第四章:并发编程
本章论述了并发编程,介绍了并行计算的概念,指出了并行计算的重要性;比较了顺序算法与并行算法, 以及并行性与并发性;解释了线程的原理及其相对于进程的优势;解释了死锁问题, 并说明了如何防止并发程序中的死锁问题;讨论了信号量, 并论证了它们相对千条件变量的优点;还解释了支待 Linux 中线程的独特方式。
并行计算
- 基于分治原则(如二叉树查找和快速排序等)的算法经常表现出高度的并行性,可通过使用并行或并发执行米提高计算速度。并行计算是一种计算方案,它尝试使用多个执行并行算法的处理器 更快速地解决问题。
并行性和并发性
- 并行算法只识别可执行的任务。理想情况下,并行算法中的所有任务都应该同时实时执行
- 并发性是通过多任务处理实现的
线程
- 线程的原理:在内核模式下各进程在唯一地址空间上执行,与其他进程分开
- 每个进程都是一个独立单元,只有一个执行路径
- 线程是某进程同一地址空间上的独立执行单元(如果只有一个主线程,那么进程和线程并没有什么本质区别)
- 线程的优点:1)线程创建和切换速度更快。2)线程的响应速度更快。3)线程更适合并行计算
- 线程的缺点:1)由于地址空间共享,线程需要来自用户的明确同步。2)许多库函数可能对线程不安全。3)在单CPU系统上,使用线程解决间题实际上要比使用顺序程序慢,这是由在运行时创建线程和切换上下文的系统开销造成的。
- 线程操作:线程可在内核模式或用户模式下执行。在用户模式下,线程在进程的相同地址空间中执行,但每个线程都有自己的执行堆栈。线程是独立的执行单元,可根据操作系统内核的调度策略,对内核进行系统调用,变为桂起激活以继续执行等。为了利用线程的共享地址空间,操作系统内核的调度策略可能会优先选择同一进程中的线程,而不是不同进程中的线程
- Pthread库提供了用于线程管理的以下APT:
pthread_create(thread, attr, function, arg): create thread
pthread_exit(status):terminate thread
pthread_cancel(thread) : cancel thread
pthread_attr_init(attr) : initialize thread attributes
pthread_attr_destroy(attr): destroy thread attribute
- 创建线程:使用pthread_create()函数创建线程。
int pthread_create (pthread_t *pthread_id,pthread_attr_t•attr,void * (*func) (void *), void *arg);
其中,attr最复杂,其使用步骤为:1)定义一个pthread展性变址pt:hread_attr_tattr。2)用pthread_attr_init(&attr)初始化屈性变掀。3)设置属性变垃并在pthread_ create()调用中使用。4)必要时,通过pthread_attr_destroy(&attr)释放attr资源。 - 线程终止:线程函数结束后,线程即终止,或者,线程可以调用函数
int pthraad_exit {void *status) - 线程连接:一个线程可以等待另一个线程的终止, 通过:
int pthread_join (pthread_t thread, void **status__ptr);
终止线程的退出状态以status_ptr返回。
线程同步
- 当多个线程试图修改同一共享变量或数据结构时,如果修改结果取决于线程的执行顺序,则称之为竞态条件
- 互斥量:在 Pthread中,锁被称为互斥量,意思是相互排斥。互斥变呈是用 ptbread_mutex_t 类型声明的在使,用之前必须对它们进行初始化。有两种方法可以初始化互斥址:
静态方法,pthreaa—mutex_t m = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;定义互斥量 m, 并使用默认属性对其进行初始化。
动态方法,使用pthread_ mutex _init()函数 - 线程通过互斥量来保护共享数据对象
死锁预防
- 死锁是一种状态,在这种状态下,许多执行实体相互等待,因此都无法继续下去
条件变量
- 作为锁,互斥量仅用于确保线程只能互斥地访间临界区中的共享数据对象。在Pthread中,使用类型pthread_cond_t来声明条件变拉,而且必须 在使用前进行初始化。与互斥变量一样,条件变量也可以通过两种方法进行初始化。
静态方法:pthread_cond_t con= PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;定义一个条件变屾con,并使用默认属性对其进行初始化。
