一致性哈希算法在1997年由麻省理工学院提出的一种分布式哈希(DHT)实现算法,设计目标是为了解决因特网中的热点(Hot spot)问题,初衷和CARP十分类似。一致性哈希修正了CARP使用的简单哈希算法带来的问题,使得分布式哈希(DHT)可以在P2P环境中真正得到应用。在了解一致性哈希算法之前,最好先了解一下缓存中的一个应用场景,了解了这个应用场景之后,再来理解一致性哈希算法,就容易多了,也更能体现出一致性哈希算法的优点,那么,我们先来描述一下这个经典的分布式缓存的应用场景。
场景描述
假设,我们有三台缓存服务器,用于缓存图片,我们为这三台缓存服务器编号为0号、1号、2号,现在,有3万张图片需要缓存,我们希望这些图片被均匀的缓存到这3台服务器上,以便它们能够分摊缓存的压力。也就是说,我们希望每台服务器能够缓存1万张左右的图片,那么,我们应该怎样做呢?如果我们没有任何规律的将3万张图片平均的缓存在3台服务器上,可以满足我们的要求吗?可以!但是如果这样做,当我们需要访问某个缓存项时,则需要遍历3台缓存服务器,从3万个缓存项中找到我们需要访问的缓存,遍历的过程效率太低,时间太长,当我们找到需要访问的缓存项时,时长可能是不能被接受的,也就失去了缓存的意义,缓存的目的就是提高速度,改善用户体验,减轻后端服务器压力,如果每次访问一个缓存项都需要遍历所有缓存服务器的所有缓存项,想想就觉得很累,那么,我们该怎么办呢?原始的做法是对缓存项的键进行哈希,将hash后的结果对缓存服务器的数量进行取模操作,通过取模后的结果,决定缓存项将会缓存在哪一台服务器上,这样说可能不太容易理解,我们举例说明,仍然以刚才描述的场景为例,假设我们使用图片名称作为访问图片的key,假设图片名称是不重复的,那么,我们可以使用如下公式,计算出图片应该存放在哪台服务器上。
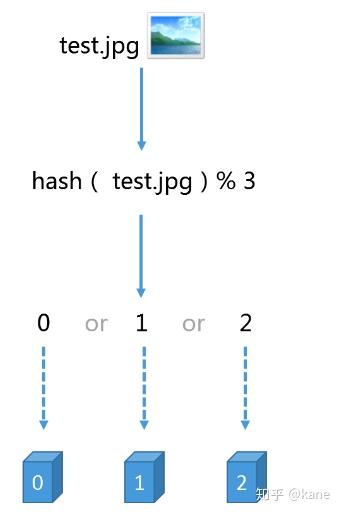
hash(图片名称)% N
因为图片的名称是不重复的,所以,当我们对同一个图片名称做相同的哈希计算时,得出的结果应该是不变的,如果我们有3台服务器,使用哈希后的结果对3求余,那么余数一定是0、1或者2,没错,正好与我们之前的服务器编号相同,如果求余的结果为0, 我们就把当前图片名称对应的图片缓存在0号服务器上,如果余数为1,就把当前图片名对应的图片缓存在1号服务器上,如果余数为2,同理,那么,当我们访问任意一个图片的时候,只要再次对图片名称进行上述运算,即可得出对应的图片应该存放在哪一台缓存服务器上,我们只要在这一台服务器上查找图片即可,如果图片在对应的服务器上不存在,则证明对应的图片没有被缓存,也不用再去遍历其他缓存服务器了,通过这样的方法,即可将3万张图片随机的分布到3台缓存服务器上了,而且下次访问某张图片时,直接能够判断出该图片应该存在于哪台缓存服务器上,这样就能满足我们的需求了,我们暂时称上述算法为HASH算法或者取模算法,取模算法的过程可以用下图表示。
但是,使用上述HASH算法进行缓存时,会出现一些缺陷,试想一下,如果3台缓存服务器已经不能满足我们的缓存需求,那么我们应该怎么做呢?没错,很简单,多增加两台缓存服务器不就行了,假设,我们增加了一台缓存服务器,那么缓存服务器的数量就由3台变成了4台,此时,如果仍然使用上述方法对同一张图片进行缓存,那么这张图片所在的服务器编号必定与原来3台服务器时所在的服务器编号不同,因为除数由3变为了4,被除数不变的情况下,余数肯定不同,这种情况带来的结果就是当服务器数量变动时,所有缓存的位置都要发生改变,换句话说,当服务器数量发生改变时,所有缓存在一定时间内是失效的,当应用无法从缓存中获取数据时,则会向后端服务器请求数据,同理,假设3台缓存中突然有一台缓存服务器出现了故障,无法进行缓存,那么我们则需要将故障机器移除,但是如果移除了一台缓存服务器,那么缓存服务器数量从3台变为2台,如果想要访问一张图片,这张图片的缓存位置必定会发生改变,以前缓存的图片也会失去缓存的作用与意义,由于大量缓存在同一时间失效,造成了缓存的雪崩,此时前端缓存已经无法起到承担部分压力的作用,后端服务器将会承受巨大的压力,整个系统很有可能被压垮,所以,我们应该想办法不让这种情况发生,但是由于上述HASH算法本身的缘故,使用取模法进行缓存时,这种情况是无法避免的,为了解决这些问题,一致性哈希算法诞生了。
我们来回顾一下使用上述算法会出现的问题。
问题1:当缓存服务器数量发生变化时,会引起缓存的雪崩,可能会引起整体系统压力过大而崩溃(大量缓存同一时间失效)。
问题2:当缓存服务器数量发生变化时,几乎所有缓存的位置都会发生改变,怎样才能尽量减少受影响的缓存呢?
其实,上面两个问题是一个问题,那么,一致性哈希算法能够解决上述问题吗?
我们现在就来了解一下一致性哈希算法。
一致性哈希算法的基本概念
其实,一致性哈希算法也是使用取模的方法,只是,刚才描述的取模法是对服务器的数量进行取模,而一致性哈希算法是对2^32取模,什么意思呢?我们慢慢聊。
首先,我们把二的三十二次方想象成一个圆,就像钟表一样,钟表的圆可以理解成由60个点组成的圆,而此处我们把这个圆想象成由2^32个点组成的圆,示意图如下:
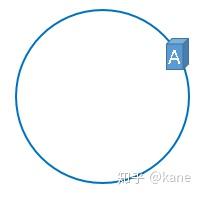
圆环的正上方的点代表0,0点右侧的第一个点代表1,以此类推,2、3、4、5、6……直到2^32-1,也就是说0点左侧的第一个点代表2^32-1
