1.Netty介绍
1.1为什么需要Netty
1.1.1不是所有的网络框架都是一样的
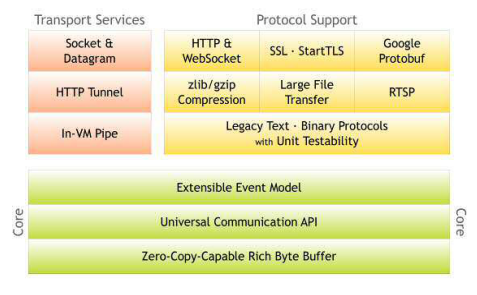
1.1.2Netty的功能非常丰富
框架组成
1.2异步设计
1.2.1Callbacks(回调)
简单的回调
public interface Fetcher { void fetchData(FetchCallback callback); } public interface FetchCallback { void onData(Data data); void onError(Throwable cause); } public class Worker { public void doWork() { Fetcher fetcher = ... fetcher.fetchData(new FetchCallback() { @Override public void onData(Data data) { //获取到数据 System.out.println("Data received: " + data); } @Override public void onError(Throwable cause) { //未获取到数据 System.err.println("An error accour: " + cause.getMessage()); } }); } }
Fetcher.fetchData()方法需传递一个FetcherCallback类型的参数,当获得数据或发生错误时被回调。对于每种情况都提供了统一的方法:FetcherCallback.onData(),将接收数据时被调用;FetcherCallback.onError(),发生错误时被调用
1.2.2Futures
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); Runnable task1 = new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { doSomeHeavyWork(); } //... } Callable<Interger> task2 = new Callable() { @Override public Integer call() { return doSomeHeavyWorkWithResul(); } //... } Future<?> future1 = executor.submit(task1); Future<Integer> future2 = executor.submit(task2); while(!future1.isDone()||!future2.isDone()){ ... // do something else ... }
Future的未来应用
public interface Fetcher { Future<Data> fetchData(); } public class Worker { public void doWork() { Fetcher fetcher = ... Future<Data> future = fetcher.fetchData(); try { while (!fetcher.isDone()) { //... // do something else } System.out.println("Data received: " + future.get()); } catch (Throwable cause) { System.err.println("An error accour: " + cause.getMessage()); } } }
1.3Java中的Blocking和non-blocking IO对比
1.3.1基于阻塞IO的EchoServer
public class PlainEchoServer { public void serve(int port) throws IOException { final ServerSocket socket = new ServerSocket(port);//绑定端口 try { while (true) { final Socket clientSocket = socket.accept(); //阻塞,直到接受新的客户端连接为止。 System.out.println("Accepted connection from " + clientSocket); new Thread(new Runnable() { //创建处理客户端连接的新线程 @Override public void run() { try { BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(clientSocket.getInputStream())); PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(clientSocket.getOutputStream(), true); while (true) { //从客户端读取数据并将其写回 writer.println(reader.readLine()); writer.flush(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); try { clientSocket.close(); } catch (IOException ex) { // ignore on close } } } }).start(); //开始执行程序 } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
1.3.2非阻塞IO基础
ByteBuffer
将数据写入ByteBuffer
调用ByteBuffer.flip()从写模式切换到读取模式
从ByteBuffer读取数据
ByteBuffer.clear()清除所有数据
Bytebuffer.compact()清除已读取数据
Channel inChannel = ....; ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(48); int bytesRead=-1; do{ bytesRead=inChannel.read(buf); //将数据从通道读取到ByteBuffer if(bytesRead!=-1){ buf.flip();//使缓冲区为读做准备 while(buf.hasRemaining()){ System.out.print((char)buf.get()); //读取ByteBuffer中的字节;每个get()操作都会将位置更新1 } buf.clear(); //让ByteBuffer准备好再写一遍 } }while(bytesRead!=-1); inChannel.close();
使用NIO选择器
1.创建一个或多个选择器,其中可以注册打开的通道(套接字)。
2.注册信道时,指定您感兴趣侦听的事件。以下四个可用事件(或操作/操作)为:接收、连接、读取、等待
3.在注册通道时,您可以调用Selector.select()方法来阻塞,直到发生这些事件之一。
4.当该方法解除阻塞时,您可以获得所有SelectionKey实例(这些实例保存对已注册通道和所选操作的引用)并执行一些操作。 您到底做了什么取决于哪个操作已经准备好了。SelectedKey可以在任何给定时间包含多个操作。
1.3.3基于NIO的EchoServer
public class PlainNioEchoServer { public void serve(int port) throws IOException { System.out.println("Listening for connections on port " + port); ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); ServerSocket ss = serverChannel.socket(); InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(port); ss.bind(address);//将服务器绑定到端口 serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);//设置为非阻塞 Selector selector = Selector.open(); serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);//向选择器注册通道,以便对被接受的新客户端连接感兴趣 while (true) { try { selector.select();//阻塞,直到选定某物为止。 } catch (IOException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); // handle in a proper way break; } Set readyKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); //获取所有SelectedKey实例 Iterator iterator = readyKeys.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) iterator.next(); iterator.remove();//从迭代器中删除SelectedKey try { if (key.isAcceptable()) { ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel(); SocketChannel client = server.accept();//接受客户端连接 System.out.println("Accepted connection from " + client); client.configureBlocking(false);//设置为非阻塞 client.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE | SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(100));//注册到选择器的连接并设置ByteBuffer } if (key.isReadable()) {//检查SelectedKey的阅读 SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); ByteBuffer output = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment(); client.read(output); //读取数据到ByteBuffer } if (key.isWritable()) {//检查SelectedKey的写 SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); ByteBuffer output = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment(); output.flip(); client.write(output); output.compact();//将数据从ByteBuffer写入信道 } } catch (IOException ex) { key.cancel(); try { key.channel().close(); } catch (IOException cex) { } } } } } }