动态方法:使用pthread_cond_init()函数,可通过attr参数设置条件变量。为简便起见,我们总是使用NULLattr参数作为默认属性。
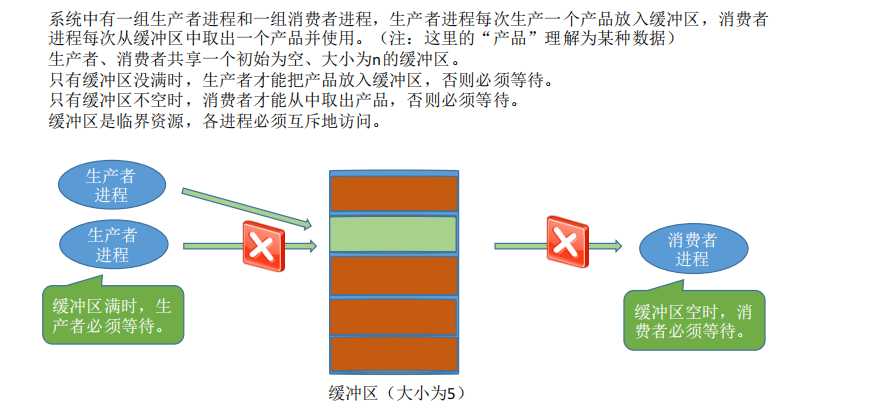
生产者-消费者问题
实践
4.2
点击查看代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
typedef struct{
int upperbound;
int lowerbound;
}PARM;
#define N 10
int a[N]={5,1,6,4,7,2,9,8,0,3};// unsorted data
int print(){//print current a[] contents
int i;
printf("[");
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
printf("%d ",a[i]);
printf("]
");
}
void *Qsort(void *aptr){
PARM *ap, aleft, aright;
int pivot, pivotIndex,left, right,temp;
int upperbound,lowerbound;
pthread_t me,leftThread,rightThread;
me = pthread_self();
ap =(PARM *)aptr;
upperbound = ap->upperbound;
lowerbound = ap->lowerbound;
pivot = a[upperbound];//pick low pivot value
left = lowerbound - 1;//scan index from left side
right = upperbound;//scan index from right side
if(lowerbound >= upperbound)
pthread_exit (NULL);
while(left < right){//partition loop
do{left++;} while (a[left] < pivot);
do{right--;}while(a[right]>pivot);
if (left < right ) {
temp = a[left];a[left]=a[right];a[right] = temp;
}
}
print();
pivotIndex = left;//put pivot back
temp = a[pivotIndex] ;
a[pivotIndex] = pivot;
a[upperbound] = temp;
//start the "recursive threads"
aleft.upperbound = pivotIndex - 1;
aleft.lowerbound = lowerbound;
aright.upperbound = upperbound;
aright.lowerbound = pivotIndex + 1;
printf("%lu: create left and right threadsln", me) ;
pthread_create(&leftThread,NULL,Qsort,(void * )&aleft);
pthread_create(&rightThread,NULL,Qsort,(void *)&aright);
//wait for left and right threads to finish
pthread_join(leftThread,NULL);
pthread_join(rightThread, NULL);
printf("%lu: joined with left & right threads
",me);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
PARM arg;
int i, *array;
pthread_t me,thread;
me = pthread_self( );
printf("main %lu: unsorted array = ", me);
print( ) ;
arg.upperbound = N-1;
arg. lowerbound = 0 ;
printf("main %lu create a thread to do QS
" , me);
