--------------------MongoDB聚合--------------------
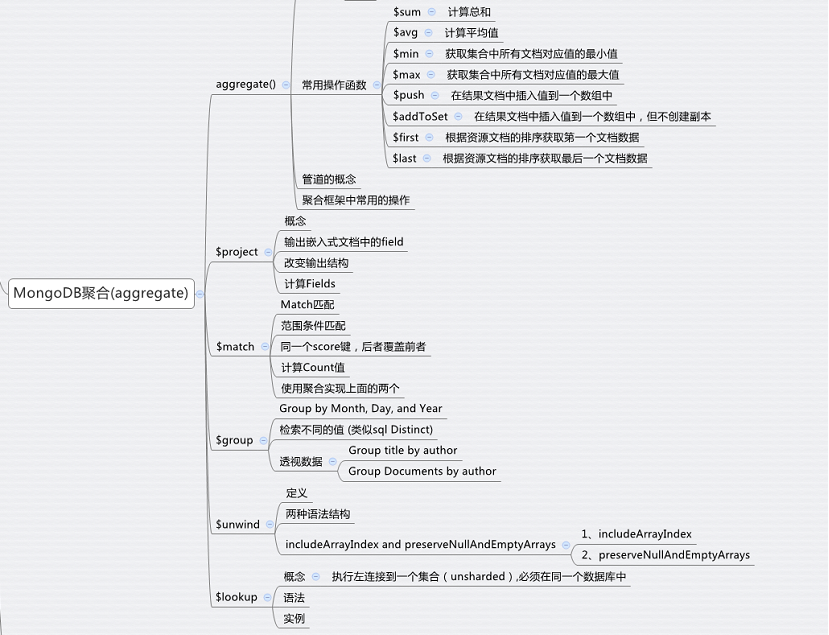
1、aggregate():
1、概念:
1、简介
MongoDB中聚合(aggregate)主要用于处理数据(诸如统计平均值,求和等),并返回计算后的数据结果。有点类似sql语句中的 count(*), sum(), avg()。
2、语法
db.集合名.aggregate(聚合表达式)
例:
sql语句:
>select by_user,count(*) as num_tutorial from mycol group by by_user
mongoDB语句:
>db.mycol.aggregate([
{
$group:{
_id:"by_user",
num_tutorial:{$sum:1}
}
}
])
2、常用操作函数:
1、$sum:计算总和:
sql语句:
>select _id,count(likes) as num_tutorial from mycol group by by_user
mongoDB语句:
>db.mycol.aggregate([
{
$group:{
_id:"$by_user",
num_tutorial:{$sum:"$likes"}
}
}
])
2、$avg:计算平均值:
>db.mycol.aggregate([
{
$group:{
_id:"$by_user",
num_tutorial:{$avg:"$likes"}
}
}
])
3、$min:获取集合中所有文档对应值的最小值:
>db.mycol.aggregate([
{
$group:{
_id:"$by_user",
num_tutorial:{$min:"$likes"}
}
}
])
4、$max:获取集合中所有文档对应值的最大值:
>db.mycol.aggregate([
{
group:{
_id:"$by_user",
num_tutorial:{$max:"$like"}
}
}
])
5、$push:在结果文档中插入值到一个数组中:
>db.mycol.aggregate([
{
group:{
_id:"$by_user",
url:{$push:"$url"}
}
}
])
结果:
{ "_id" : "Neo4j", "url" : [ "http://www.neo4j.com" ] }
{ "_id" : "w3cschool.cc", "url" : [ "http://www.w3cschool.cc", "http://www.w3cschool.cc" ] }
6、$addToSet:在结果文档中插入值到一个数组中,但不创建副本
>db.mycol.aggregate([
{
$group:{
_id:"$by_user",
url:{addToSet:"$url"}
}
}
])
结果:
{ "_id" : "Neo4j", "url" : [ "http://www.neo4j.com" ] }
{ "_id" : "w3cschool.cc", "url" : [ "http://www.w3cschool.cc" ] }
7、$first:根据资源文档的排序获取第一个文档数据:
>db.mycol.aggregate([
{
$group:{
_id:"by_user",
first_url:{$first:"$url"}
}
}
])
结果:
{ "_id" : "by_user", "first_url" : "http://www.w3cschool.cc" }
8、$last:根据资源文档的排序获取最后一个文档数据:
>db.mycol.aggregate([
{
$group:{
_id:"by_user",
last_url:{$last:"$url"}
}
}
])
结果:
{ "_id" : "by_user", "last_url" : "http://www.neo4j.com" }
9、$substr:对指定的字符串进行对应的切割操作:
>db.books.aggregate([
{
$project:{
_id:0,
isbn:{
prefix:{$substr:["$isbn",1,3]}
}
}
}
])
结果:{ "isbn" : { "prefix" : "001" } }
3、管道的概念:
1、管道在unix和linux中一般用于将当前命令的输出结果作为下一个命令的输入。
ls|grep git
2、MongoDB的聚合管道将MongoDB文档在一个管道处理完毕后将结果传递给下一个管道处理。管道操作是可以重复的。表达式:处理输入文档并输出。表达式是无状态的,只能用于计算当前聚合管道的文档,不能处理其它的文档。
例:
Select cust_id,sum(amount)as total from orders where status= "A"
>db.orders.aggregate([
{
$match:{status:"A"}
},
{
$group:{
cust_id:"$cust_id",
total:{$sum:"$amount"}
}
}
])
4、聚合框架中常用的操作:
