1.Render函数:render是用来替换temlate的,需要更灵活的模板的写法的时候,用render。
官网API地址:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/render-function.html
通常写的h为createElement的缩写,createElement 会返回虚拟节点 (virtual node)”,也常简写它为“VNode,因为它所包含的信息会告诉 Vue 页面上需要渲染什么样的节点,包括及其子节点的描述信息。
- 第一个参数为{String | Object | Function}是一个 HTML 标签名、组件选项对象,为必选项。
- 第二个参数为 {Object},是一个与模板中属性对应的数据对象。可选。
- 第三个参数为{String | Array},是子级虚拟节点 (VNodes),由 `createElement()` 构建而成,也可以使用字符串来生成“文本虚拟节点”。可选。
1.1一个最简单的render函数例子:
import Vue from "vue"; import App from "./App.vue"; import router from "./router"; import store from "./store"; import Bus from "./lib/bus"; import $ from "jquery"; Vue.config.productionTip = false; Vue.prototype.$bus = Bus; new Vue({ router, store, //render: h => h(App) render(h) { return h('div', { attrs: { id:"box" }, style: { color:"blue" } },"Caoqi"); }, }).$mount("#app");

1.2当第一个参数为组件时的写法如下,引入的组件为之前博客中讲过的Count-To组件(https://www.cnblogs.com/qicao/p/10805715.html)
import Vue from "vue"; import App from "./App.vue"; import router from "./router"; import store from "./store"; import Bus from "./lib/bus"; import $ from "jquery"; import CountTo from "_c/count-to"; Vue.config.productionTip = false; Vue.prototype.$bus = Bus; new Vue({ router, store, render: function(h) { return h(CountTo, { /** * class作为一个保留字必须用引号包裹 * 接受一个字符串、对象或字符串和对象组成的数组 */ // 'class':'count-up wrapper', //class: ["count-to", true ? "classA" : "classB"], class: { "count-to": 1 === 1 }, // 组件 prop props: { endVal: 200 }, // DOM 属性 domProps: { //innerHTML: "baz" }, /** * 事件监听器在 `on` 属性内, * 但不再支持如 `v-on:keyup.enter` 这样的修饰器。需要在处理函数中手动检查 keyCode。 */ on: { "on-animation-end": function(val) { console.log("animation end"); } }, /** * 仅用于组件,用于监听原生事件,而不是组件内部使用`vm.$emit` 触发的事件。 */ nativeOn: { click: () => console.log("I am clicked!") }, /*自定义指令*/ directives: [], // 如果组件是其它组件的子组件,需为插槽指定名称 slot: "name-of-slot" }); } }).$mount("#app");
显示效果:
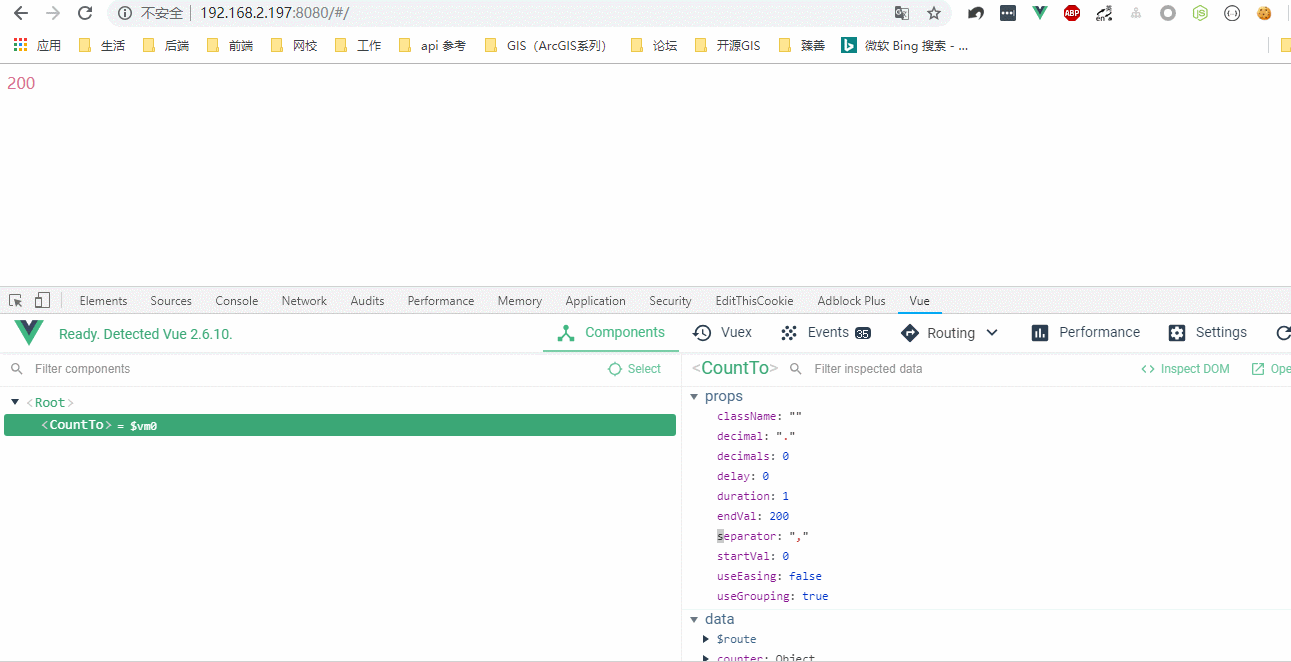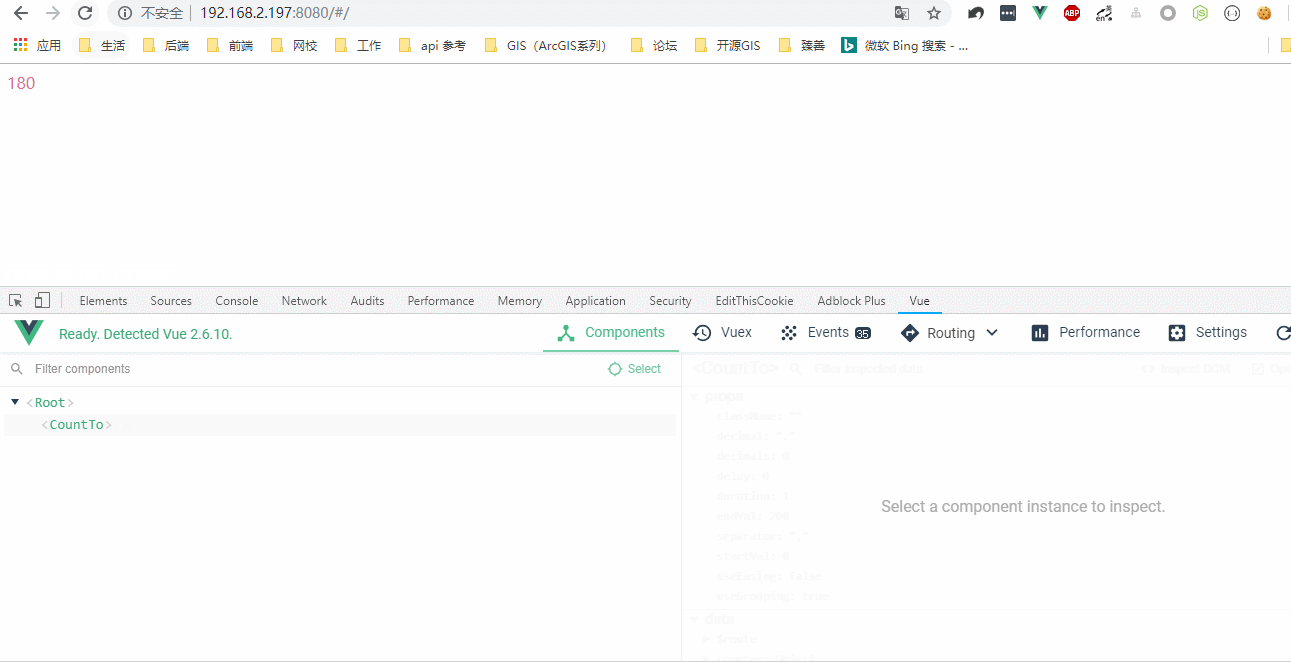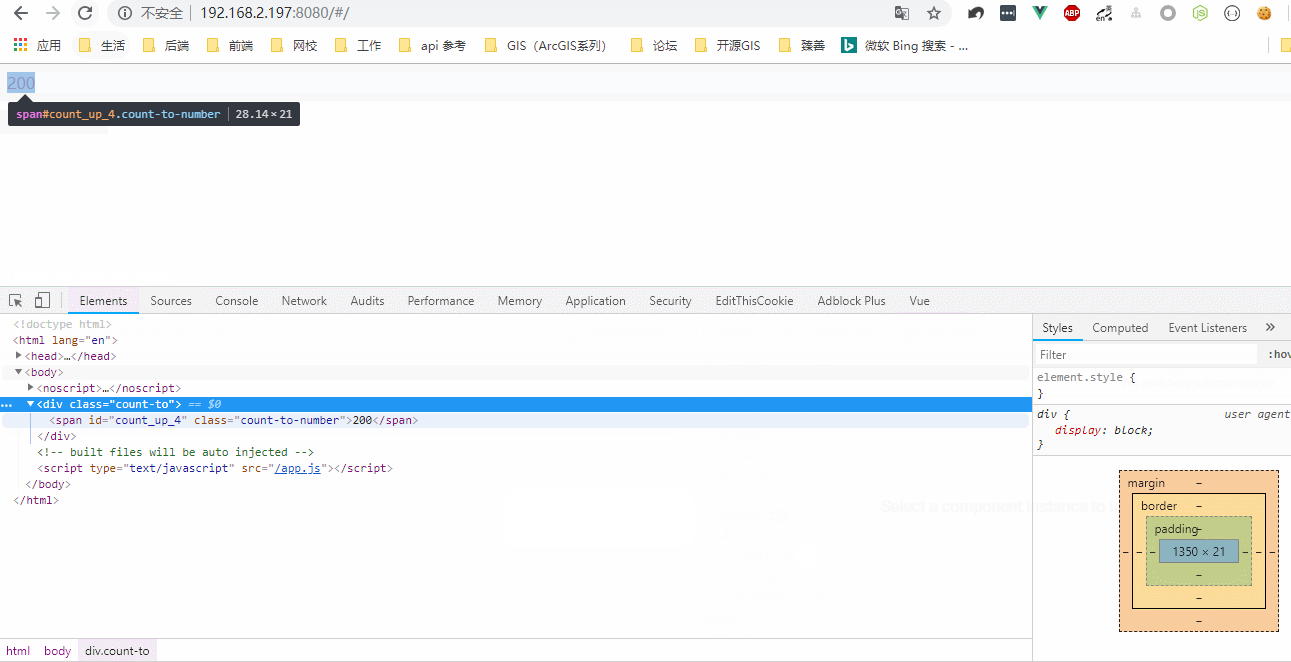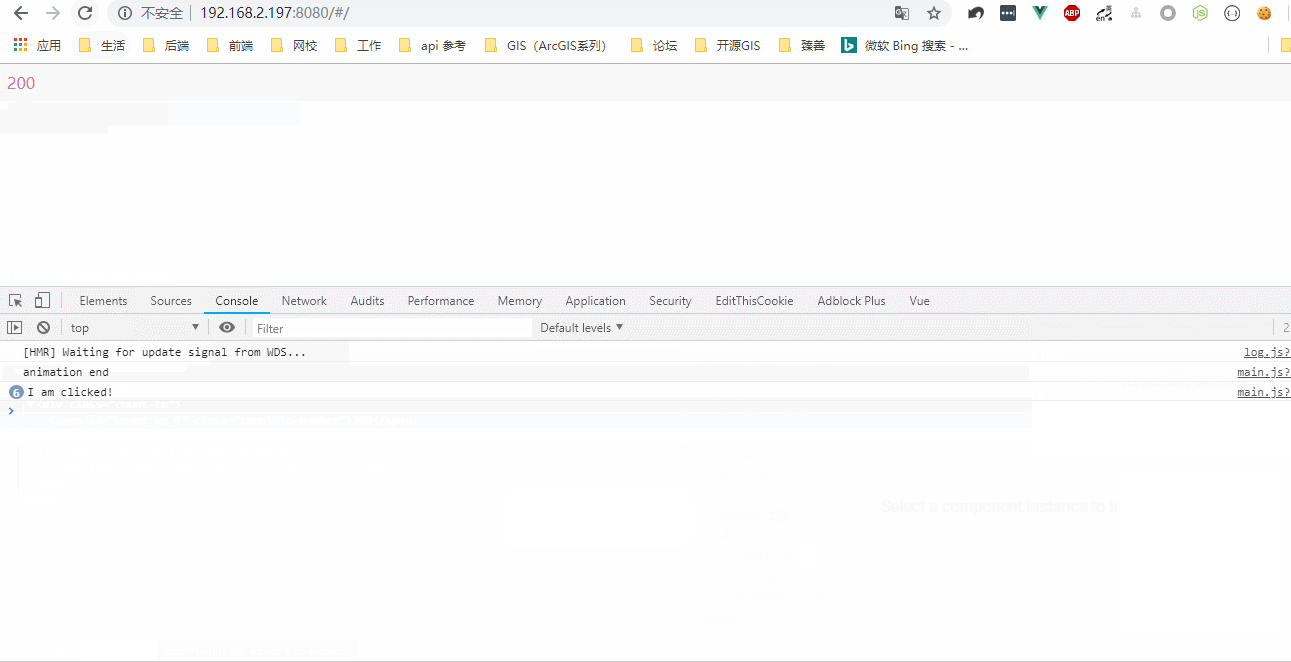
1.3 创建子级虚拟节点:
import Vue from "vue"; import App from "./App.vue"; import router from "./router"; import store from "./store"; import Bus from "./lib/bus"; import $ from "jquery"; import CountTo from "_c/count-to"; Vue.config.productionTip = false; Vue.prototype.$bus = Bus; new Vue({ router, store, /** * @param {String | Array} h * 子级虚拟节点 (VNodes),由 `createElement()` 构建而成,也可以使用字符串来生成“文本虚拟节点”。可选。 */ //render:h=>h('div','123') render:function(h) { return h('div', [ h('span','span1'), h('span','span2'), ]) } }).$mount("#app");
1.4使用 JavaScript 代替模板功能
模板代码:
<template> <div> <ul @click="handlerClick"> <li @click.stop="handlerClick" v-for="(item,index) in list" :key="`list_item_${index}`" >{{item.name}}</li> </ul> </div> </template> <script> export default { data() { return { list: [ { name: "张三" }, { name: "李四" } ] }; }, methods: { handlerClick: function(event) { console.log(event); } } }; </script>
main.js:
import Vue from "vue";
import App from "./App.vue";
import router from "./router";
import store from "./store";
import Bus from "./lib/bus";
import $ from "jquery";
import CountTo from "_c/count-to";
Vue.config.productionTip = false;
Vue.prototype.$bus = Bus;
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount("#app");
若使用render函数中的js代替模板:只要在原生的 JavaScript 中可以轻松完成的操作,Vue 的渲染函数就不会提供专有的替代方法。比如,在模板中使用的 v-if 和 v-for需要用JavaScript 的 if/else 和 map 来重写:
import Vue from "vue"; import App from "./App.vue"; import router from "./router"; import store from "./store"; import Bus from "./lib/bus"; import $ from "jquery"; import CountTo from "_c/count-to"; Vue.config.productionTip = false; Vue.prototype.$bus = Bus; const handleClick = event => { console.log(event); event.stopPropagation(); }; let list = [{ name: "张三" }, { name: "李四" }]; /** * Array map用法: * 功能:将原数组映射成新数组 * https://www.zhangxinxu.com/wordpress/2013/04/es5%E6%96%B0%E5%A2%9E%E6%95%B0%E7%BB%84%E6%96%B9%E6%B3%95/#map */ const getLiEleArr = h => { return list.map((item,index) => h( "li", { on: { click: handleClick }, key:`list_item_${index}` }, item.name ) ); }; /**等效于 */ /*function getLiEleArr(h) { return list.map(function(item, index) { return h( "li", { on: { click: handleClick }, key: `list_item_${index}` }, item.name ); }); }*/ new Vue({ router, store, render: function(h) { return h( "ul", { on: { click: handleClick } }, getLiEleArr(h) ); } }).$mount("#app");
2.函数式组件:函数组件可以用render方式,可以用模板方式。函数组件主要用来做组件的外壳,也就是写模板之前,可以先对传进来的上下文做一些处理。这个“壳”的作用有点类似模板语法里的<template>标签,本身不会渲染,只是做包裹。
官方API地址:https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/render-function.html#%E5%87%BD%E6%95%B0%E5%BC%8F%E7%BB%84%E4%BB%B6
我们可以把函数式组件想像成组件里的一个函数,输入参数是渲染上下文(render context),返回值是渲染好的HTML
对于函数式组件,可以这样定义:
- Stateless(无状态):组件自身是没有状态的
- Instanceless(无实例):组件自身没有实例,也就是没有this,事件只能由父组件传递
例子:
<div id="app"> <smart-list :items=items></smart-list> </div>
app.vue:
//当父组件传过来的是空items时 var EmptyList = {template: '<p>Empty list</p>'}; //当父组件传来的items元素为对象类型时 var TableList = 'ul' // 当父组件定义了isOrdered变量且为true var UnorderedList = 'ul' //定义组件 Vue.component('smart-list', { //标记为函数式组件 functional: true, //render函数 render: function (createElement, context) { // console.log(context)//若不理解可以打印出来context来看看里面都有些什么东西 //规定组件的渲染规则 function appropriateListComp() { //获取父组件传来的数据 var items = context.props.items; //若空,则返回前面定义的emptylist if (items.length === 0) return EmptyList; //若为对象 if (typeof items[0] === 'object') return TableList; //其他 return UnorderedList } //生成模板 return createElement( //模板标记为渲染规则函数返回值 appropriateListComp(), //模板子元素,返回一个数组 Array.apply(null, {length: context.props.items.length}).map(function (value, index) { return createElement('li',context.props.items[index].name) }) ) }, props: { items: { type: Array, required: true }, isOrdered: Boolean } }); new Vue({ el: '#app', data:{ items:[ { name:'a', id:0 }, { name:'b', id:1 }, { name:'c', id:2 } ] } })
最终浏览器渲染结果:
<div id="app"> <ul> <li>a</li> <li>b</li> <li>c</li> </ul> </div>
再举一个例子,代码目录结构如下:
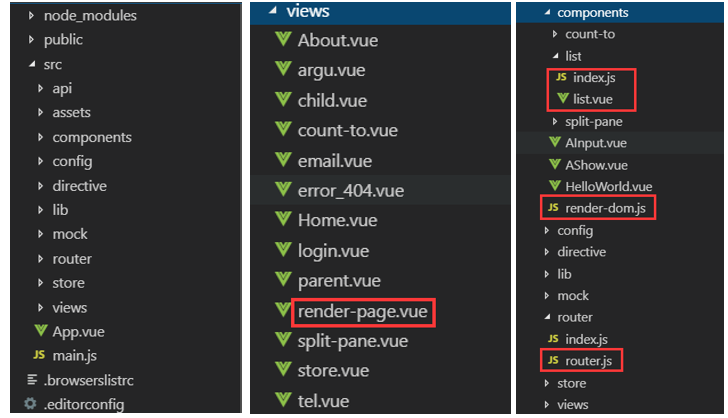
render-page:
<template>
<div>
<list :list="list" :render="renderFunc"></list>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import List from "_c/list";
export default {
data() {
return {
list: [
{
name: "张三"
},
{
name: "李四"
}
]
};
},
components: {
List
},
methods: {
renderFunc: function(h, name) {
return h("i", {
style: {
color: "pink"
}
},name);
}
}
};
</script>
router.js:
import Home from "@/views/Home.vue"; export default [ { path: "/", alias: "/home_page", name: "home", //加上name属性 命名路由 component: Home, props: route => ({ food: route.query.food }), beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => { // if (from.name === "about") alert("这是从about来的"); // else alert("这不是从about来的"); next(); } }, { path: '/render_page', name: 'render_page', component: () => import('@/views/render-page.vue') } { path: "*", component: () => import("@/views/error_404.vue") } ];
list/index.js:
import List from "./list.vue"; export default List;
list/list.vue:
<template>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in list" :key="`item_${index}`">
<span v-if="!render">{{item.name}}</span>
<render-dom v-else :render-func="render" :name="item.name"></render-dom>
</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
import RenderDom from "_c/render-dom";
export default {
name: "List",
components: {
RenderDom
},
props: {
list: {
type: Array,
default: () => []
},
render: {
type: Function,
default: () => {}
}
}
};
</script>
render-dom.js:
export default { functional: true, // Props 是可选的 props: { name: String, renderFunc: Function }, // 为了弥补缺少的实例,提供第二个参数作为上下文 render: (h, ctx) => { return ctx.props.renderFunc(h, ctx.props.name); } };
运行效果:
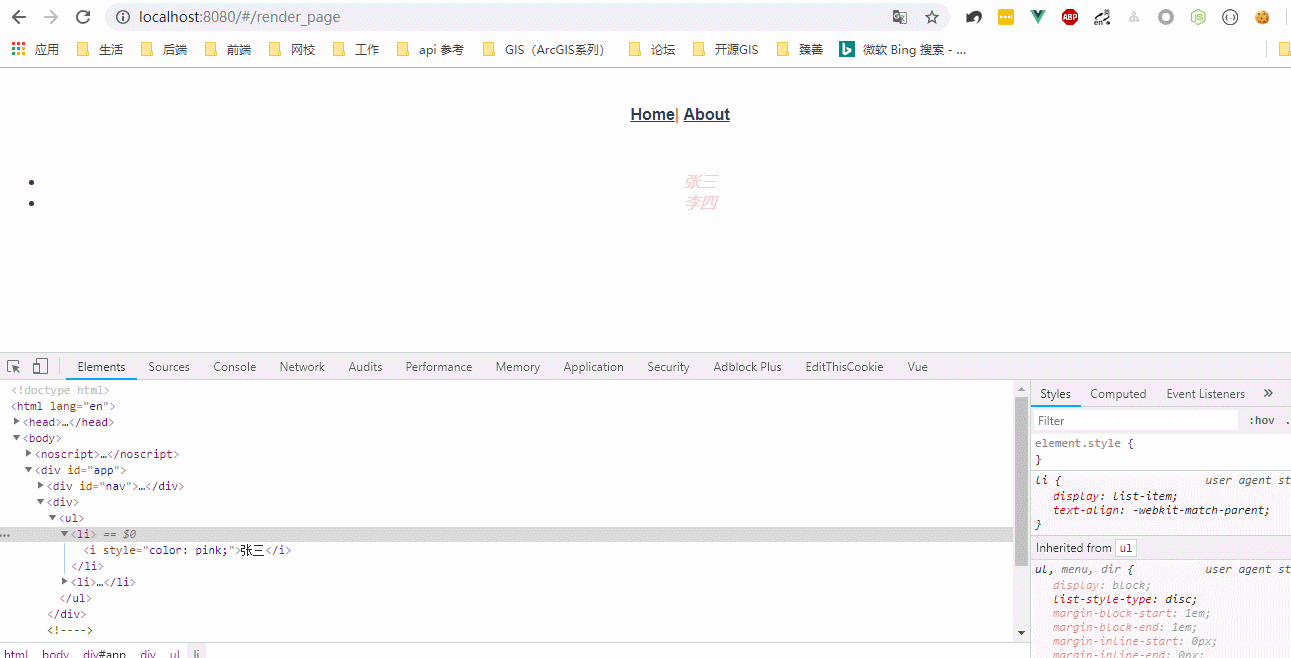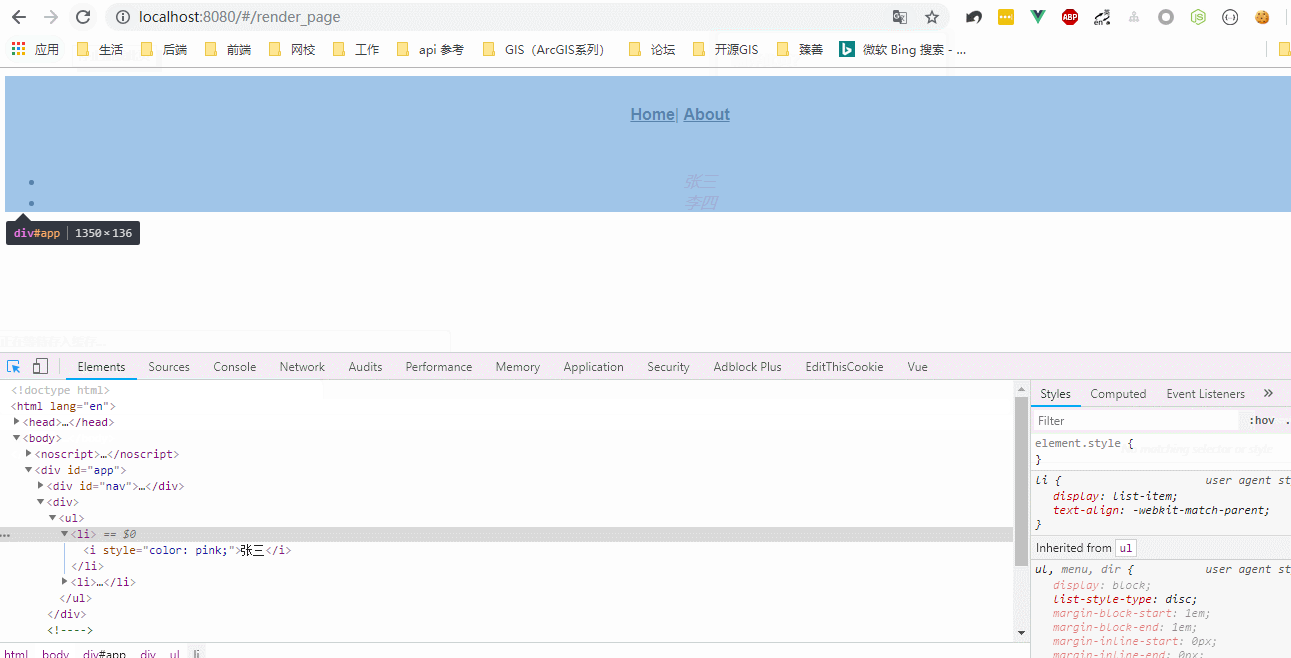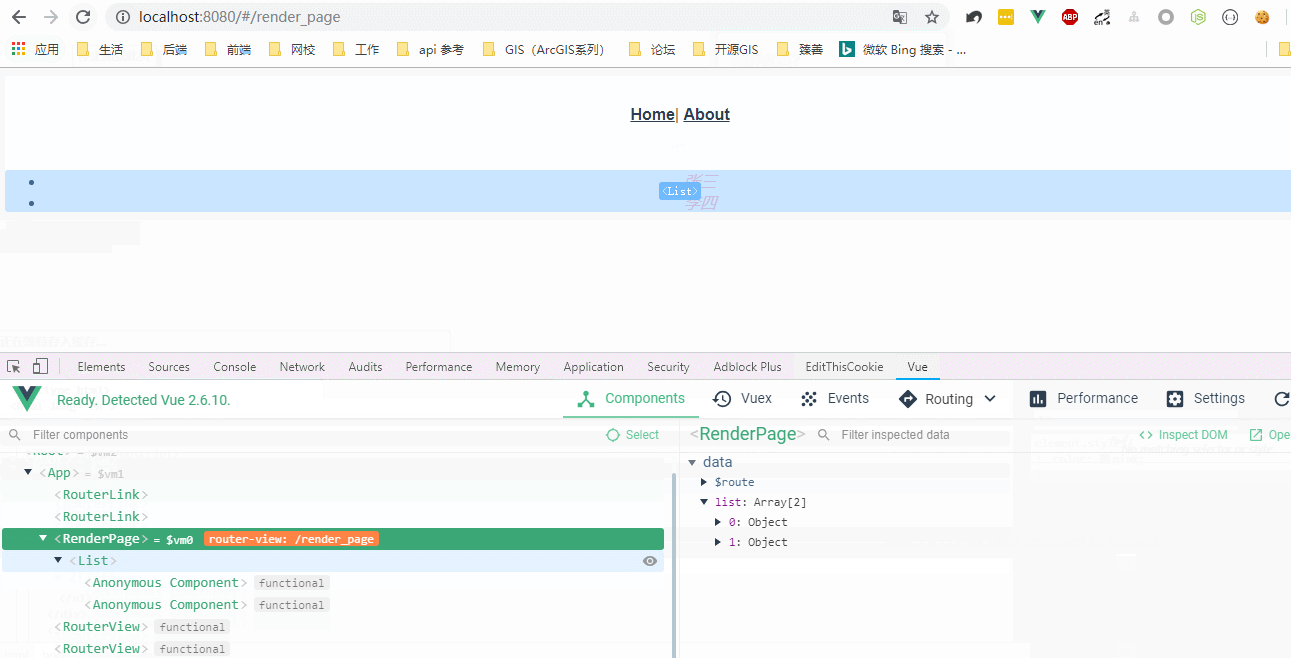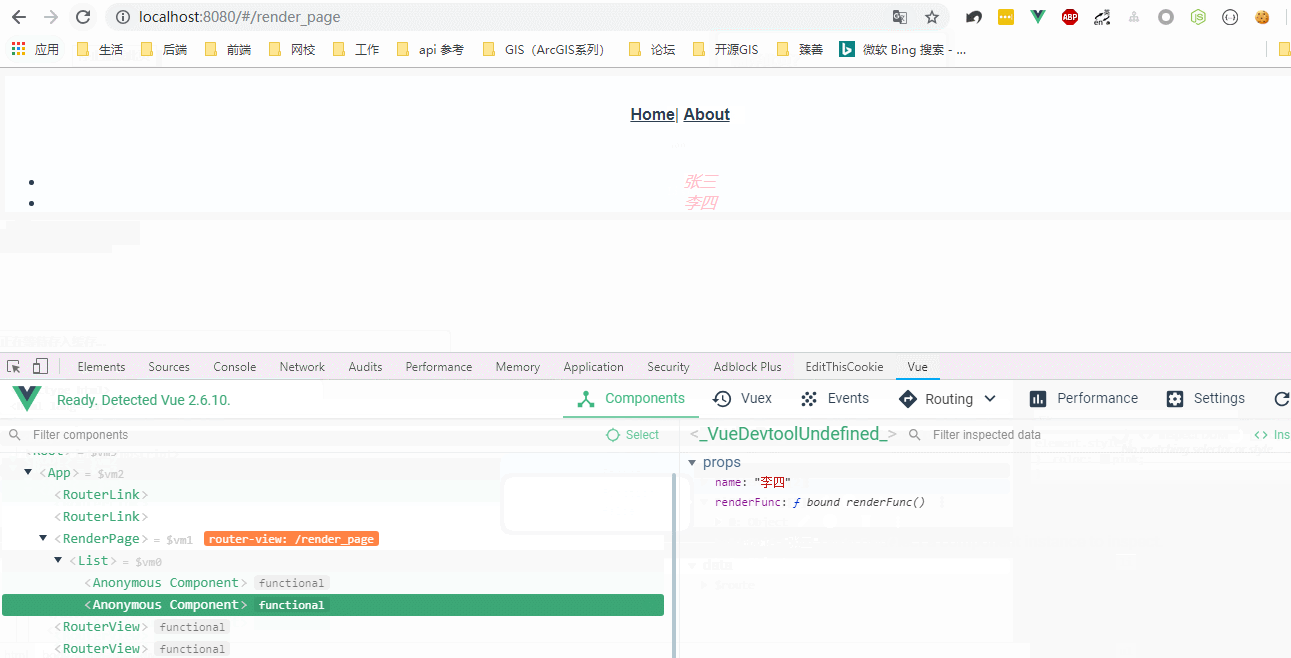
JSX(可参考https://juejin.im/post/5affa64df265da0b93488fdd):
什么是JSX:
JSX就是Javascript和XML结合的一种格式。React发明了JSX,利用HTML语法来创建虚拟DOM。当遇到<,JSX就当HTML解析,遇到{就当JavaScript解析。
将刚才的例子中的render-page.vue中的render函数改为jsx语法(它可以让我们回到更接近于模板的语法上):
<template>
<div>
<list :list="list" :render="render"></list>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import List from "_c/list";
export default {
data() {
return {
list: [
{
name: "张三"
},
{
name: "李四"
}
]
};
},
components: {
List
},
methods: {
render: function(h, name) {
// return h("i", {
// style: {
// color: "pink"
// }