我们把这个由2的32次方个点组成的圆环称为hash环。
那么,一致性哈希算法与上图中的圆环有什么关系呢?我们继续聊,仍然以之前描述的场景为例,假设我们有3台缓存服务器,服务器A、服务器B、服务器C,那么,在生产环境中,这三台服务器肯定有自己的IP地址,我们使用它们各自的IP地址进行哈希计算,使用哈希后的结果对2^32取模,可以使用如下公式示意。
hash(服务器A的IP地址) % 2^32
通过上述公式算出的结果一定是一个0到2^32-1之间的一个整数,我们就用算出的这个整数,代表服务器A,既然这个整数肯定处于0到2^32-1之间,那么,上图中的hash环上必定有一个点与这个整数对应,而我们刚才已经说明,使用这个整数代表服务器A,那么,服务器A就可以映射到这个环上,用下图示意
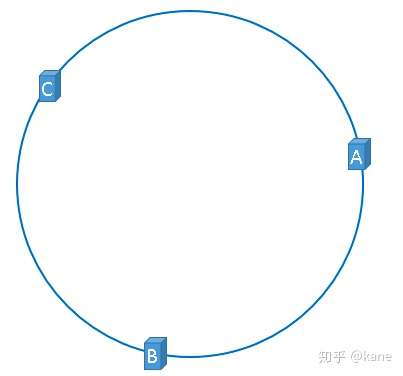
同理,服务器B与服务器C也可以通过相同的方法映射到上图中的hash环中
hash(服务器B的IP地址) % 2^32
hash(服务器C的IP地址) % 2^32
通过上述方法,可以将服务器B与服务器C映射到上图中的hash环上,示意图如下

假设3台服务器映射到hash环上以后如上图所示(当然,这是理想的情况,我们慢慢聊)。
好了,到目前为止,我们已经把缓存服务器与hash环联系在了一起,我们通过上述方法,把缓存服务器映射到了hash环上,那么使用同样的方法,我们也可以将需要缓存的对象映射到hash环上。
假设,我们需要使用缓存服务器缓存图片,而且我们仍然使用图片的名称作为找到图片的key,那么我们使用如下公式可以将图片映射到上图中的hash环上。
hash(图片名称) % 2^32
映射后的示意图如下,下图中的橘黄色圆形表示图片
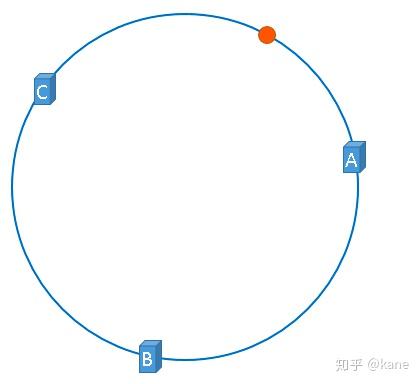
好了,现在服务器与图片都被映射到了hash环上,那么上图中的这个图片到底应该被缓存到哪一台服务器上呢?上图中的图片将会被缓存到服务器A上,为什么呢?因为从图片的位置开始,沿顺时针方向遇到的第一个服务器就是A服务器,所以,上图中的图片将会被缓存到服务器A上,如下图所示。
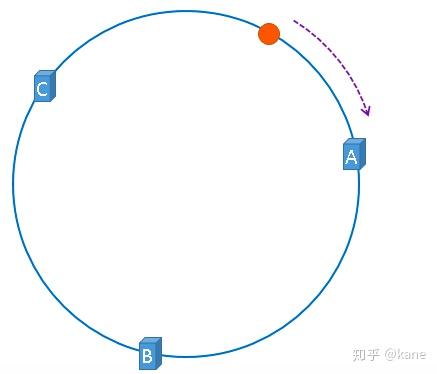
没错,一致性哈希算法就是通过这种方法,判断一个对象应该被缓存到哪台服务器上的,将缓存服务器与被缓存对象都映射到hash环上以后,从被缓存对象的位置出发,沿顺时针方向遇到的第一个服务器,就是当前对象将要缓存于的服务器,由于被缓存对象与服务器hash后的值是固定的,所以,在服务器不变的情况下,一张图片必定会被缓存到固定的服务器上,那么,当下次想要访问这张图片时,只要再次使用相同的算法进行计算,即可算出这个图片被缓存在哪个服务器上,直接去对应的服务器查找对应的图片即可。
刚才的示例只使用了一张图片进行演示,假设有四张图片需要缓存,示意图如下

1号、2号图片将会被缓存到服务器A上,3号图片将会被缓存到服务器B上,4号图片将会被缓存到服务器C上。
一致性哈希算法的优点
经过上述描述,我想兄弟你应该已经明白了一致性哈希算法的原理了,但是话说回来,一致性哈希算法能够解决之前出现的问题吗,我们说过,如果简单的对服务器数量进行取模,那么当服务器数量发生变化时,会产生缓存的雪崩,从而很有可能导致系统崩溃,那么使用一致性哈希算法,能够避免这个问题吗?我们来模拟一遍,即可得到答案。
假设,服务器B出现了故障,我们现在需要将服务器B移除,那么,我们将上图中的服务器B从hash环上移除即可,移除服务器B以后示意图如下。
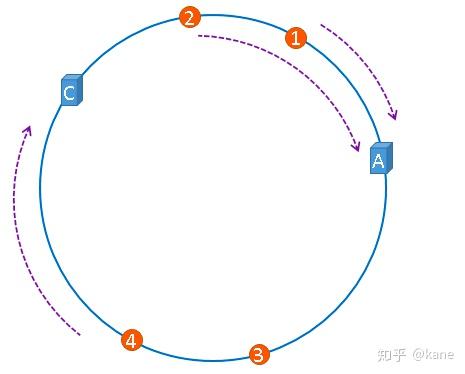
在服务器B未移除时,图片3应该被缓存到服务器B中,可是当服务器B移除以后,按照之前描述的一致性哈希算法的规则,图片3应该被缓存到服务器C中,因为从图片3的位置出发,沿顺时针方向遇到的第一个缓存服务器节点就是服务器C,也就是说,如果服务器B出现故障被移除时,图片3的缓存位置会发生改变
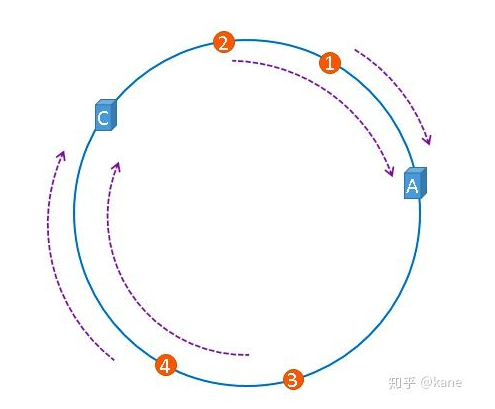
但是,图片4仍然会被缓存到服务器C中,图片1与图片2仍然会被缓存到服务器A中,这与服务器B移除之前并没有任何区别,这就是一致性哈希算法的优点,如果使用之前的hash算法,服务器数量发生改变时,所有服务器的所有缓存在同一时间失效了,而使用一致性哈希算法时,服务器的数量如果发生改变,并不是所有缓存都会失效,而是只有部分缓存会失效,前端的缓存仍然能分担整个系统的压力,而不至于所有压力都在同一时间集中到后端服务器上。
这就是一致性哈希算法所体现出的优点。
hash环的偏斜
在介绍一致性哈希的概念时,我们理想化的将3台服务器均匀的映射到了hash环上,如下图所示
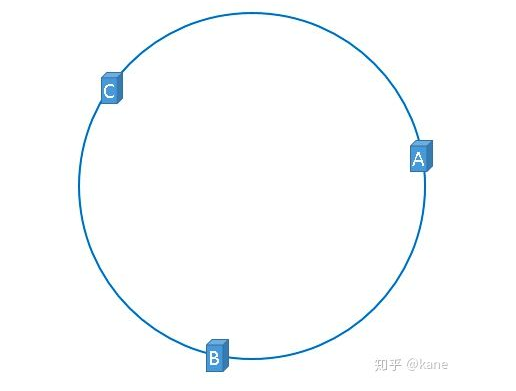
但是,理想很丰满,现实很骨感,我们想象的与实际情况往往不一样。
在实际的映射中,服务器可能会被映射成如下模样。

聪明如你一定想到了,如果服务器被映射成上图中的模样,那么被缓存的对象很有可能大部分集中缓存在某一台服务器上,如下图所示。
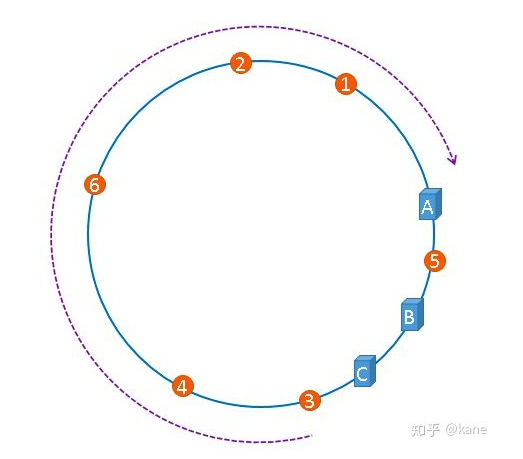