1、$project:修改输入文档的结构。可以用来重命名、增加或删除域,也可以用于创建计算结果以及嵌套文档。
2、$match:用于过滤数据,只输出符合条件的文档。$match使用MongoDB的标准查询操作。
3、$limit:用来限制MongoDB聚合管道返回的文档数。
4、$sum:$sum:1相当于count/$sum:"$字段名"相当于sum()
5、$skip:在聚合管道中跳过指定数量的文档,并返回余下的文档。
6、$unwind:将文档中的某一个数组类型字段拆分成多条,每条包含数组中的一个值。
7、$group:将集合中的文档分组,可用于统计结果。
8、$sort:将输入文档排序后输出。
9、$lookup:执行左连接到一个集合(unsharded),必须在同一数据库中。
2、$project:
1、插入测试数据:
db.books.insert(
{
"_id" : 1,
title: "abc123",
isbn: "0001122223334",
author: { last: "zzz", first: "aaa" },
copies: 5
}
)
2、概念:
修改输入文档的结构。可以用来重命名、增加或删除字段(域),也可以用于创建计算结果以及嵌套文档。
例:
>db.books.aggregate([
{
$project:{
_id:0,
title:1,
author:1
}
}
])
结果:
{ "title" : "abc123", "author" : { "last" : "zzz", "first" : "aaa" } }
3、输出嵌入式文档中的field:
>db.books.aggregate([
{
$project:{
_id:0,
title:1,
"author.last":1
}
}
])
结果:
{ "title" : "abc123", "author" : { "last" : "zzz" } }
4、改变数据结构:
>db.books.aggregate([
{
$project:{
_id:0,
title:1,
"lastName":"$author.last"
}
}
])
结果:
{ "title" : "abc123", "lastName" : "zzz" }
5、计算Fields:
利用 $project 新增字段 isbn, lastName, and copiesSold:
>db.books.aggregate([
{
$project:{
title:1,
isbn:{
prefix:{$substr:["$isbn",1,3]},
},
lastName:"$author.last",
copiesSold:"$copies"
}
}
])
3、$match:
1、插入测试数据:
db.articles.insert([
{ "_id" : 1, "author" : "dave", "score" : 80, "views" : 100 },
{ "_id" : 2, "author" : "dave", "score" : 85, "views" : 521 },
{ "_id" : 3, "author" : "ahn", "score" : 60, "views" : 1000 },
{ "_id" : 4, "author" : "li", "score" : 55, "views" : 5000 },
{ "_id" : 5, "author" : "annT", "score" : 60, "views" : 50 },
{ "_id" : 6, "author" : "li", "score" : 94, "views" : 999 },
{ "_id" : 7, "author" : "ty", "score" : 95, "views" : 1000 }
])
2、match匹配
>db.articles.aggregate([
{
$match:{author:"dave"}
}
])
结果:
{ "_id" : 1, "author" : "dave", "score" : 80, "views" : 100 }
{ "_id" : 2, "author" : "dave", "score" : 85, "views" : 521 }
3、范围条件匹配
例:统计 articles 集合中 score在70~90中间,或者views大于等于1000
>db.articles.find(
{
$or:[
{score:{$gt:70,$lt:90}},//同一个score键,后者覆盖前者
{views:{$gte:1000}}
]
}
)
结果:
{ "_id" : 1, "author" : "dave", "score" : 80, "views" : 100 }
{ "_id" : 2, "author" : "dave", "score" : 85, "views" : 521 }
{ "_id" : 3, "author" : "ahn", "score" : 60, "views" : 1000 }
{ "_id" : 4, "author" : "li", "score" : 55, "views" : 5000 }