// },name);
return (
////绑定事件需要用on前缀
<i on-click={this.handlerClick} style={{color:'pink'}}>{name}</i>
);
},
handlerClick(event){
console.log(event);
}
}
};
</script>
在JSX中使用组件(使用和上一个例子同样的目录结构):
注意在render或者JSX中写的组件是不需要在components中注册的。
render-page.vue:
<template>
<div>
<list :list="list" :render="render"></list>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import List from "_c/list";
import CountTo from "_c/count-to";
export default {
data() {
return {
list: [
{
number: 100
},
{
number: 200
}
]
};
},
components: {
List
},
methods: {
render: function(h, number) {
return (
//绑定事件需要用on-开头 绑定原生事件用nativeOn-开头
<CountTo nativeOn-click={this.nativeHandlerOn} on-on-animation-end={this.handlerEnd} endVal={number} />
);
},
handlerClick(event) {
console.log(event);
},
handlerEnd() {
console.log("End!!!");
},
nativeHandlerOn(){
console.log("这是原生事件");
}
}
};
</script>
list.vue:
<template>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in list" :key="`item_${index}`">
<span v-if="!render">{{item.number}}</span>
<render-dom v-else :render-func="render" :number="item.number"></render-dom>
</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
import RenderDom from "_c/render-dom";
export default {
name: "List",
components: {
RenderDom
},
props: {
list: {
type: Array,
default: () => []
},
render: {
type: Function,
default: () => {}
}
}
};
</script>
render-dom.js:
export default { functional: true, // Props 是可选的 props: { number: Number, renderFunc: Function }, // 为了弥补缺少的实例,提供第二个参数作为上下文 render: (h, ctx) => { return ctx.props.renderFunc(h, ctx.props.number); } };
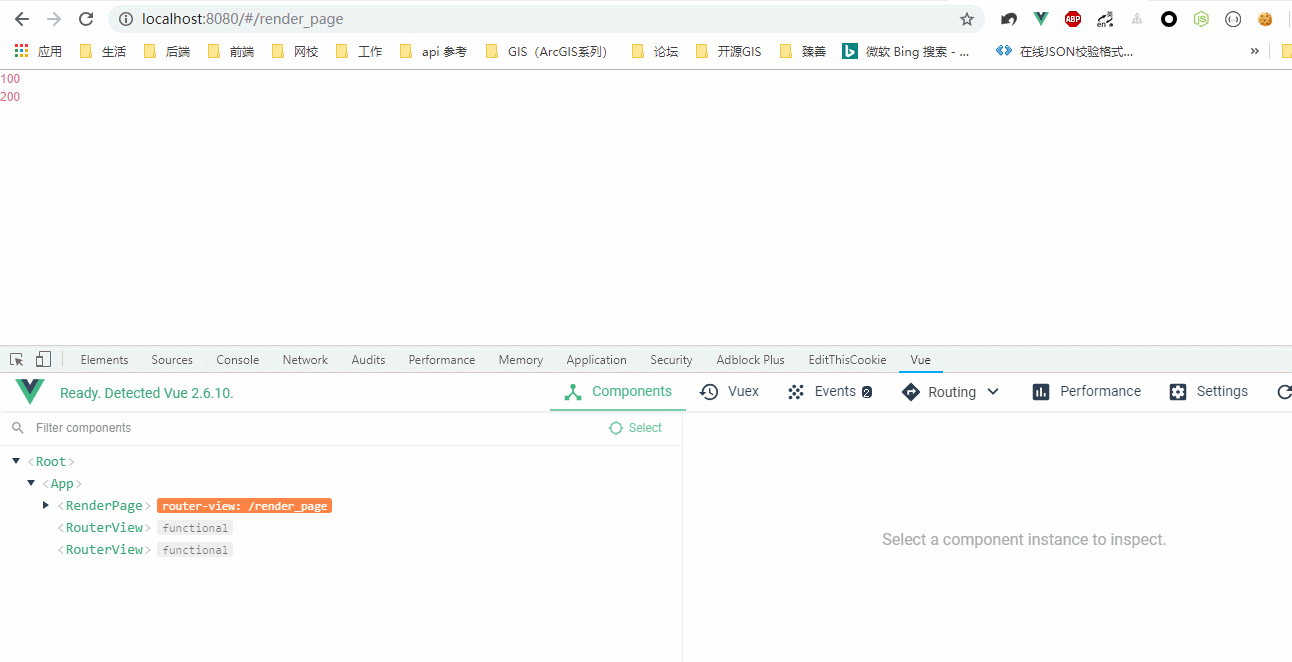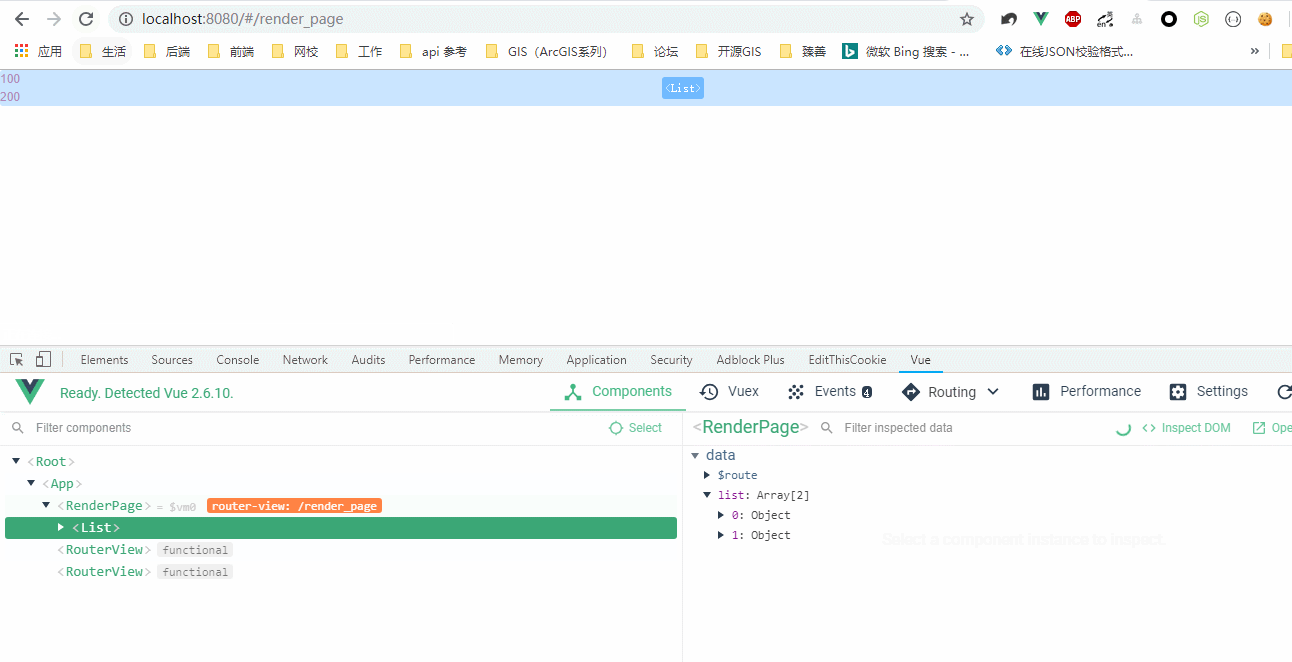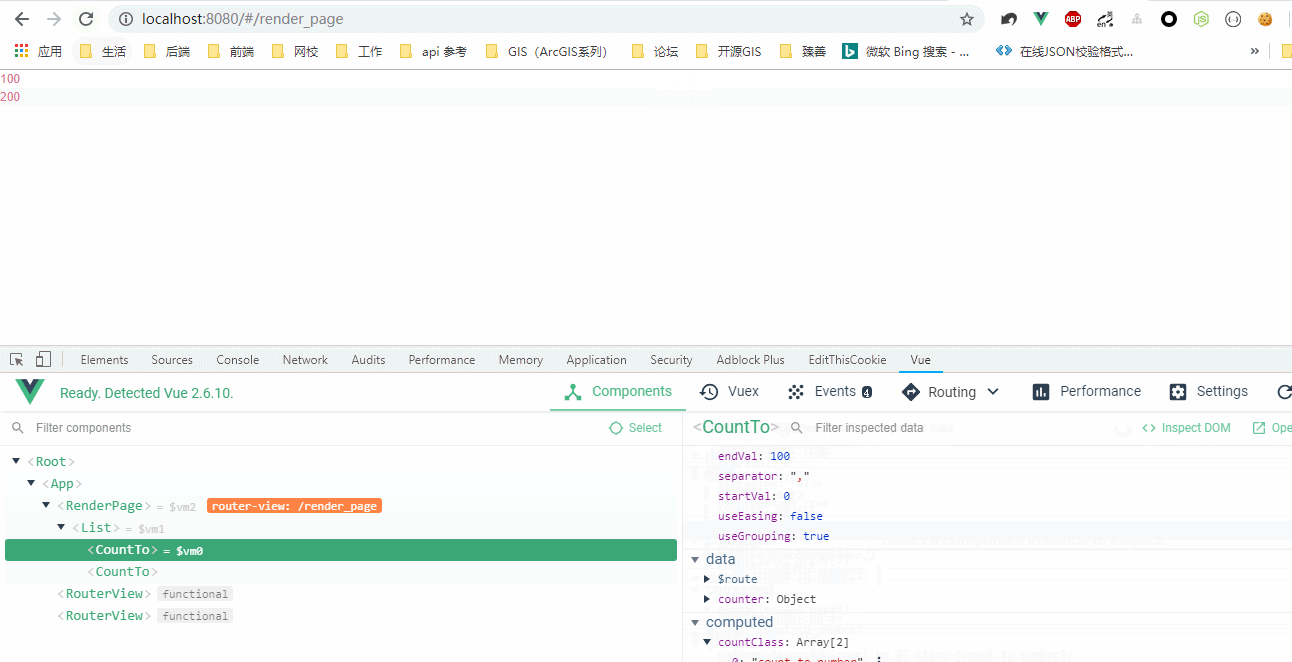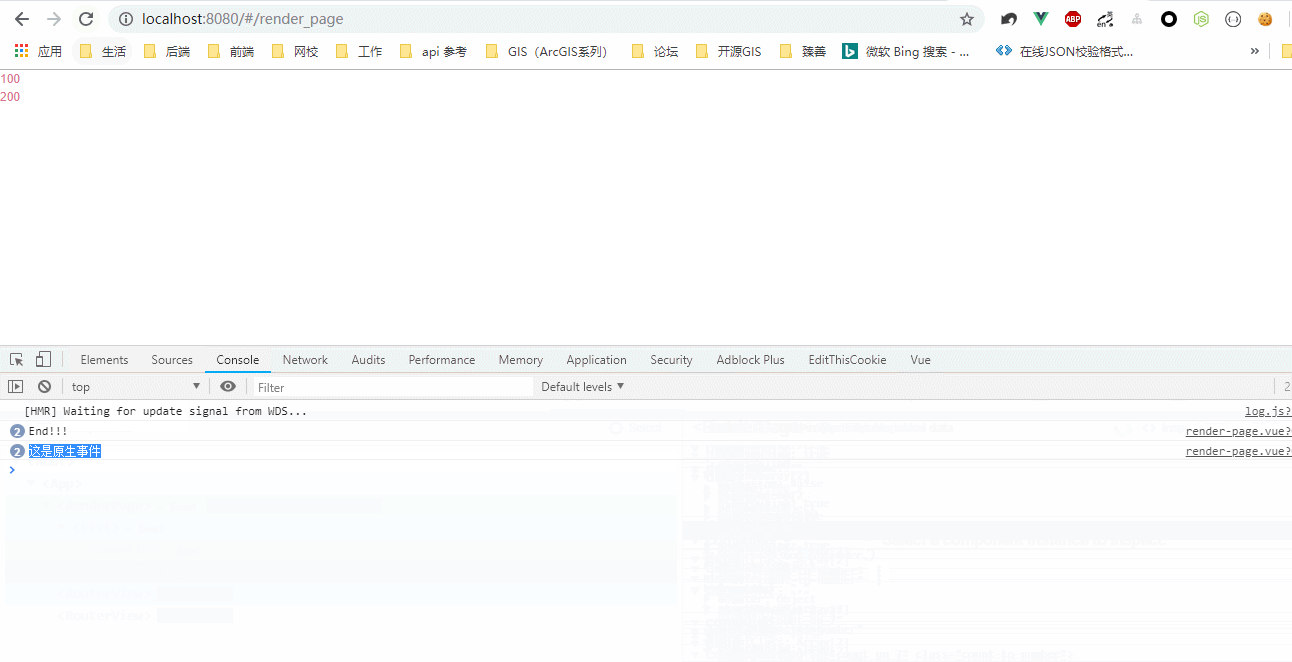
效果图:
作用域插槽
作用域插槽就是父组件在调用子组件的时候给子组件传了一个插槽,这个插槽为作用域插槽,该插槽必须放在template标签里面,同时声明从子组件接收的数据放在一个自定义属性内,并定义该数据的渲染方式。适合的场景是至少包含三级以上的组件层级,是一种优秀的组件化方案!
render-page.vue:
<template>
<div>
<list :list="list">
<count-to slot-scope="count" :endVal="count.number"></count-to>
</list>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import List from "_c/list";
import CountTo from "_c/count-to";
export default {
data() {
return {
list: [
{
number: 100
},
{
number: 200
}
]
};
},
components: {
List,
CountTo
},
methods: {
}
};
</script>
list.vue:
<template>
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in list" :key="`item_${index}`">
<!-- <span v-if="!render">{{item.number}}</span>
<render-dom v-else :render-func="render" :number="item.number"></render-dom> -->
<slot :number="item.number"></slot>
</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
import RenderDom from "_c/render-dom";
export default {
name: "List",
components: {
RenderDom
},
props: {
list: {
type: Array,
default: () => []
},
render: {
type: Function,
default: () => {}
}
}
};
</script>