1.3.4基于NIO.2的EchoServer
与最初的NIO实现不同,NIO.2允许您发出IO操作并提供所谓的完成处理程序
public class PlainNio2EchoServer { public void serve(int port) throws IOException { System.out.println("Listening for connections on port " + port); final AsynchronousServerSocketChannel serverChannel = AsynchronousServerSocketChannel.open(); InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(port); serverChannel.bind(address); final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1); serverChannel.accept(null, new CompletionHandler<AsynchronousSocketChannel, Object>() { //开始接受新的客户端连接。一旦其中一个被接受,CompletionHandler就会被调用。 @Override public void completed(final AsynchronousSocketChannel channel, Object attachment) { serverChannel.accept(null, this); //再次接受新的客户端连接 ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(100); channel.read(buffer, buffer, new EchoCompletionHandler(channel)); //触发通道上的读取操作,一旦读取某个消息,将通知给定的PrimeTyHand处理程序。 } @Override public void failed(Throwable throwable, Object attachment) { try { serverChannel.close(); //关闭套接字错误 } catch (IOException e) { // ingnore on close } finally { latch.countDown(); } } }); try { latch.await(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } private final class EchoCompletionHandler implements CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer> { private final AsynchronousSocketChannel channel; EchoCompletionHandler(AsynchronousSocketChannel channel) { this.channel = channel; } @Override public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer buffer) { buffer.flip(); channel.write(buffer, buffer, new CompletionHandler<Integer, ByteBuffer>() { //触发通道上的写操作,给定的CompletionHandler一写就会被通知 @Override public void completed(Integer result, ByteBuffer buffer) { if (buffer.hasRemaining()) { channel.write(buffer, buffer, this); //如果ByteBuffer中有东西,则再次触发写操作。 } else { buffer.compact(); channel.read(buffer, buffer, EchoCompletionHandler.this); //触发通道上的读取操作,一旦读取某个消息,将通知给定的PrimeTyHand处理程序。 } } @Override public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) { try { channel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // ingnore on close } } }); } @Override public void failed(Throwable exc, ByteBuffer attachment) { try { channel.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // ingnore on close } } } }
1.4NIO的问题和Netty中是如何解决这些问题的
1.4.1 跨平台和兼容性问题
1.4.2扩展ByteBuffer.或者不扩展
1.4.3散射和聚集可能会泄漏
1.4.4解决著名的epoll空轮询bug
1.5小结
2.第一个Netty程序
2.1搭建开发环境
2.2Netty客户机和服务器概述
2.3编写Echo服务器
2.3.1引导服务器
public class EchoServer { private final int port; public EchoServer(int port) { this.port = port; } public void start() throws Exception { EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); //创建引导服务器 b.group(group); b.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);//指定nio传输、本地套接字地址。 b.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port)); b.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { //将处理程序添加到通道管道 @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoServerHandler()); //绑定服务器,等待服务器关闭,并释放资源。 } }); ChannelFuture f = b.bind().sync(); //绑定服务器,然后等待绑定完成,对sync()方法的调用将导致阻塞,直到服务器绑定。 System.out.println(EchoServer.class.getName() + "ì started and listen on ì" + f.channel().localAddress());//应用程序将等到服务器通道关闭。 f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { group.shutdownGracefully().sync(); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { if (args.length != 1) { System.err.println("ìUsage:" + EchoServer.class.getSimpleName() + " < port > "); } int port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); new EchoServer(port).start(); } }
2.3.2实现服务器/业务逻辑
@ChannelHandler.Sharable //使用@Sharable注释,以便在各通道之间共享 public class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { @Override public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) { System.out.println("Server received: " + msg); ctx.write(msg);//把收到的消息写回去。请注意,这将不会将消息刷新到远程对等端。 } @Override public void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.EMPTY_BUFFER).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); //将所有以前的书面消息(挂起)刷新到远程对等端,并在操作完成后关闭通道。 } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) { cause.printStackTrace(); //异常日志 ctx.close(); //异常关闭通道 } }