上图中,1号、2号、3号、4号、6号图片均被缓存在了服务器A上,只有5号图片被缓存在了服务器B上,服务器C上甚至没有缓存任何图片,如果出现上图中的情况,A、B、C三台服务器并没有被合理的平均的充分利用,缓存分布的极度不均匀,而且,如果此时服务器A出现故障,那么失效缓存的数量也将达到最大值,在极端情况下,仍然有可能引起系统的崩溃,上图中的情况则被称之为hash环的偏斜,那么,我们应该怎样防止hash环的偏斜呢?一致性hash算法中使用"虚拟节点"解决了这个问题,我们继续聊。
虚拟节点
话接上文,由于我们只有3台服务器,当我们把服务器映射到hash环上的时候,很有可能出现hash环偏斜的情况,当hash环偏斜以后,缓存往往会极度不均衡的分布在各服务器上,聪明如你一定已经想到了,如果想要均衡的将缓存分布到3台服务器上,最好能让这3台服务器尽量多的、均匀的出现在hash环上,但是,真实的服务器资源只有3台,我们怎样凭空的让它们多起来呢,没错,就是凭空的让服务器节点多起来,既然没有多余的真正的物理服务器节点,我们就只能将现有的物理节点通过虚拟的方法复制出来,这些由实际节点虚拟复制而来的节点被称为"虚拟节点"。加入虚拟节点以后的hash环如下。
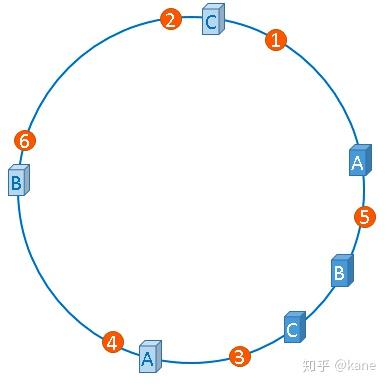
"虚拟节点"是"实际节点"(实际的物理服务器)在hash环上的复制品,一个实际节点可以对应多个虚拟节点。
从上图可以看出,A、B、C三台服务器分别虚拟出了一个虚拟节点,当然,如果你需要,也可以虚拟出更多的虚拟节点。引入虚拟节点的概念后,缓存的分布就均衡多了,上图中,1号、3号图片被缓存在服务器A中,5号、4号图片被缓存在服务器B中,6号、2号图片被缓存在服务器C中,如果你还不放心,可以虚拟出更多的虚拟节点,以便减小hash环偏斜所带来的影响,虚拟节点越多,hash环上的节点就越多,缓存被均匀分布的概率就越大。
php实现
理论说完了,就要说实现了,来看一下具体的php实现:
一致性hash算法的PHP实现1 <?php 2 /** 3 * Flexihash - A simple consistent hashing implementation for PHP. 4 * 5 * The MIT License 6 * 7 * Copyright (c) 2008 Paul Annesley 8 * 9 * Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy 10 * of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal 11 * in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights 12 * to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell 13 * copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is 14 * furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions: 15 * 16 * The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in 17 * all copies or substantial portions of the Software. 18 * 19 * THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR 20 * IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, 21 * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE 22 * AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER 23 * LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, 24 * OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN 25 * THE SOFTWARE. 26 * 27 * @author Paul Annesley 28 * @link http://paul.annesley.cc/ 29 * @copyright Paul Annesley, 2008 30 * @comment by MyZ (http://blog.csdn.net/mayongzhan) 31 */ 32 33 /** 34 * A simple consistent hashing implementation with pluggable hash algorithms. 35 * 36 * @author Paul Annesley 37 * @package Flexihash 38 * @licence http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php 39 */ 40 class Flexihash 41 { 42 /** 43 * The number of positions to hash each target to. 44 * 45 * @var int 46 * @comment 虚拟节点数,解决节点分布不均的问题 47 */ 48 private $_replicas = 64; 49 50 /** 51 * The hash algorithm, encapsulated in a Flexihash_Hasher implementation. 52 * @var object Flexihash_Hasher 53 * @comment 使用的hash方法 : md5,crc32 54 */ 55 private $_hasher; 56 57 /** 58 * Internal counter for current number of targets. 59 * @var int 60 * @comment 节点记数器 61 */ 62 private $_targetCount = 0; 63 64 /** 65 * Internal map of positions (hash outputs) to targets 66 * @var array { position => target, ... } 67 * @comment 位置对应节点,用于lookup中根据位置确定要访问的节点 68 */ 69 private $_positionToTarget = array(); 70 71 /** 72 * Internal map of targets to lists of positions that target is hashed to. 73 * @var array { target => [ position, position, ... ], ... } 74 * @comment 节点对应位置,用于删除节点 75 */ 76 private $_targetToPositions = array(); 77 78 /** 79 * Whether the internal map of positions to targets is already sorted. 80 * @var boolean 81 * @comment 是否已排序 82 */ 83 private $_positionToTargetSorted = false; 84 85 /** 86 * Constructor 87 * @param object $hasher Flexihash_Hasher 88 * @param int $replicas Amount of positions to hash each target to. 89 * @comment 构造函数,确定要使用的hash方法和需拟节点数,虚拟节点数越多,分布越均匀,但程序的分布式运算越慢 90 */ 91 public function __construct(Flexihash_Hasher $hasher = null, $replicas = null) 92 { 93 $this->_hasher = $hasher ? $hasher : new Flexihash_Crc32Hasher(); 94 if (!empty($replicas)) $this->_replicas = $replicas; 95 } 96 97 /** 98 * Add a target. 99 * @param string $target 100 * @chainable 101 * @comment 添加节点,根据虚拟节点数,将节点分布到多个虚拟位置上 102 */ 103 public function addTarget($target) 104 { 105 if (isset($this->_targetToPositions[$target])) 106 { 107 throw new Flexihash_Exception("Target '$target' already exists."); 108 } 109 110 $this->_targetToPositions[$target] = array(); 111 112 // hash the target into multiple positions 113 for ($i = 0; $i < $this->_replicas; $i++) 114 { 115 $position = $this->_hasher->hash($target . $i); 116 $this->_positionToTarget[$position] = $target; // lookup 117 $this->_targetToPositions[$target] []= $position; // target removal 118 } 119 120 $this->_positionToTargetSorted = false; 121 $this->_targetCount++; 122 123 return $this; 124 } 125 126 /** 127 * Add a list of targets. 128 * @param array $targets 129 * @chainable 130 */ 131 public function addTargets($targets) 132 { 133 foreach ($targets as $target) 134 { 135 $this->addTarget($target); 136 } 137 138 return $this; 139 } 140 141 /** 142 * Remove a target. 143 * @param string $target 144 * @chainable 145 */ 146 public function removeTarget($target) 147 { 148 if (!isset($this->_targetToPositions[$target])) 149 { 150 throw new Flexihash_Exception("Target '$target' does not exist."); 151 } 152 153 foreach ($this->_targetToPositions[$target] as $position) 154 { 155 unset($this->_positionToTarget[$position]); 156 } 157 158 unset($this->_targetToPositions[$target]); 159 160 $this->_targetCount--; 161 162 return $this; 163 } 164 165 /** 166 * A list of all potential targets 167 * @return array 168 */ 169 public function getAllTargets() 170 { 171 return array_keys($this->_targetToPositions); 172 } 173 174 /** 175 * A list of all potential targets 176 * @return array 177 */ 178 public function getAll() 179 { 180 return array( 181 "targers"=>$this->_positionToTarget, 182 "positions"=>$this->_targetToPositions); 183 } 184 185 /** 186 * Looks up the target for the given resource. 187 * @param string $resource 188 * @return string 189 */ 190 public function lookup($resource) 191 { 192 $targets = $this->lookupList($resource, 1); 193 if (empty($targets)) throw new Flexihash_Exception('No targets exist'); 194 return $targets[0]; //0表示返回离资源位置最近的机器节点 195 } 196 197 /** 198 * Get a list of targets for the resource, in order of precedence. 199 * Up to $requestedCount targets are returned, less if there are fewer in total. 200 * 201 * @param string $resource 202 * @param int $requestedCount The length of the list to return 203 * @return array List of targets 204 * @comment 查找当前的资源对应的节点, 205 * 节点为空则返回空,节点只有一个则返回该节点, 206 * 对当前资源进行hash,对所有的位置进行排序,在有序的位置列上寻找当前资源的位置 207 * 当全部没有找到的时候,将资源的位置确定为有序位置的第一个(形成一个环) 208 * 返回所找到的节点 209 */ 210 public function lookupList($resource, $requestedCount) 211 { 212 if (!$requestedCount) 213 throw new Flexihash_Exception('Invalid count requested'); 214 215 // handle no targets 216 if (empty($this->_positionToTarget)) 217 return array(); 218 219 // optimize single target 220 if ($this->_targetCount == 1) 221 return array_unique(array_values($this->_positionToTarget)); 222 223 // hash resource to a position 224 $resourcePosition = $this->_hasher->hash($resource); 225 226 $results = array(); 227 $collect = false; 228 229 $this->_sortPositionTargets(); 230 231 // search values above the resourcePosition 232 foreach ($this->_positionToTarget as $key => $value) 233 { 234 // start collecting targets after passing resource position 235 if (!