文章目录
资料原文
util.format
util.inspect
作者笔记pdf
util.format()
语法: util.format(format[, ...args])
参数: format <string>
- 一个类似 printf 的格式字符串
- 包含0个或多个格式占位符(形如 %s %d 的语法结构)
- 每个占位符与后续的参数一一对应
- 最终输出时,每个占位符会被对应参数转换后的值所替换
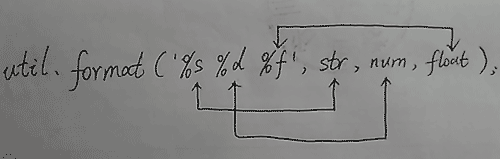
占位符
格式占位符与参数之间的转换总结:
-
第一类–调用js自身的转换函数
%s:
(1)BigInt–转为字符n
(2)定义了toString的对象–调用toString
(3)未定义toString的对象–调用配置为{depth:0,colors:false,compact:3}的 util.inspect()
%d: 使用Number()强制转换
%i: 使用parseInt(value,10)强制转换
%f: 使用parseFloat(value)强制转换 -
第二类–调用node的util.inspect()函数
%o: 调用{showHidden:true,showProxy:true}的util.inspect()
%O: 调用无选项(默认)的util.inspect() -
说明: 只有用到了util.inspect的占位符,换言之也就是%o与%O,配置colors等才有用
-
其余类
(1)%%: 百分号自身,不消耗参数
(2) %j: JSON.如果参数包含循环引用会转为’[Circular]’
util.format注意事项
-
无参数,不替换
util.format('%s:%s', 'foo'); // 返回: 'foo:%s' -
多余参数转字串,空格分割拼后面
util.format('%s:%s', 'foo', 'bar', 'baz'); // 返回: 'foo:bar baz' -
首参不是字符串,参数转为字符串,空格分割拼后面
util.format(1, 2, 3); // 返回: '1 2 3' -
单参原样输出
util.format('%% %s'); // 返回: '%% %s'
util.formatWithOptions(inspectOptions, format[, …args])–仅对%o与%O有效
等同于util.format,但附加了一个传给util.inspect()的inspectOptions配置对象
因为util.format的占位符中,仅%o/%O调用了util.inspect,所以仅对这两个占位符有效
参数:
- inspectOptions
<Object> - format
<string>
util.inspect()
语法1: util.inspect(object[, options])
语法2: util.inspect(object[, showHidden[, depth[, colors]]])
参数:
-
object:
<any>任何js类型(被检查的对象) -
options
<Object>util.inspect()的配置对象-
showHidden
<boolean>: 设为rue, 不可枚举的symbol值和属性,WeakMap和WeakSet实体等会被包含到检查之中(默认false) -
depth
<number>: 格式化检查对象时的递归深度,默认为2const util = require('util'); var obj1 = { l1: { l2: { name: 'peter' }, wife: 'selena', friend: 'laurance' } }; console.log(util.inspect(obj1,{depth:0})); console.log(util.inspect(obj1,{depth:1})); console.log(util.inspect(obj1,{depth:2})); //输出: // { l1: [Object] } // { l1: { l2: [Object], wife: 'selena', friend: 'laurance' } } // { l1: { l2: { name: 'peter' }, wife: 'selena', friend: 'laurance' } } -
colors
<boolean>: 设置为true,输出会被ANSI颜色标记,颜色是可以自定义的(默认false) -
customInspect
<boolean>: 设置为false,[util.inspect.custom](depth,opts)函数不会被调用(绕过对象自定义的inspect检查函数),默认true -
showProxy
<boolean>: 设置为true,Proxy检查会包含target和handler对象.默认为false -
maxArrayLength
<integer>:- 检查对象时, 设置检查Array, TypedArray, WeakMap和WeakSet元素的最大值.
- 设为null或Infinity,检查所有元素.
- 设为0或负值检查0个元素. 默认值100.
-
breakLength
<integer>:- 设置单行最大字符串,超出部分分割为多行.
- 设为Infinity(
compact设为true或任意不小于1的值)来将所有字符串格式化为一行.默认80.
-
compact
<booean>|<integer>:- 设为false, 对象每一个属性都会显示到新的一行;
- 设为true, 启用紧凑型的输出,但一行字符数如超出breakLength,仍会显示到新行
-
sorted
<boolean>|<Function>:- 设为true, 对象,Set和Map实体的所有属性名在结果字符串里会进行排序,此时使用default sort来排序.
