torch.nn.Module()类有一些重要属性,我们可用其下面几个属性来实现对神经网络层结构的提取:
torch.nn.Module.children()
torch.nn.Module.modules()
torch.nn.Module.named_children()
torch.nn.Module.named_moduless()
为方面说明,我们首先搭建一个简单的神经网络模型,后面所有的内容都是基于这个模型展开的。
1 import torch.nn as nn 2 3 class Net(nn.Module): 4 def __init__(self): 5 super(Net, self).__init__() # input shape (1, 28, 28) 6 self.conv1 = nn.Sequential() 7 self.conv1.add_module('conv1', nn.Conv2d(1, 16, 5, 1, 2)) # output shape (16, 28, 28) 8 self.conv1.add_module('ReLU1', nn.ReLU()) 9 self.conv1.add_module('pool1', nn.MaxPool2d(2)) # output shape (16, 14, 14) 10 11 self.conv2 = nn.Sequential() 12 self.conv2.add_module('conv2', nn.Conv2d(16, 32, 5, 1, 2)) # output shape (32, 14, 14) 13 self.conv2.add_module('ReLU2', nn.ReLU()) 14 self.conv2.add_module('pool2', nn.MaxPool2d(2)) # output shape (32, 7, 7) 15 16 self.linear = nn.Linear(32 * 7 * 7, 10) 17 18 def forward(self, x): 19 x = self.conv1(x) 20 x = self.conv2(x) 21 x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) 22 output = self.linear(x) 23 return output 24 25 net = Net() 26 print(net)
运行结果:
1 Net( 2 (conv1): Sequential( 3 (conv1): Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) 4 (ReLU1): ReLU() 5 (pool1): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) 6 ) 7 (conv2): Sequential( 8 (conv2): Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) 9 (ReLU2): ReLU() 10 (pool2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) 11 ) 12 (linear): Linear(in_features=1568, out_features=10, bias=True) 13 )
torch.nn.Modules.children()
children()这个属性返回下一级模块的迭代器(可与下一小节中的modules()模块对照,更容易理解)。
1 i = 1 2 for layer in net.children(): 3 print('{}th layer:'.format(i)) 4 print(layer) 5 i += 1
运行结果:
1 1th layer: 2 Sequential( 3 (conv1): Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) 4 (ReLU1): ReLU() 5 (pool1): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) 6 ) 7 2th layer: 8 Sequential( 9 (conv2): Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) 10 (ReLU2): ReLU() 11 (pool2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) 12 ) 13 3th layer: 14 Linear(in_features=1568, out_features=10, bias=True)
torch.nn.Modules.modules()
modules()属性返回神经网络每一级的内容。
1 for layer in net.modules(): 2 print(layer) 3 print()
运行结果:
1 Net( 2 (conv1): Sequential( 3 (conv1): Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) 4 (ReLU1): ReLU() 5 (pool1): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) 6 ) 7 (conv2): Sequential( 8 (conv2): Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) 9 (ReLU2): ReLU() 10 (pool2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) 11 ) 12 (linear): Linear(in_features=1568, out_features=10, bias=True) 13 ) 14 15 Sequential( 16 (conv1): Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) 17 (ReLU1): ReLU() 18 (pool1): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) 19 ) 20 21 Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) 