2.3.3捕获异常
2.4编写回送客户端
2.4.1引导客户端
public class EchoClient { private final String host; private final int port; public EchoClient(String host, int port) { this.host = host; this.port = port; } public void start() throws Exception { EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); //为客户端创建引导程序 b.group(group); //指定EventLoopGroup来处理客户端事件。使用NioEventLoopGroup,因为应该使用NIO-传输 b.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);//指定通道类型;为NIO-传输使用正确的通道类型 b.remoteAddress(new InetSocketAddress(host, port));//设置客户端连接的InetSocketAddress b.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { //使用ChannelInitiators指定ChannelHandler,一旦连接建立并创建通道,就调用它 @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new EchoClientHandler());//将EchoClientHandler添加到属于通道的Channel管道。管道拥有所有通道的通道处理器 } }); ChannelFuture f = b.connect().sync(); //将客户端连接到远程对等端;等待sync()完成连接 f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); //等到ClientChannel关闭。这会挡住。 } finally { group.shutdownGracefully().sync(); //关闭引导程序和线程池;释放所有资源 } } public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { if (args.length != 2) { System.err.println("Usage: " + EchoClient.class.getSimpleName() + " <host> <port>"); return; } // Parse options. final String host = args[0]; final int port = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); new EchoClient(host, port).start(); } }
2.4.2实现客户端逻辑
@ChannelHandler.Sharable //使用@Sharable注释,因为它可以在通道之间共享 public class EchoClientHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> { @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) { ctx.write(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Netty rocks!", CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); //现在写入通道连接的消息 } @Override public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in) { System.out.println("Client received: " + ByteBufUtil.hexDump(in.readBytes(in.readableBytes()))); //以己转储的形式记录接收到的消息 } @Override public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {//日志异常和关闭通道 cause.printStackTrace(); ctx.close(); } }
2.5编译和运行回送客户端和服务器
2.5.1编译服务器和客户端
2.5.2运行服务器和客户端
2.6小结
3.Netty核心概念
3.1Netty速成班
3.2通道、事件和输入/输出(IO)
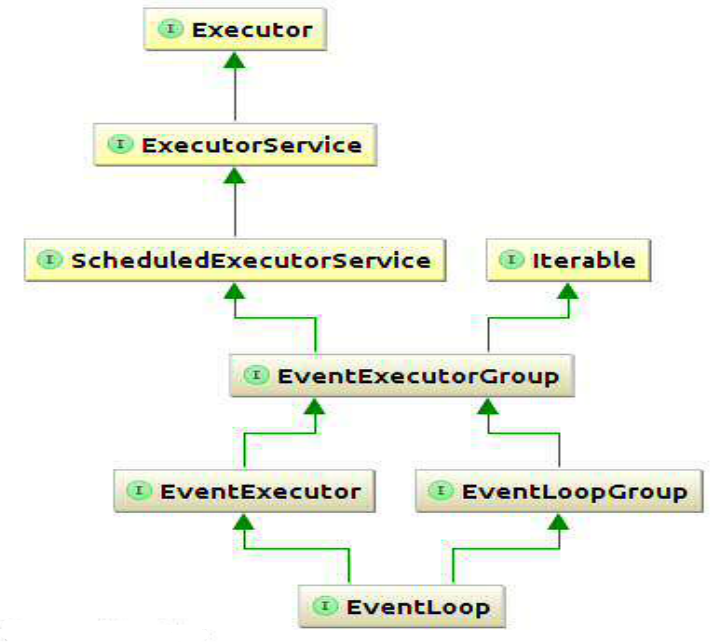
EventLoops与EventLoopGroups的关系。
3.3引导:什么和为什么
3.4通道处理程序和数据流
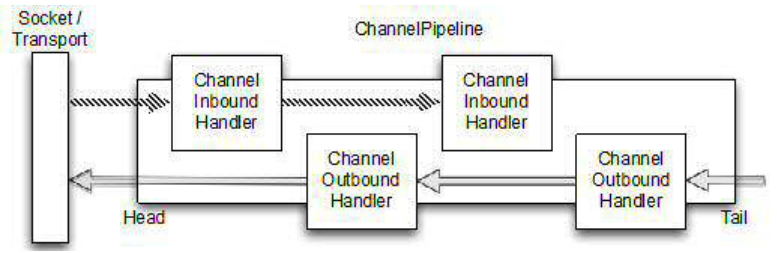
3.4.1把它拼凑在一起,管道和处理程序
管道安排的示例。
3.5编码器、解码器和域逻辑:对处理程序的深入观察
3.5.1Encodes,Deodes
3.5.2域逻辑
4.Transports(传输)
4.1案例研究:运输迁移
4.1.1使用无网络的I/O和NIO
public class PlainOioServer { public void serve(int port) throws IOException { final ServerSocket socket = new ServerSocket(port); try { while (true) { final Socket clientSocket = socket.accept(); System.out.println("Accepted connection from " + clientSocket); //创建新线程来处理连接 new Thread(() -> { OutputStream out; try { out = clientSocket.getOutputStream(); out.write("Hi! ".getBytes(Charset.forName("UTF-8"))); //向连接的客户端写入消息 out.flush(); clientSocket.close(); //一旦消息被写入并刷新,就关闭连接。 } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); try { clientSocket.close(); } catch (IOException ex) { // ignore on close } } }).start(); //启动线程开始处理 } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
4.1.2没有Netty的异步网络
public class PlainNioServer { public void serve(int port) throws IOException { System.out.println("Listening for connections on port " + port); ServerSocketChannel serverChannel; Selector selector; serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); ServerSocket ss = serverChannel.socket(); InetSocketAddress address = new InetSocketAddress(port); ss.bind(address); serverChannel.configureBlocking(false); selector = Selector.open();//打开处理通道的选择器 serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); //将erverSocket注册到选择器,并指定它对新接受的客户端感兴趣。 final ByteBuffer msg = ByteBuffer.wrap("Hi! ".getBytes()); while (true) { try { selector.select(); //等待已准备好进行处理的新事件。这将阻止直到发生什么事情 } catch (IOException ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); // handle in a proper way break; } Set<SelectedKey> readyKeys = selector.selectedKeys(); //获取接收事件的所有SelectionKey实例 Iterator<SelectedKey> iterator = readyKeys.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey key = iterator.next(); iterator.remove(); try { if (key.isAcceptable()) { //检查事件是否是因为新客户端准备接受 ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel(); SocketChannel client = server.accept(); System.out.println("Accepted connection from " + client); client.configureBlocking(false); client.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE | SelectionKey.OP_READ, msg.duplicate()); //接受客户端并将其注册到选择器 } if (key.isWritable()) { //检查事件是否因为套接字已准备好写入数据 SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) key.channel(); ByteBuffer buffer = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment(); while (buffer.hasRemaining()) { if (client.write(buffer) == 0) { //将数据写入连接的客户端。如果网络饱和,这可能不会写入所有数据。如果是这样的话,它将捡起未写入的数据,并在网络再次可写时将其写入。 break; } } client.close(); } } catch (IOException ex) { key.cancel(); try { key.channel().close(); } catch (IOException cex) { } } } } } }