$collect && $key > $resourcePosition) 236 { 237 $collect = true; 238 } 239 240 // only collect the first instance of any target 241 if ($collect && !in_array($value, $results)) 242 { 243 $results []= $value; 244 //var_dump($results); 245 } 246 // return when enough results, or list exhausted 247 //var_dump(count($results)); 248 //var_dump($requestedCount); 249 if (count($results) == $requestedCount || count($results) == $this->_targetCount) 250 { 251 return $results; 252 } 253 } 254 255 // loop to start - search values below the resourcePosition 256 foreach ($this->_positionToTarget as $key => $value) 257 { 258 if (!in_array($value, $results)) 259 { 260 $results []= $value; 261 } 262 263 // return when enough results, or list exhausted 264 if (count($results) == $requestedCount || count($results) == $this->_targetCount) 265 { 266 return $results; 267 } 268 } 269 270 // return results after iterating through both "parts" 271 return $results; 272 } 273 274 public function __toString() 275 { 276 return sprintf( 277 '%s{targets:[%s]}', 278 get_class($this), 279 implode(',', $this->getAllTargets()) 280 ); 281 } 282 283 // ---------------------------------------- 284 // private methods 285 286 /** 287 * Sorts the internal mapping (positions to targets) by position 288 */ 289 private function _sortPositionTargets() 290 { 291 // sort by key (position) if not already 292 if (!$this->_positionToTargetSorted) 293 { 294 ksort($this->_positionToTarget, SORT_REGULAR); 295 $this->_positionToTargetSorted = true; 296 } 297 } 298 299 } 300 301 /** 302 * Hashes given values into a sortable fixed size address space. 303 * 304 * @author Paul Annesley 305 * @package Flexihash 306 * @licence http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php 307 */ 308 interface Flexihash_Hasher 309 { 310 311 /** 312 * Hashes the given string into a 32bit address space. 313 * 314 * Note that the output may be more than 32bits of raw data, for example 315 * hexidecimal characters representing a 32bit value. 