22 23 ReLU() 24 25 MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) 26 27 Sequential( 28 (conv2): Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) 29 (ReLU2): ReLU() 30 (pool2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) 31 ) 32 33 Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) 34 35 ReLU() 36 37 MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) 38 39 Linear(in_features=1568, out_features=10, bias=True)
从上面的运行结果可以看出来,modules()模块以迭代器的形式返回神经网络逐级的内容。
torch.nn.Modules.named_children()和torch.nn.Modules.named_modules()
named_children()和named_modules()这两个模块不仅返回模块的迭代器,而且还会返回网络层的名字。
1 for layer in net.named_modules(): 2 print(layer)
运行结果:
1 ('', Net( 2 (conv1): Sequential( 3 (conv1): Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) 4 (ReLU1): ReLU() 5 (pool1): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) 6 ) 7 (conv2): Sequential( 8 (conv2): Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) 9 (ReLU2): ReLU() 10 (pool2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) 11 ) 12 (linear): Linear(in_features=1568, out_features=10, bias=True) 13 )) 14 ('conv1', Sequential( 15 (conv1): Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) 16 (ReLU1): ReLU() 17 (pool1): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) 18 )) 19 ('conv1.conv1', Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))) 20 ('conv1.ReLU1', ReLU()) 21 ('conv1.pool1', MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)) 22 ('conv2', Sequential( 23 (conv2): Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) 24 (ReLU2): ReLU() 25 (pool2): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False) 26 )) 27 ('conv2.conv2', Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))) 28 ('conv2.ReLU2', ReLU()) 29 ('conv2.pool2', MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)) 30 ('linear', Linear(in_features=1568, out_features=10, bias=True))
只提取模型中的卷积层
如果希望只提取卷积层,可以这样操作:
1 conv_net = nn.Sequential() 2 for layer in net.named_modules(): 3 if isinstance(layer[1], nn.Conv2d): 4 conv_net.add_module(layer[0][:5], layer[1]) # layer[1] is the net layer, layer[0] is its name. 5 print(conv_net)
运行结果:
Sequential( (conv1): Conv2d(1, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) (conv2): Conv2d(16, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2)) )
参数初始化
参数初始化需用到torch.nn.init,下面几个函数比较常用,截图摘自PyTorch中文文档。
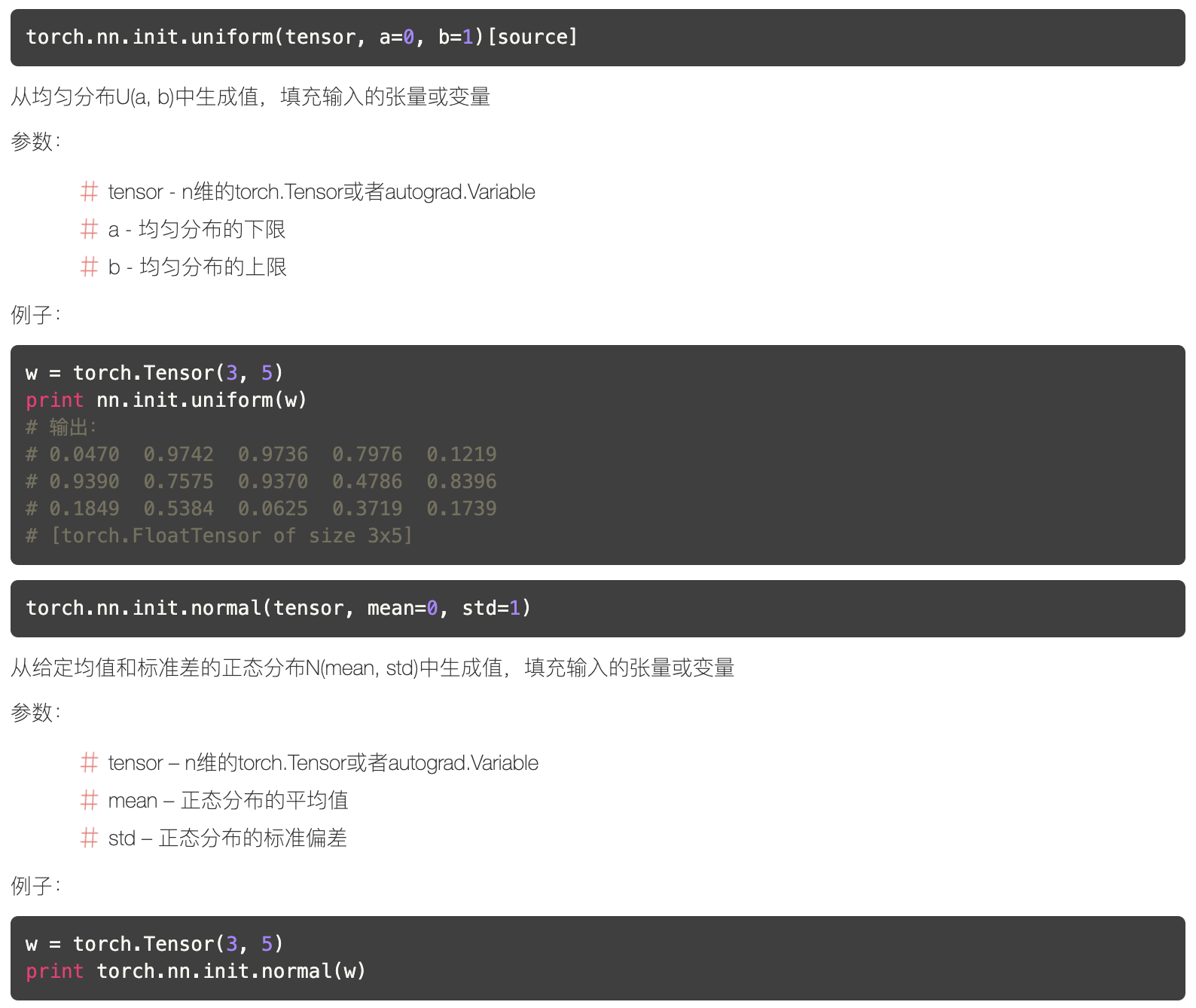


在神经网络中,模型参数就是weights和bias,weights和bias在PyTorch中是Variable,所以我们只需取出weights的data属性,并填充数值就可以了。比如对卷积层进行参数初始化:
1 for m in net.modules(): 2 if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): 3 nn.init.normal(m.weight.data) 4 # nn.init.xavier_normal(m.weight.data) 5 # nn.init.kaiming_normal(m.weight.data) 6 elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear): 7 m.weight.data.normal_() 8 m.bias.data.fill_(0)
参考文献:
深度学习之PyTorch第四章,廖星宇.