4.1.3在Netty中使用I/O和NIO
public class NettyOioServer { public void server(int port) throws Exception { final ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.unreleaseableBuffer(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hi! ", Charset.forName("UTF-8"))); EventLoopGroup group = new OioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); b.group(group); b.channel(OioServerSocketChannel.class);//使用OioEventLoopGroupIto允许阻塞模式(旧-IO) b.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port)); b.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { //指定将为每个接受的连接调用的信道初始化器 @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() { //添加ChannelHandler来拦截事件并允许对它们作出反应 @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { ctx.write(buf.duplicate()).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);//向客户端写入消息,并在消息写入后添加ChannelFutureListener以关闭连接 } }); } }); ChannelFuture f = b.bind().sync(); //绑定服务器以接受连接 f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { group.shutdownGracefully().sync(); //释放所有资源 } } }
4.1.4实现异步支持
public class NettyNioServer { public void server(int port) throws Exception { final ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.unreleaseableBuffer(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hi! ", Charset.forName("UTF-8"))); EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); b.group(group); b.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);//使用OioEventLoopGroupIto允许阻塞模式(旧-IO) b.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port)); b.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { //指定将为每个接受的连接调用的信道初始化器 @Override public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() { //添加ChannelHandler来拦截事件并允许对它们作出反应 @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { ctx.write(buf.duplicate()).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);//向客户端写入消息,并在消息写入后添加ChannelFutureListener以关闭连接 } }); } }); ChannelFuture f = b.bind().sync(); //绑定服务器以接受连接 f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { group.shutdownGracefully().sync(); //释放所有资源 } } }
4.2传输API
通道接口层次结构
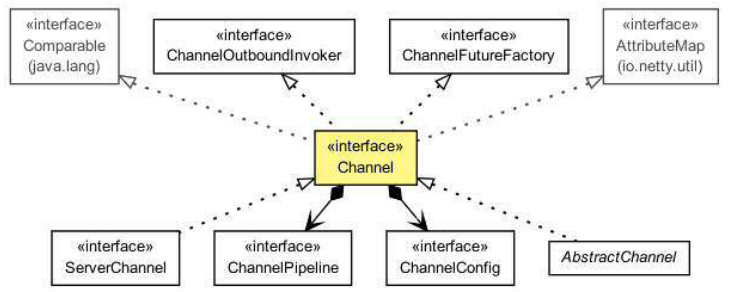
最重要的信道方法
eventLoop()返回分配给通道的EVELATIORE
pipeline()返回分配给通道的通道管道。
isActive()如果通道处于活动状态,则返回该通道,这意味着它已连接到远程对等端。
localAddress()返回绑定到本地的SocketAddress
remoteAddress()返回绑定远程的SocketAddress
write()将数据写入远程对等程序。这些数据是通过管道传递的。
写信给频道
Channel channel = ... ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(..your data, CharsetUtil.UTF_8);//创建保存要写入的数据的ByteBuf ChannelFuture cf = channel.write(buf);//写数据 cf.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { //添加ChannelFutureListener,以便在写入完成后得到通知 @Override public void operationComplete (ChannelFuture future){ if (future.isSuccess()) { //写入操作完成,没有错误。 System.out.println("Write successful"); } else { System.err.println("Write error"); //写入操作已完成,但由于错误 future.cause().printStacktrace(); } } });
使用来自多个线程的通道
final Channel channel = ... final ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(..your data", CharsetUtil.UTF_8); //创建保存要写入的数据的ByteBuf Runnable writer = new Runnable() { //创建Runnable将数据写入通道 @Override public void run() { channel.write(buf.duplicate()); } }; Executor executor = Executors.newChachedThreadPool();//获取对执行程序的引用,该执行器使用线程执行任务。 // write in one thread executor.execute(writer); //将写任务交给Executor,以便在线程中执行。 // write in another thread executor.execute(writer); //将另一个写任务交给Executor,以便在线程中执行。
4.3包括运输
4.3.1NiO非阻塞I/O
选择操作位集
OP_ACCEPT一旦新连接被接受并创建了一个通道,就会得到通知。
OP_CONNECT一旦连接尝试完成,就会收到通知。
OP_READ一旦数据准备好从通道中读取,就会得到通知。
OP_WRITE一旦有可能将更多的数据写入通道,就会得到通知。大多数情况下,这是可能的,但可能不是因为OS套接字缓冲区已完全填满。 您编写得更快,远程对等程序就可以处理它。
选择器逻辑
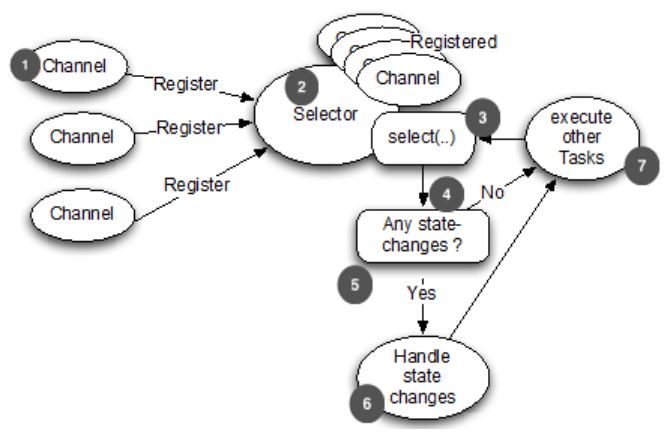
4.3.2OIO旧阻塞I/O
4.3.3VM传输中的局部
4.3.4嵌入式传输
4.4何时使用各种运输方式
低并发连接计数->OIO
高并发连接计数->NIO
低延时->OIO
基本模块代码->OIO
在同一个JVM中进行通信->Local
测试ChannelHandler实现->Embedded
5.Buffers(缓冲)
5.1缓冲API
5.2字节数据容器
5.2.1工作原理
5.2.2不同类型的ByteBuf
Heap Buffer(堆缓冲区)
ByteBuf heapBuf = ...; if (heapBuf.hasArray()) { //检查ByteBuf是否由数组支持 byte[] array = heapBuf.array(); //获取对数组的引用 int offset = heapBuf.arrayOffset() + heapBuf.position(); //计算其中第一个字节的偏移量 int length = heapBuf.readableBytes(); //获取可读字节的数量 YourImpl.method(array, offset, length); //使用数组、偏移量、长度作为参数的调用方法 }
Direct Buffer(直接缓冲区)
ByteBuf directBuf = ...; if (!directBuf.hasArray()){ //检查ByteBuf是否不受数组支持,对于直接缓冲区,数组为false int length = directBuf.readableBytes(); //获取可读字节数 byte[] array = new byte[length]; //分配具有可读字节长度的新数组 directBuf.getBytes(array); //将字节读入数组 YourImpl.method(array, 0, array.length);//以数组、偏移量、长度为参数的Call方法 }
Composite Buffer(复合缓冲区)
编写遗留的JDK ByteBuffer
//Use an array to composite them ByteBuffer[] message = new ByteBuffer[] { header, body }; // Use copy to merge both ByteBuffer message2 = ByteBuffer.allocate(header.remaining()+ body.remaining(); message2.put(header); message2.put(body); message2.flip();
CompositeByteBuf
CompositeByteBuf compBuf = ...; ByteBuf heapBuf = ...; ByteBuf directBuf = ...; compBuf.addComponent(heapBuf, directBuf); //将ByteBuf实例追加到复合 ..... compBuf.removeComponent(0); //在索引0 bytebuf remove(heapbuf这里) for (ByteBuf buf: compBuf) { //循环遍历所有组合的ByteBuf System.out.println(buf.toString()); }
[计]存取数据
CompositeBuf compBuf = ...; if (!compBuf.hasArray()) { //检查ByteBuf是否不受数组支持,这对于复合缓冲区来说是false int length = compBuf.readableBytes(); //获取可读字节的数量 byte[] array = new byte[length];//分配具有可读字节长度的新数组 compBuf.getBytes(array); //将字节读入数组 YourImpl.method(array, 0, array.length);//以数组、偏移量、长度为参数的Call方法 }
5.3 ByteBuf的字节操作
5.3.1 随机访问索引
ByteBuf buffer = ...; for (int i = 0; i < buffer.capacity(); i ++) { byte b = buffer.getByte(i); System.out.println((char) b); }
5.3.2 顺序访问索引
5.3.3Discardable bytes废弃字节
5.3.4 可读字节(实际内容)
ByteBuf buffer = ...; while (buffer.readable()) { System.out.println(buffer.readByte()); }
5.3.5 可写字节Writable bytes
ByteBuf buffer = ...; while (buffer.writableBytes() >= 4) { buffer.writeInt(random.nextInt()); }
5.3.6 清除缓冲区索引Clearing the buffer indexs
5.3.7 搜索操作Search operations
5.3.8 标准和重置Mark and reset
5.3.9 衍生的缓冲区Derived buffers
Charset utf8 = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Netty in Action rocks!", utf8); //创建ByteBuf,它包含给定字符串的字节
ByteBuf sliced = buf.slice(0, 14); //创建ByteBuf的新片段,从索引0开始,以索引14结束
System.out.println(sliced.toString(utf8); //包含在行动中的Netty
buf.setByte(0, (byte) íJí); //更新索引0上的字节
assert buf.get(0) == sliced.get(0);//不会失败,因为ByteBuf共享相同的内容,因此对其中一个的修改在另一个上也是可见的
5.3.10 读/写操作以及其他一些操作
5.4 ByteBufHolder
5.4.1 ByteBufAllocator
5.4.2 Unpooled
5.4.3 ByteBufUtil
6.ChannelHandler
6.1 ChannelPipeline
修改ChannelPipeline的方法
addFirst(...),添加ChannelHandler在ChannelPipeline的第一个位置
addBefore(...),在ChannelPipeline中指定的ChannelHandler名称之前添加ChannelHandler
addAfter(...),在ChannelPipeline中指定的ChannelHandler名称之后添加ChannelHandler
addLast(ChannelHandler...),在ChannelPipeline的末尾添加ChannelHandler
remove(...),删除ChannelPipeline中指定的ChannelHandler
replace(...),替换ChannelPipeline中指定的ChannelHandler
6.2 ChannelHandlerContext
6.2.1 通知下一个ChannelHandler
ChannelHandlerContext、ChannelHandler、ChannelPipeline的关系
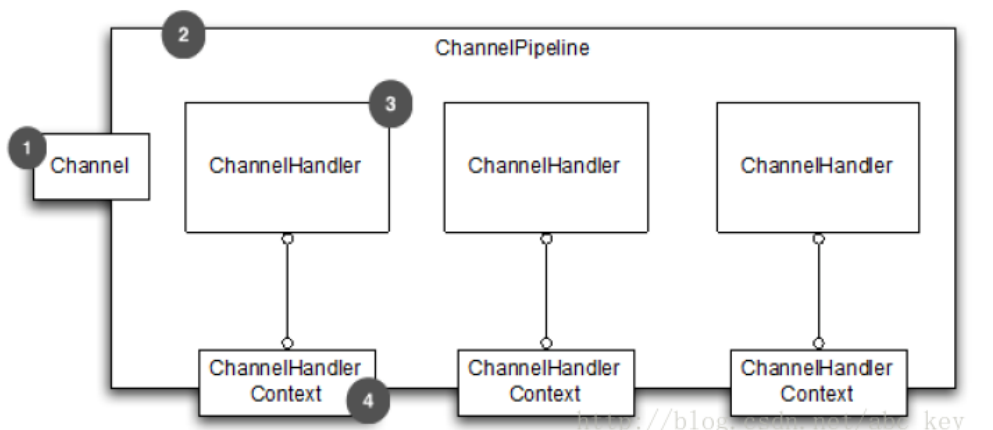
事件通过渠道
ChannelHandlerContext ctx = ..; Channel channel = ctx.channel(); //获取属于ChannelHandlerContext的通道的引用 channel.write(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Netty in Action",CharsetUtil.UTF_8));//通过通道写入缓冲器
信道管道事件
ChannelHandlerContext ctx = ..; ChannelPipeline pipeline = ctx.pipeline(); pipeline.write(Unpooled.copiedBuffer(ìNetty in Actionì,CharsetUtil.UTF_8));
通过Channel或ChannelPipeline的通知:
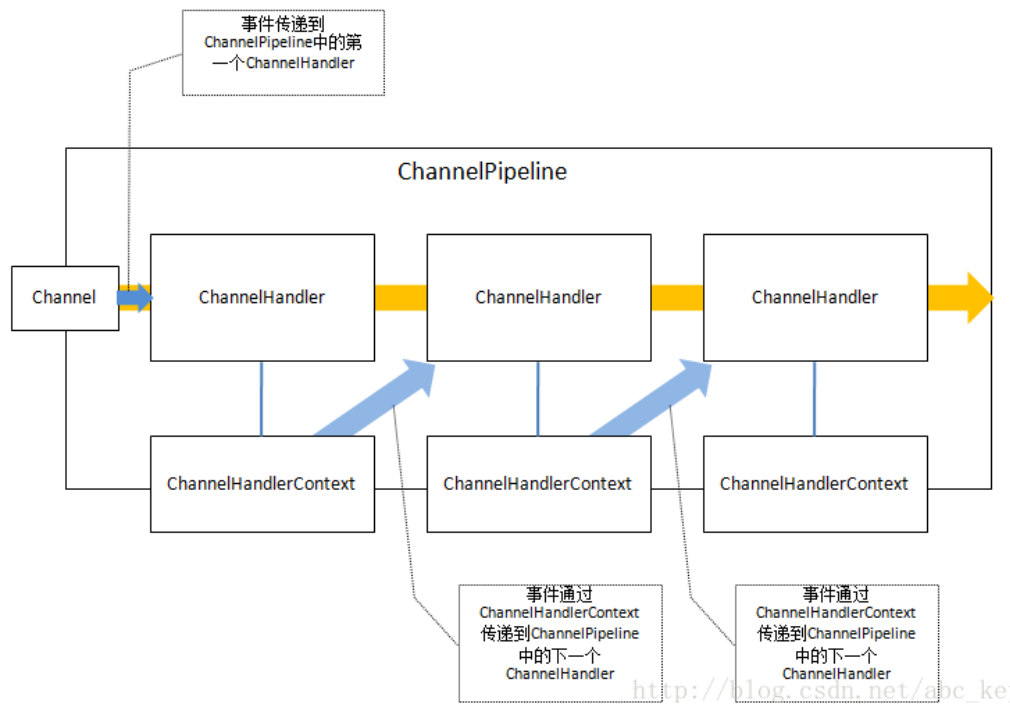
6.2.2 修改ChannelPipeline
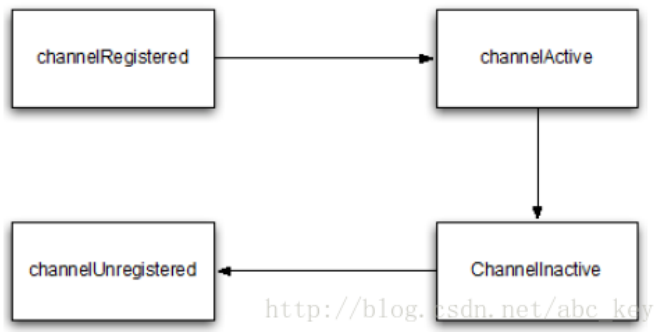
6.3 状态模型
6.4 ChannelHandler和其子类
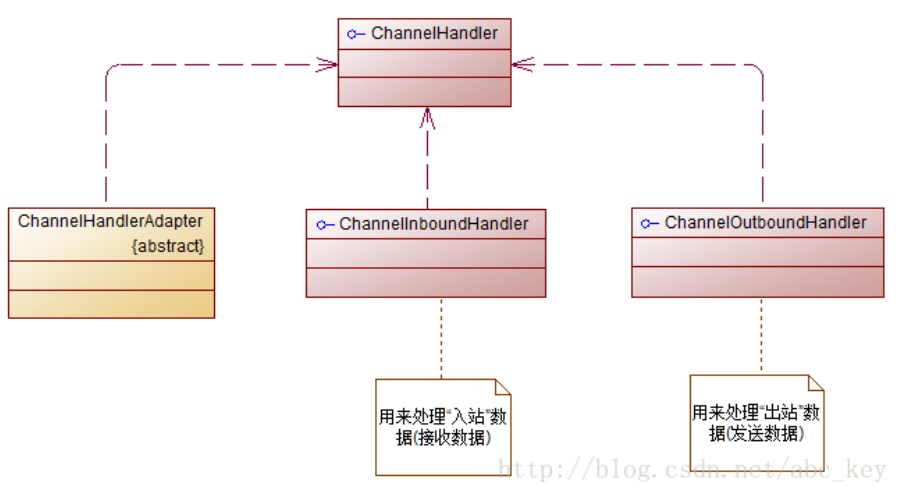
6.4.1 ChannelHandler中的方法
6.4.2 ChannelInboundHandler
channelRegistered,ChannelHandlerContext的Channel被注册到EventLoop;
channelUnregistered,ChannelHandlerContext的Channel从EventLoop中注销
channelActive,ChannelHandlerContext的Channel已激活
channelInactive,ChannelHanderContxt的Channel结束生命周期
channelRead,从当前Channel的对端读取消息
channelReadComplete,消息读取完成后执行
userEventTriggered,一个用户事件被处罚
channelWritabilityChanged,改变通道的可写状态,可以使用Channel.isWritable()检查
exceptionCaught,重写父类ChannelHandler的方法,处理异常
6.4.3 ChannelOutboundHandler
bind,Channel绑定本地地址
connect,Channel连接操作
disconnect,Channel断开连接
close,关闭Channel
deregister,注销Channel
read,读取消息,实际是截获ChannelHandlerContext.read()
write,写操作,实际是通过ChannelPipeline写消息,Channel.flush()属性到实际通道
flush,刷新消息到通道
7.编解码器Codec
7.1 编解码器Codec
7.2 解码器
7.2.1 ByteToMessageDecoder
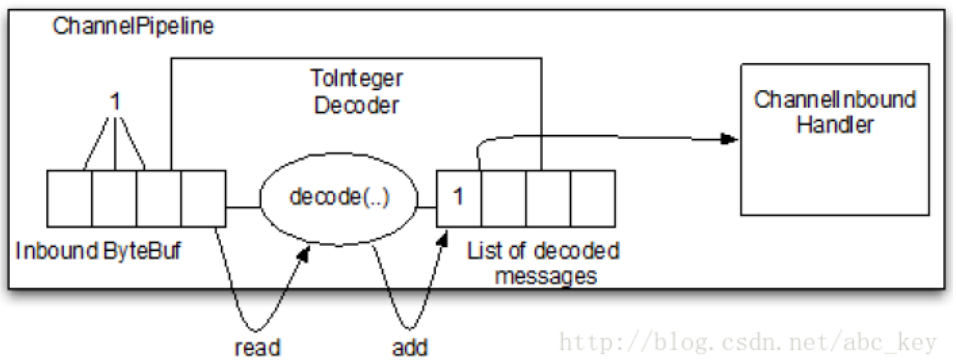
7.2.2 ReplayingDecoder
读取缓冲区的数据之前需要检查缓冲区是否有足够的字节,使用ReplayingDecoder就无需自己检查;
7.2.3 MessageToMessageDecoder
7.3 编码器
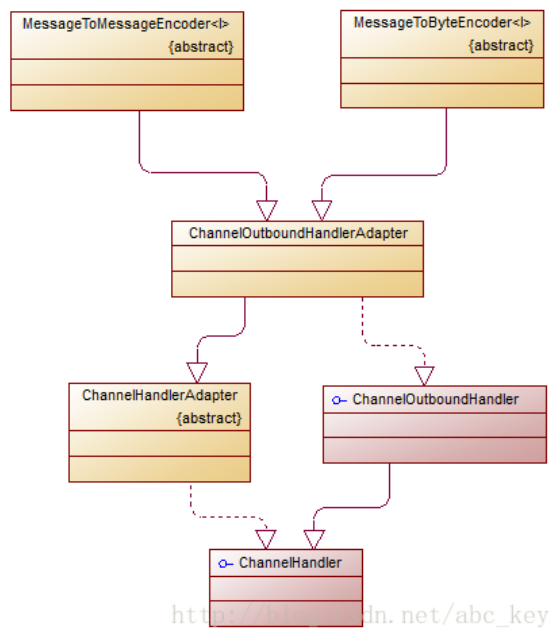 .
.
7.3.1 MessageToByteEncoder
7.3.2 MessageToMessageEncoder
7.4 编解码器
7.4.1 byte-to-byte编解码器
7.4.2 ByteToMessageCodec
7.4.3 MessageToMessageCodec
7.5 其他编解码方式
7.5.1 CombinedChannelDuplexHandler
8.附带的ChannelHandler和Codec
8.1 使用SSL/TLS创建安全的Netty程序
public class SslChannelInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { private final SSLContext context; private final boolean client; private final boolean startTls; public SslChannelInitializer(SSLContext context, boolean client, boolean startTls) { this.context = context; this.client = client; this.startTls = startTls; } @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { SSLEngine engine = context.createSSLEngine(); engine.setUseClientMode(client); ch.pipeline().addFirst("ssl", new SslHandler(engine, startTls)); } }
setHandshakeTimeout(long handshakeTimeout, TimeUnit unit),设置握手超时时间,ChannelFuture将得到通知
setHandshakeTimeoutMillis(long handshakeTimeoutMillis),设置握手超时时间,ChannelFuture将得到通知
getHandshakeTimeoutMillis(),获取握手超时时间值
setCloseNotifyTimeout(long closeNotifyTimeout, TimeUnit unit),设置关闭通知超时时间,若超时,ChannelFuture会关闭失败
setHandshakeTimeoutMillis(long handshakeTimeoutMillis),设置关闭通知超时时间,若超时,ChannelFuture会关闭失败
getCloseNotifyTimeoutMillis(),获取关闭通知超时时间
handshakeFuture(),返回完成握手后的ChannelFuture
close(),发送关闭通知请求关闭和销毁
8.2 使用Netty创建HTTP/HTTPS程序
8.2.1 Netty的HTTP编码器,解码器和编解码器
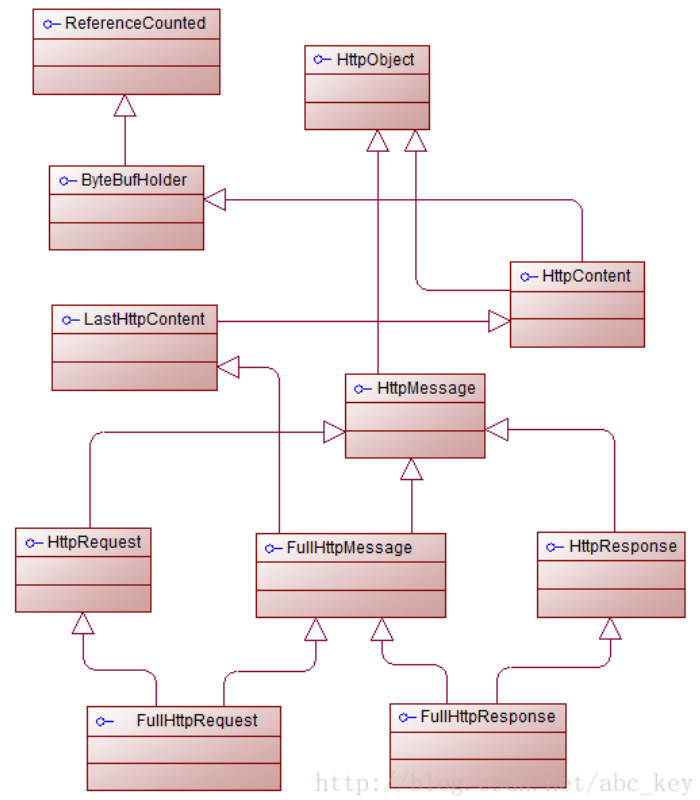
HttpRequestEncoder,将HttpRequest或HttpContent编码成ByteBuf
HttpRequestDecoder,将ByteBuf解码成HttpRequest和HttpContent
HttpResponseEncoder,将HttpResponse或HttpContent编码成ByteBuf
HttpResponseDecoder,将ByteBuf解码成HttpResponse和HttpContent
8.2.2 HTTP消息聚合
public class HttpAggregatorInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { private final boolean client; public HttpAggregatorInitializer(boolean client) { this.client = client; } @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); if (client) { pipeline.addLast("codec", new HttpClientCodec()); } else { pipeline.addLast("codec", new HttpServerCodec()); } pipeline.addLast("aggegator", new HttpObjectAggregator(512 * 1024)); } }
8.2.3 HTTP压缩
8.2.4 使用HTTPS
8.2.5 WebSocket
BinaryWebSocketFrame,包含二进制数据
TextWebSocketFrame,包含文本数据
ContinuationWebSocketFrame,包含二进制数据或文本数据,BinaryWebSocketFrame和TextWebSocketFrame的结合体
CloseWebSocketFrame,WebSocketFrame代表一个关闭请求,包含关闭状态码和短语
PingWebSocketFrame,WebSocketFrame要求PongWebSocketFrame发送数据
PongWebSocketFrame,WebSocketFrame要求PingWebSocketFrame响应
public class WebSocketServerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerCodec(), new HttpObjectAggregator(65536), new WebSocketServerProtocolHandler("/websocket"), new TextFrameHandler(), new BinaryFrameHandler(), new ContinuationFrameHandler()); } public static final class TextFrameHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<TextWebSocketFrame> { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, TextWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception { // handler text frame } } public static final class BinaryFrameHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<BinaryWebSocketFrame> { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, BinaryWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception { //handler binary frame } } public static final class ContinuationFrameHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ContinuationWebSocketFrame> { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ContinuationWebSocketFrame msg) throws Exception { //handler continuation frame } } }
8.2.6 SPDY
SPDY(读作“SPeeDY”)是Google开发的基于TCP的应用层协议,用以最小化网络延迟,提升网络速度,优化用户的网络使用体验。
8.3 处理空闲连接和超时
IdleStateHandler,当一个通道没有进行读写或运行了一段时间后出发IdleStateEvent
ReadTimeoutHandler,在指定时间内没有接收到任何数据将抛出ReadTimeoutException
WriteTimeoutHandler,在指定时间内有写入数据将抛出WriteTimeoutException
public class IdleStateHandlerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(0, 0, 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)); pipeline.addLast(new HeartbeatHandler()); } public static final class HeartbeatHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter { private static final ByteBuf HEARTBEAT_SEQUENCE = Unpooled.unreleasableBuffer(Unpooled.copiedBuffer( "HEARTBEAT", CharsetUtil.UTF_8)); @Override public void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception { if (evt instanceof IdleStateEvent) { ctx.writeAndFlush(HEARTBEAT_SEQUENCE.duplicate()).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE); } else { super.userEventTriggered(ctx, evt); } } } }
8.4 解码分隔符和基于长度的协议
使用LineBasedFrameDecoder提取" "分隔帧:
/** * 处理换行分隔符消息 * * @author c.k */ public class LineBasedHandlerInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(65 * 1204), new FrameHandler()); } public static final class FrameHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf> { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception { // do something with the frame } } }
8.4.2 长度为基础的协议
8.5 写大数据
8.6 序列化数据
8.6.1 普通的JDK序列化
8.6.2 通过JBoss编组序列化
public class MarshallingInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { private final MarshallerProvider marshallerProvider; private final UnmarshallerProvider unmarshallerProvider; public MarshallingInitializer(MarshallerProvider marshallerProvider, UnmarshallerProvider unmarshallerProvider) { this.marshallerProvider = marshallerProvider; this.unmarshallerProvider = unmarshallerProvider; } @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new MarshallingDecoder(unmarshallerProvider)) .addLast(new MarshallingEncoder(marshallerProvider)) .addLast(new ObjectHandler()); } public final class ObjectHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<Serializable> { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Serializable msg) throws Exception { // do something } } }