316 * 317 * The data must have 0xFFFFFFFF possible values, and be sortable by 318 * PHP sort functions using SORT_REGULAR. 319 * 320 * @param string 321 * @return mixed A sortable format with 0xFFFFFFFF possible values 322 */ 323 public function hash($string); 324 325 } 326 327 /** 328 * Uses CRC32 to hash a value into a signed 32bit int address space. 329 * Under 32bit PHP this (safely) overflows into negatives ints. 330 * 331 * @author Paul Annesley 332 * @package Flexihash 333 * @licence http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php 334 */ 335 class Flexihash_Crc32Hasher 336 implements Flexihash_Hasher 337 { 338 339 /* (non-phpdoc) 340 * @see Flexihash_Hasher::hash() 341 */ 342 public function hash($string) 343 { 344 return crc32($string); 345 } 346 347 } 348 349 /** 350 * Uses CRC32 to hash a value into a 32bit binary string data address space. 351 * 352 * @author Paul Annesley 353 * @package Flexihash 354 * @licence http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php 355 */ 356 class Flexihash_Md5Hasher 357 implements Flexihash_Hasher 358 { 359 360 /* (non-phpdoc) 361 * @see Flexihash_Hasher::hash() 362 */ 363 public function hash($string) 364 { 365 return substr(md5($string), 0, 8); // 8 hexits = 32bit 366 367 // 4 bytes of binary md5 data could also be used, but 368 // performance seems to be the same. 369 } 370 371 } 372 373 /** 374 * An exception thrown by Flexihash. 375 * 376 * @author Paul Annesley 377 * @package Flexihash 378 * @licence http://www.opensource.org/licenses/mit-license.php 379 */ 380 class Flexihash_Exception extends Exception 381 { 382 } 383 384 测试代码 385 $hash = new Flexihash(); 386 $targets=array( 387 "192.168.1.1:11011", 388 "192.168.1.1:11012", 389 "192.168.1.1:11013", 390 "192.168.1.1:11014", 391 "192.168.1.1:11015", 392 ); 393 $hash->addTargets($targets); 394 for ($i=0; $i < 25; $i++) { 395 $resource = sprintf("format %d",$i); 396 var_dump($resource." --> ".$hash->lookup($resource)); 397 } 398 399 输出 400 401 string(30) "format 0 --> 192.168.1.1:11015" 402 string(30) "format 1 --> 192.168.1.1:11015" 403 string(30) "format 2 --> 192.168.1.1:11015" 404 string(30) "format 3 --> 192.168.1.1:11015" 405 string(30) "format 4 --> 192.168.1.1:11011" 406 string(30) "format 5 --> 192.168.1.1:11011" 407 string(30) "format 6 --> 