- 如果设为function(一个比较函数), 该function被调用用于排序.
const {inspect} = require('util'); var obj = { name: 'peter', age: 18, birth: 2002, gender: 'male' }; var t0 = inspect(obj,{sorted: true}); var t1 = inspect(obj,{sorted: compare}); console.log(t0); //{ age: 18, birth: 2002, gender: 'male', name: 'peter' },默认是对属性名/键名排序 console.log(t1); //{ name: 'peter', gender: 'male', birth: 2002, age: 18 } //函数定义区域---------------------------------------------------------------- function compare(a,b){ if(a>=b){ return -1; } } -
getters
<boolean>|<string>: 默认false- 设为true: 对象所有的getter的返回值被取得并保存在输出结果中
- 设为 ‘get’: 仅无对应setter的getter的返回值会被取得并保存到结果字符串
- 设为 ‘set’: 仅有对应setter的getter的返回值会被取得并保存到结果字符串
const {inspect} = require('util'); var obj = { name: 'peter', age: 18, get getName(){ //无对应setter return this.name; }, get Age(){ //有对应setter return this.age; }, set Age(age){ this.age = age; return age; } }; console.log(inspect(obj,{getters:true})); console.log(inspect(obj,{getters:'get'})); console.log(inspect(obj,{getters:'set'})); //----用Object.defineProperty定义getter和setter------------ var obj2 = { _name: 'peter', _age: 18 }; Object.defineProperty(obj2,'name',{ get:function(){return this.name;} }); Object.defineProperty(obj2,'age',{ get:function(){return this.name;}, set:function(age){this._age=28;} }); obj2.age = 40; console.log(inspect(obj2,{getters:true})); console.log(inspect(obj2,{getters:'get'})); console.log(inspect(obj2,{getters:'set'})); //输出: // { // name: 'peter', // age: 18, // getName: [Getter: 'peter'], //取到了getName的getter的返回值peter // Age: [Getter/Setter: 18] //取到了Age的getter的返回值18 // } // { // name: 'peter', // age: 18, // getName: [Getter: 'peter'], //取到了getName的getter的返回值peter // Age: [Getter/Setter] //未取到Age的getter的返回值18 // } // { name: 'peter', age: 18, getName: [Getter], Age: [Getter/Setter: 18] } //取到了Age的getter的返回值18,未取到Age的getter的返回值18 // { _name: 'peter', _age: 28 } //Object.defineProperty定义的getter均未取到 // { _name: 'peter', _age: 28 } // { _name: 'peter', _age: 28 }
-
-
util.inspect的返回值: 返回一个用于debug的代表被检查对象的字符串.
-
注: util.inspect会使用构造器名称或@@toStringTag来标识一个被检查的值
class Foo { get [Symbol.toStringTag]() { return 'bar'; } } class Bar {} const baz = Object.create(null, { [Symbol.toStringTag]: { value: 'foo' } }); util.inspect(new Foo()); // 'Foo [bar] {}' util.inspect(new Bar()); // 'Bar {}' util.inspect(baz); // '[foo] {}'
自定义颜色-util.inspect.colors/styles
可以通过 util.inspect.styles 和 util.inspect.colors 属性全局地自定义 util.inspect 的颜色输出(如果已启用).
自定义util.inspect的颜色:
指的是:
-
将一个新的ANSI颜色码加入util.inspect.colors集合,并为之关联一个样式名
-
为util.inspect.styles内置的类型名指定一个新的样式名
-
注: 无法在util.inspect.styles中自定义一个类型名
const {inspect} = require('util'); inspect.styles.date = 'blue'; console.log(inspect(inspect.colors,{colors:true,compact:true})); console.log(inspect(inspect.styles,{colors:true,compact:true})); console.log(inspect(new Date(),{colors:true}));
自定义查看函数[util.inspect.custom]
对象可以定义自己的[util.inspect.custom](depth, opts)函数,util.inspect() 检查该对象会调用它并使用其返回的结果.
具体流程:
const {inspect} = require('util');
var obj = {
[util.inspect.custom](depth,opts){
return 'I am an empty object';
}
};
console.log(inspect(obj));
- util.inspect()调用obj的
[util.inspect.custom](depth, opts)函数 - 得到其返回值 ‘I am an empty object’
- util.inspect将上述返回值转换为字符串作为util.inspect的最终输出
注: 在util.inspect(obj,{customInspect: false});中会忽略obj自定义的检查函数.
自定义默认配置项options–util.inspect.defaultOptions
默认配置项: 即 以无配置项形式调用util.inspect()时默认使用的配置设置.
语法: util.inspect.defaultOptions.配置项目 = 配置值;