pthread_create(&thread,NULL,Qsort,(void * ) &arg);//wait for Qs thread to finish
pthread_join(thread,NULL);
printf ("main %lu sorted array = ", me);
print () ;
}
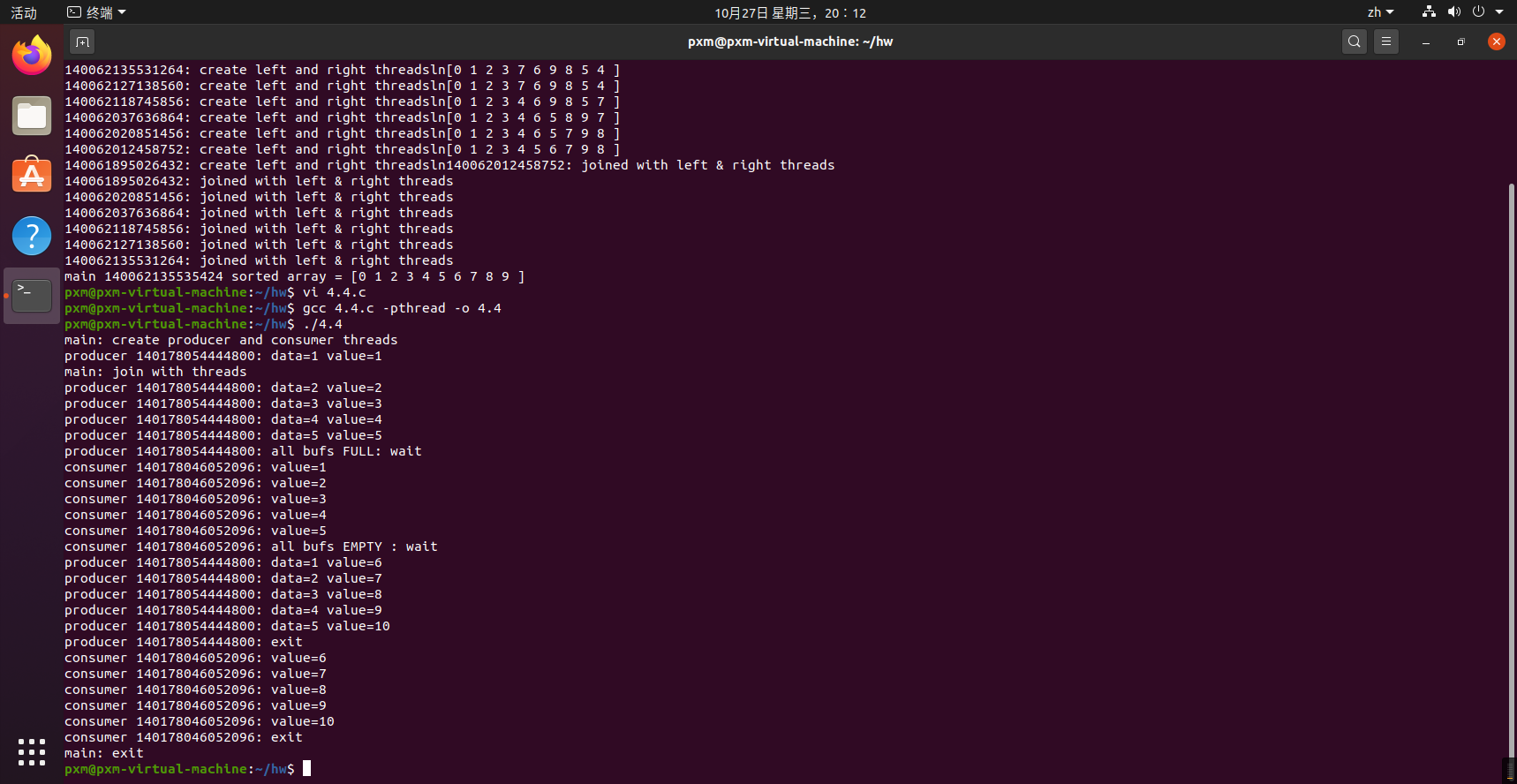
运行结果:

4.4
点击查看代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define NBUF 5
#define N 10
//shared g1obal variab1es
int buf [NBUF];//circular buffers
int head, tail;//indices
int data;//number of full buffers
pthread_mutex_t mutex;//mutex lock
pthread_cond_t empty,full;//condition variables
int init(){
head = tail = data = 0;
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&full,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&empty,NULL);
}
void *producer (){
int i;
pthread_t me = pthread_self() ;
for (i=0; i<N; i++){ //try to put N items into buf[ ]
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//lock mutex
if(data == NBUF) {
printf("producer %lu: all bufs FULL: wait
",me);
pthread_cond_wait(&empty, &mutex);//wait
}
buf[head++] = i+1;//item = 1,2锛?.锛孨
head %=NBUF;//circular bufs
data++;//inc data by 1
printf("producer %lu: data=%d value=%d
",me,data,i+1);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//unlock mutex
pthread_cond_signal(&full);//unblock a consumer锛?if any
}
printf("producer %lu: exit
",me);
}
void *consumer(){
int i, c;
pthread_t me = pthread_self();
for(i=0;i<N;i++){
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//1ock mutex
if(data == 0){
printf ("consumer %lu: all bufs EMPTY : wait
",me);
pthread_cond_wait(&full,&mutex);//wait
}
c=buf[tail++];//get an item
tail%=NBUF;
data--;//dec data by 1
printf("consumer %lu: value=%d
",me,c);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//unlock mutex
pthread_cond_signal(&empty);//unblock a producer锛宨f any
}
printf("consumer %lu: exit
",me);
}
int main(){
pthread_t pro, con;
init();
printf("main: create producer and consumer threads
");
pthread_create(&pro,NULL, producer,NULL);
pthread_create (&con,NULL,consumer,NULL);
printf("main: join with threads
");
pthread_join(pro,NULL);
pthread_join(con,NULL);
printf("main: exit
");
}
运行结果: