一、(续day11异常)
7、标准异常类
标准异常类在下面的这个路径的头文件中有声明

C++语言本身或者标准库抛出的异常都是 exception 的子类,称为标准异常(Standard Exception)。通过下面的语句来捕获所有的标准异常:
- try{
- //可能抛出异常的语句
- }catch(exception &e){
- //处理异常的语句
- }
之所以使用引用,是为了提高效率。如果不使用引用,就要经历一次对象拷贝(要调用拷贝构造函数)的过程。
exception 类位于 <exception> 头文件中
它的声明如下:
class exception{ public: exception () throw(); //构造函数 exception (const exception&) throw(); //拷贝构造函数 exception& operator= (const exception&) throw(); //运算符重载 virtual ~exception() throw(); //虚析构函数 virtual const char* what() const throw(); //虚函数}
这里需要说明的是 what() 函数。what() 函数返回一个能识别异常的字符串,正如它的名字“what”一样,可以粗略地告诉你这是什么异常。不过C++标准并没有规定这个字符串的格式,各个编译器的实现也不同,所以 what() 的返回值仅供参考。
下图展示了 exception 类的继承层次:
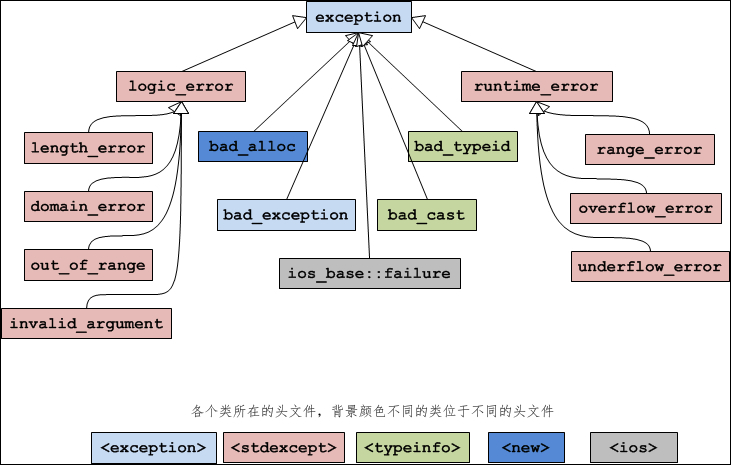
图:exception 类的继承层次以及它们所对应的头文件
先来看一下 exception 类的直接派生类:
| 异常名称 | 说 明 |
|---|---|
| logic_error | 逻辑错误。 |
| runtime_error | 运行时错误。 |
| bad_alloc | 使用 new 或 new[ ] 分配内存失败时抛出的异常。 |
| bad_typeid | 使用 typeid 操作一个 NULL 指针,而且该指针是带有虚函数的类,这时抛出 bad_typeid 异常。 |
| bad_cast | 使用 dynamic_cast 转换失败时抛出的异常。 |
| ios_base::failure | io 过程中出现的异常。 |
| bad_exception | 这是个特殊的异常,如果函数的异常列表里声明了 bad_exception 异常,当函数内部抛出了异常列表中没有的异常时,如果调用的 unexpected() 函数中抛出了异常,不论什么类型,都会被替换为 bad_exception 类型。 |
logic_error 的派生类:
| 异常名称 | 说 明 |
|---|---|
| length_error | 试图生成一个超出该类型最大长度的对象时抛出该异常,例如 vector 的 resize 操作。 |
| domain_error | 参数的值域错误,主要用在数学函数中,例如使用一个负值调用只能操作非负数的函数。 |
| out_of_range | 超出有效范围。 |
| invalid_argument | 参数不合适。在标准库中,当利用string对象构造 bitset 时,而 string 中的字符不是 0 或1 的时候,抛出该异常。 |
runtime_error 的派生类:
| 异常名称 | 说 明 |
|---|---|
| range_error | 计算结果超出了有意义的值域范围。 |
| overflow_error | 算术计算上溢。 |
| underflow_error | 算术计算下溢。 |
例:
class FileError:public exception{ public: const char* what(void) const throw(){ return "文件访问失败"; } }; int main(void){ try{ //throw FileError(); char* p=new char[0xffffffff] } catch(exception& ex){//使用标准异常类,可以只写一个catch,利用多态就可以完成。 cout<<ex.what()<<endl; return -1; } }
执行结果:

注意:
自定义异常类的时候,最好继承标准异常类,并且重写what()函数,让其对标准的what()函数形成覆盖,通过多态的语法特征,在子类的what函数中处理子类异常。
8、构造函数异常
class A{ public: A(void){ cout<<"A::A()"<<endl; } ~A(void){ cout<<"A::~A()"<<endl; } }; class B{ public: B(void):m_a(new A){ FILE* fp=fopen("none.txt","r") if(!fp){ delete m_a;//释放不完整类 throw -1; } fclose(fp); } ~B(void){ delete m_a; } private: A* m_a; }; int main(void){ try{ B b; } catch(int& ex){ cout<<"异常"<<ex<<endl; return -1; } return 0; }
注意:
构造函数抛出异常之后,对象将会被不完整构造,这样的对象其析构函数不会被执行,因此在构造函数抛出异常之前,需要手动销毁所有在异常产生之前的动态资源。
9、析构函数异常
析构函数最好不要抛出异常(了解)
class A{ public: void func(void){ throw -1; } ~A(void){ throw -2; } };
