此博客链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/ping2yingshi/p/14089282.html
二叉树的中序遍历
题目
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它的 中序 遍历。
示例 1:
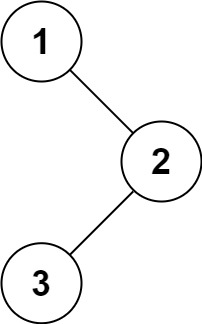
输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[1,3,2]
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[1]
示例 4:
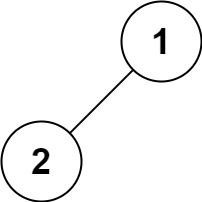
输入:root = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 5:
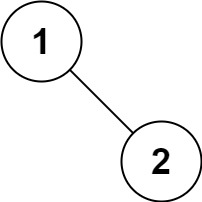
输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:[1,2]
提示:
树中节点数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
题解
思路1:递归
递归遍历二叉树的左子树,根,右子树。
方法1:
1.先定义一个递归函数用来递归遍历二叉树。
2.把根的左子树当成函数参数,先遍历左子树。
3.函数出口为当节点为空时返回空。
4.定义一个数组,把按顺序遍历的节点放入到数组中。
代码
class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List <Integer> list=new ArrayList(); indor(root,list); return list; } public void indor(TreeNode mid,List<Integer> list) { if(mid==null) return ; indor(mid.left,list); list.add(mid.val); indor(mid.right,list); } }
结果1
思路2:栈
使用栈中序遍历二叉树,先把二叉树的左子树全部放入到栈中,取出左子树最下端的一个节点,加入到结果集中,然后遍历右子树。
方法2:
1.
代码
class Solution { public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List <Integer> list=new ArrayList(); Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack(); while(root!=null||!stack.isEmpty()){ while(root!=null){ stack.push(root); root=root.left; } root=stack.pop(); list.add(root.val); root=root.right; } return list; } }
结果2
