1. 问题背景:如何保证发布出去的bin文件是最终测试通过的版本?
一般的来讲,代码到了测试后期,master分支就不会频繁的提交了,并且提交也会更加谨慎。
但是人为操作总会出现纰漏,希望只要代码被重新编译过,那么bin文件就包含新的时间信息,而这个信息是可以从外部通信或printf来查看的。
在嵌入式开发中,版本号一般的都是一个int变量或字符串变量。但是若修改了代码而没有改version变量或宏定义,那么从version上就看不出来文件的变化。
那么最终编译的版本到底是哪个版本,是否与测试的版本完全一致,这个问题尤为突出。
目标文件中带有编译时间可以防止代码被改动过,只要代码被重新编译,那么就生成新的时间信息。
git能够记录文件修改信息,但是调试信息或工程配置等,很多文件都是ignore的,这些信息代表着最终的bin文件的运行环境。
某些复杂bug情况下,只有运行环境一致,仿真器才能attach到目标文件。
2. 如何获取时间:__DATA__, __TIME__
这两个宏是日期和时间,格式如下。如果把这两个宏加入到代码,那么就得到了时间的字符串信息。
// Example of __DATE__ string: "Dec 27 2017" // Example of __TIME__ string: "15:06:19"
const char *BuildInfo = "Version: " VERSION " " __DATE__ " " __TIME__;
代码实现获取日期和时间的方法很多,比如:
1 unsigned int mk_Build_Date(void) 2 { 3 int year = 0, month = 0, day = 0; 4 int hour = 0, minute = 0, seconds = 0; 5 char m[4] = {0}; 6 7 sscanf(__DATE__, "%3s %2d %4d", m, &day, &year); 8 9 for (month = 0; month < 12; month++) 10 { 11 if (strcmp(m, short_char_months[month]) == 0) 12 { 13 break; 14 } 15 } 16 17 sscanf(__TIME__, "%2d:%2d:%2d", &hour, &minute, &seconds); 18 19 #ifdef SHORT_DATA_CHAR__ 20 printf("[null] ** Build at: %04u-%02u-%02us %02u:%02u:%02u ", 21 year, month, day, 22 hour, minute,seconds); 23 24 #else 25 printf("[null] ** Build at: %04u-%02u-%02u %02u:%02u:%02u ", 26 year, month, day, 27 hour, minute,seconds); 28 #endif 29 30 DEBUG("buildDate: %s %s ", __DATE__, __TIME__); 31 32 return 0; 33 }
把上面的函数加入到代码中,就能获取工程编译的时间。
但是如果该代码所在的文件没有被修改,在非build-all情况下,编译器不会再次编译此文件,所以时间信息也就不会被更新。
如果每次都使用re-build all,一来繁琐,二来也不能保证每次都会记得点击build all按钮,靠技术手段来保证每次build都更新时间信息才是正道。
3. 如何保证时间每次编译都更新:使用预编译指令,每次更新包含时间宏的文件或对应的链接文件。
在IAR环境下,官方已经给出了解决的方法(Using pre-build actions for time stamping)。
Technical Note 99436
https://www.iar.com/support/tech-notes/ide/build-actions-pre-build-and-post-build/
方法1:修改文件的时间,引起编译器对文件进行重新编译。
cmd /c "touch /cygdrive/d/test.c"
方法虽好,可惜IAR用户大多数是Windows用户,包括我在内,touch是linux命令,必须Cywin环境。如果安装过这个环境的话,那就大功告成了。
Cygwin touch command You can enter "cygwin-application.exe" on the pre- and post-build command lines, if the environment variable PATH includes the directory where the "cygwin-application.exe" is located. You can run the Cygwin command "touch" on the pre-build command line, but if you add a file path, for example "touch d:/test.c", the file path is not accepted by Cygwin. Cygwin expects the POSIX path /cygdrive/d/test.c so the resulting command line would be "touch /cygdrive/d/test.c", however this command cannot be executed directly on the pre- and post-build command. Instead you have to run indirectly using: cmd /c "touch /cygdrive/d/test.c" The .bat file (located in project directory) alternative would look like: Pre-build command line: $PROJ_DIR$pre-build.bat File pre-build.bat: touch /cygdrive/d/test.c
方法2:修改文件对应的链接文件,触发编译器重新编译该文件,生成新的链接文件,那么就会生成新的带有时间信息的目标文件。
An alternative to the "touch" command is to have a pre-build action that deletes the object file, for example the Pre-build command line: cmd /c "del "$OBJ_DIR$ est.o""
在pre-build中加入上面的命令,就会在编译前删除test.o文件。
在这种模式下,工程代码只要任何位置发生变化,代码重新编译,就会触发删除test.o,然后链接过程发现没有test.o文件,那么就会重新编译一次test.c,那么新的时间信息就会记录下来了。
虽有些曲线救国的味道,但还是很顺利的实现了目标。
只要工程的任何地方有改动,生成新的目标文件,那么目标文件中就会带有最新的编译时间。
方法3:直接告诉编译器每次重新编译某个文件更直接,MDK支持此功能。
时隔一年半再次来这里,发现当时自己简直是小白,还洋洋得意曲线救国,实际上舍近求远罢了。
如果对工具多一些了解,万万是不会用上面的方法的,当然上面的方法也是通用想法,是通用型知识点,容易想到,也能达到目标。
新的方法,不需要写任何脚本,如果想让代码每次都编译更新DATA 和 TIME两个宏,那么让这个文件每次都编译一次就可以了,不需要删除它的obj文件然后让编译器找不到文件而触发重新编一次,其实直接告诉编译器每次重新编译更直接,MDK支持此功能。
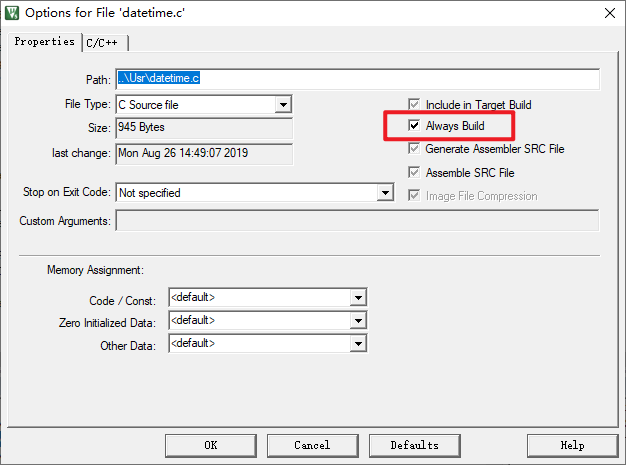
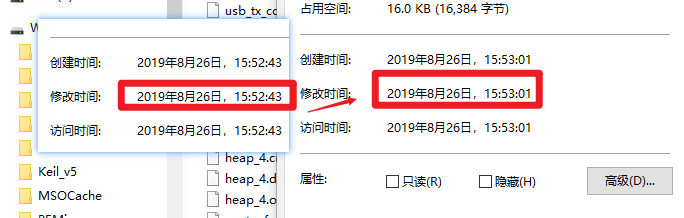
下面是测试的效果:
其他:How to use __DATE__ and __TIME__ predefined macros in as two integers, then stringify?
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/11697820/how-to-use-date-and-time-predefined-macros-in-as-two-integers-then-stri