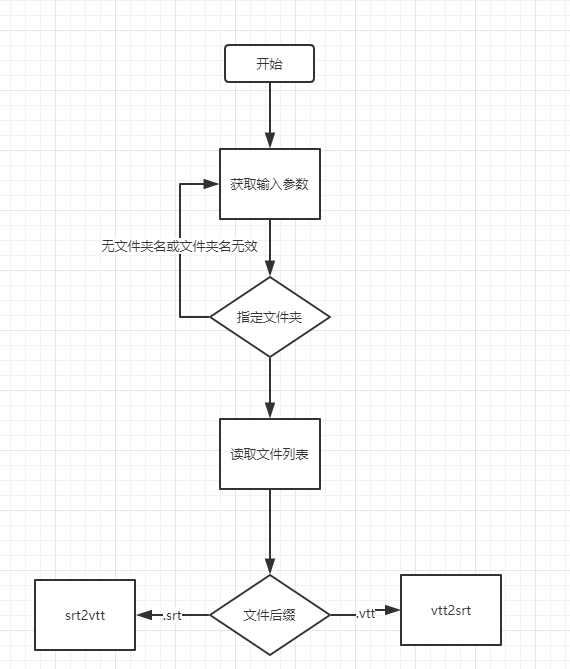
基于python写了一个简单的脚本对其进行批量修改
-
1 引入依赖库
- os获取文件信息
- sys获取命令行输入args
- re对获取的文件内容进行匹配或更换
import os import sys import re
-
2 定义主函数
-
if __name__ == '__main__': args = sys.argv print(args) if os.path.isdir(args[1]): file_list = get_file_name(args[1], ".vtt") for file in file_list: vtt2srt(file) elif os.path.isfile(args[1]): vtt2srt(args[1]) else: print("arg[0] should be file name or dir") -
3 定义获取文件名称函数get_file_name
-
def get_file_name(dir, file_extension): f_list = os.listdir(dir) result_list = [] for file_name in f_list: if os.path.splitext(file_name)[1] == file_extension: result_list.append(os.path.join(dir, file_name)) return result_list -
4 定义转换逻辑
-
def vtt2srt(file_name): content = open(file_name, "r", encoding="utf-8").read() # 删除WEBVTT行 content = re.sub("WEBVTT ",'',content) # 替换“.”为“,” content = re.sub("(d{2}:d{2}:d{2}).(d{3})", lambda m: m.group(1) + ',' + m.group(2), content) output_file = os.path.splitext(file_name)[0] + '.srt' open(output_file, "w", encoding="utf-8").write(content) def srt2vtt(file_name): content = open(file_name, "r", encoding="utf-8").read() # 添加WEBVTT行 content = "WEBVTT " + content # 替换“,”为“.” content = re.sub("(d{2}:d{2}:d{2}),(d{3})", lambda m: m.group(1) + '.' + m.group(2), content) output_file = os.path.splitext(file_name)[0] + '.vtt' open(output_file, "w", encoding="utf-8").write(content) -
5 完整代码
-
import os import sys import re def get_file_name(dir, file_extension): f_list = os.listdir(dir) result_list = [] for file_name in f_list: if os.path.splitext(file_name)[1] == file_extension: result_list.append(os.path.join(dir, file_name)) return result_list def vtt2srt(file_name): content = open(file_name, "r", encoding="utf-8").read() # 删除WEBVTT行 content = re.sub("WEBVTT ",'',content) # 替换“.”为“,” content = re.sub("(d{2}:d{2}:d{2}).(d{3})", lambda m: m.group(1) + ',' + m.group(2), content) output_file = os.path.splitext(file_name)[0] + '.srt' open(output_file, "w", encoding="utf-8").write(content) def srt2vtt(file_name): content = open(file_name, "r", encoding="utf-8").read() # 添加WEBVTT行 content = "WEBVTT " + content # 替换“,”为“.” content = re.sub("(d{2}:d{2}:d{2}),(d{3})", lambda m: m.group(1) + '.' + m.group(2), content) output_file = os.path.splitext(file_name)[0] + '.vtt' open(output_file, "w", encoding="utf-8").write(content) if __name__ == '__main__': args = sys.argv if os.path.isdir(args[1]): file_list = get_file_name(args[1], ".vtt") for file in file_list: vtt2srt(file) elif os.path.isfile(args[1]): vtt2srt(args[1]) print('done') else: print("arg[0] should be file name or dir")
注意:
保存代码到trans.py
若vtt文件在d: mpvtt 文件里,
则写代码:
trans.py d: mpvtt