192.168.1.1:11011" 408 string(30) "format 7 --> 192.168.1.1:11011" 409 string(30) "format 8 --> 192.168.1.1:11012" 410 string(30) "format 9 --> 192.168.1.1:11013" 411 string(31) "format 10 --> 192.168.1.1:11013" 412 string(31) "format 11 --> 192.168.1.1:11011" 413 string(31) "format 12 --> 192.168.1.1:11012" 414 string(31) "format 13 --> 192.168.1.1:11011" 415 string(31) "format 14 --> 192.168.1.1:11014" 416 string(31) "format 15 --> 192.168.1.1:11014" 417 string(31) "format 16 --> 192.168.1.1:11014" 418 string(31) "format 17 --> 192.168.1.1:11014" 419 string(31) "format 18 --> 192.168.1.1:11012" 420 string(31) "format 19 --> 192.168.1.1:11012" 421 string(31) "format 20 --> 192.168.1.1:11013" 422 string(31) "format 21 --> 192.168.1.1:11012" 423 string(31) "format 22 --> 192.168.1.1:11012" 424 string(31) "format 23 --> 192.168.1.1:11014" 425 string(31) "format 24 --> 192.168.1.1:11012" 426 [Finished in 0.1s] 427 428 redis分布式代码设计 429 430 <?php 431 require_once("Flexihash.php"); 432 $config=array( 433 "127.0.0.1:6371", 434 "127.0.0.1:6372", 435 "127.0.0.1:6373", 436 "127.0.0.1:6374", 437 ); 438 class RedisCollect { 439 //redis实例 440 private $_redis = null; 441 //hash实例 442 private $_hash = null; 443 //初始化 444 public function __construct() { 445 global $config; 446 $this->_redis = new Redis(); 447 $this->_hash = new Flexihash(); 448 $this->_hash->addTargets($config); 449 } 450 public function set($key="", $value="") { 451 $m = $this->switchConncetion($key); 452 return $m->set($key, $value); 453 } 454 public function get($key) { 455 $m = $this->switchConncetion($key); 456 return $m->get($key); 457 } 458 private function switchConncetion($key) { 459 $hostinfo = $this->_hash->lookup($key); 460 $m = $this->connect($hostinfo); 461 return $m; 462 } 463 private function connect($hostinfo) { 464 list($host, $port) = explode(":", $hostinfo); 465 //printf("host = %s, port = %s ",$host,$port); 466 if(empty($host) || empty($port)) { 467 return false; 468 } 469 try { 470 $this->_redis->connect($host, $port); 471 return $this->_redis; 472 } catch(Exception $e) { 473 die($e->getMessage()); 474 } 475 } 476 }
转自知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/80697626?utm_source=wechat_session&utm_medium=social&utm_oi=29529401720832&from=singlemessage&isappinstalled=0&wechatShare=2&s_r=0