8.6.3 使用ProtoBuf序列化
/** * 使用protobuf序列化数据,进行编码解码 * 注意:使用protobuf需要protobuf-java-jar * * @author Administrator */ public class ProtoBufInitializer extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { private final MessageLite lite; public ProtoBufInitializer(MessageLite lite) { this.lite = lite; } @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new ProtobufVarint32FrameDecoder()) .addLast(new ProtobufEncoder()) .addLast(new ProtobufDecoder(lite)) .addLast(new ObjectHandler()); } public final class ObjectHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<Serializable> { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Serializable msg) throws Exception { // do something } } }
9.引导Netty应用程序
9.1 不同的引导类型
9.2 引导客户端和无连接协议
9.2.1 引导客户端的方法
group(...),设置EventLoopGroup,EventLoopGroup用来处理所有通道的IO事件
channel(...),设置通道类型
channelFactory(...),使用ChannelFactory来设置通道类型
localAddress(...),设置本地地址,也可以通过bind(...)或connect(...)
option(ChannelOption<T>, T),设置通道选项,若使用null,则删除上一个设置的ChannelOption
attr(AttributeKey<T>, T),设置属性到Channel,若值为null,则指定键的属性被删除
handler(ChannelHandler),设置ChannelHandler用于处理请求事件
clone(),深度复制Bootstrap,Bootstrap的配置相同
remoteAddress(...),设置连接地址
connect(...),连接远程通道
bind(...),创建一个新的Channel并绑定
9.2.2 怎么引导客户端
public class BootstrapingClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(); Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); b.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).handler(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>() { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception { System.out.println("Received data"); msg.clear(); } }); ChannelFuture f = b.connect("1", 2048); f.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { if (future.isSuccess()) { System.out.println("connection finished"); } else { System.out.println("connection failed"); future.cause().printStackTrace(); } } }); } }
9.2.3 选择兼容通道实现
9.3 使用ServerBootstrap引导服务器
9.3.1 引导服务器的方法
group(...),设置EventLoopGroup事件循环组
channel(...),设置通道类型
channelFactory(...),使用ChannelFactory来设置通道类型
localAddress(...),设置本地地址,也可以通过bind(...)或connect(...)
option(ChannelOption<T>, T),设置通道选项,若使用null,则删除上一个设置的ChannelOption
childOption(ChannelOption<T>, T),设置子通道选项
attr(AttributeKey<T>, T),设置属性到Channel,若值为null,则指定键的属性被删除
childAttr(AttributeKey<T>, T),设置子通道属性
handler(ChannelHandler),设置ChannelHandler用于处理请求事件
childHandler(ChannelHandler),设置子ChannelHandler
clone(),深度复制ServerBootstrap,且配置相同
bind(...),创建一个新的Channel并绑定
9.3.2 怎么引导服务器
public class BootstrapingServer { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>() { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception { System.out.println("Received data"); msg.clear(); } }); ChannelFuture f = b.bind(2048); f.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { if (future.isSuccess()) { System.out.println("Server bound"); } else { System.err.println("bound fail"); future.cause().printStackTrace(); } } }); } }
9.4 从Channel引导客户端
public class BootstrapingFromChannel { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>() { ChannelFuture connectFuture; @Override public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); b.channel(NioSocketChannel.class).handler( new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>() { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception { System.out.println("Received data"); msg.clear(); } }); b.group(ctx.channel().eventLoop()); connectFuture = b.connect(new InetSocketAddress("1", 2048)); } @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception { if (connectFuture.isDone()) { // do something with the data } } }); ChannelFuture f = b.bind(2048); f.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { @Override public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception { if (future.isSuccess()) { System.out.println("Server bound"); } else { System.err.println("bound fail"); future.cause().printStackTrace(); } } }); } }
9.5 添加多个ChannelHandler
public class InitChannelExample { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) .childHandler(new ChannelInitializerImpl()); ChannelFuture f = b.bind(2048).sync(); f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } static final class ChannelInitializerImpl extends ChannelInitializer<Channel> { @Override protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception { ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpClientCodec()) .addLast(new HttpObjectAggregator(Integer.MAX_VALUE)); } } }
9.6 使用通道选项和属性
public static void main(String[] args) { //创建属性键对象 final AttributeKey<Integer> id = AttributeKey.valueOf("ID"); //客户端引导对象 Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); //设置EventLoop,设置通道类型 b.group(new NioEventLoopGroup()).channel(NioSocketChannel.class) //设置ChannelHandler .handler(new SimpleChannelInboundHandler<ByteBuf>() { @Override protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg) throws Exception { System.out.println("Reveived data"); msg.clear(); } @Override public void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception { //通道注册后执行,获取属性值 Integer idValue = ctx.channel().attr(id).get(); System.out.println(idValue); //do something with the idValue } }); //设置通道选项,在通道注册后或被创建后设置 b.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true).option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 5000); //设置通道属性 b.attr(id, 123456); ChannelFuture f = b.connect("www.manning.com", 80); f.syncUninterruptibly(); }