int main(void){ A a; try{ a.func(); } catch(int& ex){ cout<<"异常"<<ex<<endl; return -1; } }
//因为已经跳出了catch,执行到},析构函数抛出的异常2将永远得不到捕获,最终将被系统所捕获int main(void){
int main(void){ try{ A a; a.func(); } catch(int& ex){ cout<<"异常"<<ex<<endl; return -1; } }
//func()抛出的异常还没来及处理,a的析构就抛出异常,这样系统会直接终止进程
二、I/O流(了解)
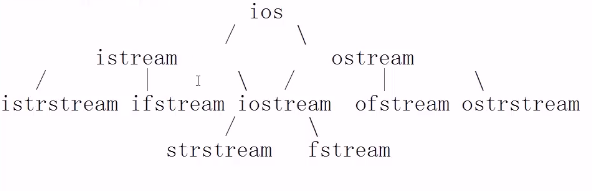
1、主要的I/O流类
2、格式化I/O
1)格式化函数:通过调用I/O对象成员函数,改变或者获取其中过得状态,进而影响格式化数据的形式。
int ios::precisoin(int);//控制浮点数精度
int ios::width(int);//控制显式的域宽
...
int main(void){ cout<<sqrt(300)<<endl; //设置显示精度 cout.precision(20); cout<<sqrt(300)<<endl; //设置科学计数法显示 cout.setf(ios::scientific); cout<<sqrt(300)<<endl; cout<<'['; cout.width(10);//设置显式位宽 cout.fill('-');//设置空白区域填充字符 cout.setf(ios::showpos);//显示正号 cout.setf(ios::internal);//内插对齐 cout<<1234; cout<<']'<<endl; return 0; }
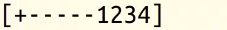
2)流控制符
通过将流控制符插入到输入输出流中,改变其中的状态,进而影响格式化数据形式。作用域是全局的。带参数的流控制符需包含头文件#include<iomanip>
setprecision(int);//设置浮点数精度
setw(int);//控制浮点数精度
...
endl;//流控制符有的可以没有参数,有的可以有参数
int main(void){ cout<<sqrt(300)<<endl; //设置显示精度 cout<<setprecision(20)<<sqrt(300)<<endl; //设置科学计数法显示 cout<<scientific<<sqrt(300)<<endl; cout<<'['; cout<<setw(10)<<//设置显式位宽 setfill('-')<<//设置空白区域填充字符 showpos<<//显示正号 internal//内插对齐 <<1234; cout<<']'<<endl; }
3、字符串流
1)新版本类(一般使用新版本)
#include<sstream>
istringstream
ostringstream
stringstream
2)旧版本的类(一般不使用旧版本)
#include<strstream>
istrtrstream
ostrstream
strstream
int main(){ int i=1234; double d=56.78; char c='T'; char str[100]="hello world"; ostringstream oss;//内部维护了一个内存缓冲区 oss<<i<<' '<<d<<' '<<c<<' '<<str;/*等价于:char buf[1024]; sprintf(buf,"%d %g %c %s",i,d,cstr);*/ //将上述字符以字符串形式写入到内存缓冲区后,也可以使用成员函数从缓冲区获取相关数据 cout<<oss.str()<<endl; istringstream iss; iss.str("100 9.99 A helloWorld"); int a; double b; char x; char y[100]; iss >>a>>b>>x>>y;//提取字符串 cout<<a<<' '<<b<<' '<<x<<' '<<y<<endl; }
4、文件流
#include<fstream>
ifstream
ostream
stream
int main(){ //类似fprintf ofstream ofs("file.txt");//没有自动创建 ofs<<1234<<' '<<3.14<<' '<<"helloworld"<<endl; ofs.close(); //类似fscanf ifstream ifs("file.txt"); int i; double d; string s; ifs>>i>>d>>s; cout<<i<<' '<<d<<' '<<s<<endl;
ifs.close();
}
5、二进制I/O
//fwrite
ostream& ostream::write(const char* buffer,size_t num)
//fread
istream& istream::read(char* buffer,streamsize num)
int main(){
ofstream ofs("text.text");
char wbuf[]="helloworld";
ofs.write(wbuf,sizeof(wbuf));
ofs.close();
ifstream ifs("text.txt");
char rbuf[100]={0};
ifs.read(rbuf,sizeof(rbuf));
ifs.closr();
return 0;
}