10.单元测试代码
10.1 General
writeInbound(Object...),写一个消息到入站通道
writeOutbound(Object...),写消息到出站通道
readInbound(),从EmbeddedChannel读取入站消息,可能返回null
readOutbound(),从EmbeddedChannel读取出站消息,可能返回null
finish(),标示EmbeddedChannel已结束,任何写数据都会失败
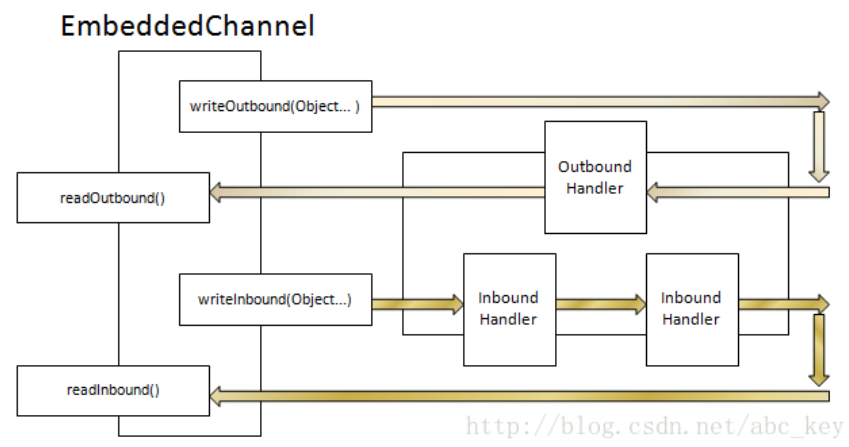
10.2 测试ChannelHandler
10.2.1 测试处理入站消息的handler
public class FixedLengthFrameDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder { private final int frameLength; public FixedLengthFrameDecoder(int frameLength) { if (frameLength <= 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "frameLength must be a positive integer: " + frameLength); } this.frameLength = frameLength; } @Override protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception { while (in.readableBytes() >= frameLength) { ByteBuf buf = in.readBytes(frameLength); out.add(buf); } } }
测试
public class FixedLengthFrameDecoderTest { @Test public void testFramesDecoded() { ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.buffer(); for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { buf.writeByte(i); } ByteBuf input = buf.duplicate(); EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel( new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(3)); // write bytes Assert.assertTrue(channel.writeInbound(input)); Assert.assertTrue(channel.finish()); // read message Assert.assertEquals(buf.readBytes(3), channel.readInbound()); Assert.assertEquals(buf.readBytes(3), channel.readInbound()); Assert.assertEquals(buf.readBytes(3), channel.readInbound()); Assert.assertNull(channel.readInbound()); } @Test public void testFramesDecoded2() { ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.buffer(); for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { buf.writeByte(i); } ByteBuf input = buf.duplicate(); EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel( new FixedLengthFrameDecoder(3)); Assert.assertFalse(channel.writeInbound(input.readBytes(2))); Assert.assertTrue(channel.writeInbound(input.readBytes(7))); Assert.assertTrue(channel.finish()); Assert.assertEquals(buf.readBytes(3), channel.readInbound()); Assert.assertEquals(buf.readBytes(3), channel.readInbound()); Assert.assertEquals(buf.readBytes(3), channel.readInbound()); Assert.assertNull(channel.readInbound()); } }
10.2.2 测试处理出站消息的handler
解码器
public class AbsIntegerEncoder extends MessageToMessageEncoder<ByteBuf> { @Override protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf msg, List<Object> out) throws Exception { while (msg.readableBytes() >= 4) { int value = Math.abs(msg.readInt()); out.add(value); } } }
测试
public class AbsIntegerEncoderTest { @Test public void testEncoded() { //创建一个能容纳10个int的ByteBuf ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.buffer(); for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { buf.writeInt(i * -1); } //创建EmbeddedChannel对象 EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(new AbsIntegerEncoder()); //将buf数据写入出站EmbeddedChannel Assert.assertTrue(channel.writeOutbound(buf)); //标示EmbeddedChannel完成 Assert.assertTrue(channel.finish()); //读取出站数据 ByteBuf output = (ByteBuf) channel.readOutbound(); for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { Assert.assertEquals(i, output.readInt()); } Assert.assertFalse(output.isReadable()); Assert.assertNull(channel.readOutbound()); } }
10.3 测试异常处理
解码器
public class FrameChunkDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder { // 限制大小 private final int maxFrameSize; public FrameChunkDecoder(int maxFrameSize) { this.maxFrameSize = maxFrameSize; } @Override protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception { // 获取可读字节数 int readableBytes = in.readableBytes(); // 若可读字节数大于限制值,清空字节并抛出异常 if (readableBytes > maxFrameSize) { in.clear(); throw new TooLongFrameException(); } // 读取ByteBuf并放到List中 ByteBuf buf = in.readBytes(readableBytes); out.add(buf); } }
测试代码
public class FrameChunkDecoderTest { @Test public void testFramesDecoded() { //创建ByteBuf并填充9字节数据 ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.buffer(); for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { buf.writeByte(i); } //复制一个ByteBuf ByteBuf input = buf.duplicate(); //创建EmbeddedChannel EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(new FrameChunkDecoder(3)); //读取2个字节写入入站通道 Assert.assertTrue(channel.writeInbound(input.readBytes(2))); try { //读取4个字节写入入站通道 channel.writeInbound(input.readBytes(4)); Assert.fail(); } catch (TooLongFrameException e) { } //读取3个字节写入入站通道 Assert.assertTrue(channel.writeInbound(input.readBytes(3))); //标识完成 Assert.assertTrue(channel.finish()); //从EmbeddedChannel入去入站数据 Assert.assertEquals(buf.readBytes(2), channel.readInbound()); Assert.assertEquals(buf.skipBytes(4).readBytes(3), channel.readInbound()); } }
11.WebSocket
12.SPDY
13.通过UDP广播事件
14..实现自定义编解码器
14.1编解码器的范围
14.2实现memcached编解码器
14.3了解memcached二进制协议
14.4 Netty编码器和解码器
15.选择正确的线程模型
15.1线程模型概述
15.2事件循环
15.2.1使用事件循环
15.2.2 Netty 4的I/O业务
15.2.3 Netty 3的I/O业务
15.2.4 Nettys线程模型内部件
15.3为以后的执行安排任务
15.3.1使用普通Java API调度任务
15.3.2使用事件循环调度任务
15.3.3计划实施内部
15.4 I/O线程分配的详细情况
16.用Eventloop注销/重新注册