{ "_id" : 7, "author" : "ty", "score" : 95, "views" : 1000 }
4、计算count值
>db.articles.count({
$or:[
{score:{$gt:70,$lt:90}},
{views:{$gte:1000}}
]
})
结果:5
5、使用聚合实现上面的两个
select count(*) as count from articles where (score>70 and score<90) or views>=1000
>db.articles.aggregate([
{
$match:{
$or:[
{score:{$gt:70,$lt:90}},
{views:{$gte:1000}}
]
}
},
{
$group:{
_id:null,
count:{$sum:1}
}
}
])
4、$group:
1、插入测试数据:
db.sales.insert([
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "abc", "price" : 10, "quantity" : 2, "date" : ISODate("2014-03-01T08:00:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 2, "item" : "jkl", "price" : 20, "quantity" : 1, "date" : ISODate("2014-03-01T09:00:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 3, "item" : "xyz", "price" : 5, "quantity" : 10, "date" : ISODate("2014-03-15T09:00:00Z") },
{ "_id" : 4, "item" : "xyz", "price" : 5, "quantity" : 20, "date" : ISODate("2014-04-04T11:21:39.736Z") },
{ "_id" : 5, "item" : "abc", "price" : 10, "quantity" : 10, "date" : ISODate("2014-04-04T21:23:13.331Z") }
])
2、Group by Month, Day, and Year
使用 $group 将文档按月、日、年组分组, 计算平均数量以及每个组的文档数:
>db.sales.aggregate([
{
$group:{
_id:{month:{$month:"$date"},day:{$dayOfMonth:"$date"},year:{$year:"$date"}},
averageQuantity:{$avg:"$quantity"},
count:{$sum:1}
}
}
])
结果:
{ "_id" : { "month" : 4, "day" : 4, "year" : 2014 }, "averageQuantity" : 15, "count" : 2 }
{ "_id" : { "month" : 3, "day" : 15, "year" : 2014 }, "averageQuantity" : 10, "count" : 1 }
{ "_id" : { "month" : 3, "day" : 1, "year" : 2014 }, "averageQuantity" : 1.5, "count" : 2 }
3、检索不同的值
>db.sales.aggregate([
{
$group:{_id:"$item"}
}
])
结果:
{ "_id" : "xyz" }
{ "_id" : "jkl" }
{ "_id" : "abc" }
4、透视数据
1、插入测试数据:
db.books.insert([
{ "_id" : 8751, "title" : "The Banquet", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 2 },
{ "_id" : 8752, "title" : "Divine Comedy", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 1 },
{ "_id" : 8645, "title" : "Eclogues", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 2 },
{ "_id" : 7000, "title" : "The Odyssey", "author" : "Homer", "copies" : 10 },
{ "_id" : 7020, "title" : "Iliad", "author" : "Homer", "copies" : 10 },
])
2、Group title by author
>db.books.aggregate([
{
$group:{
_id:"$author",
books:{$push:"$title"}
}
}
])
结果:
{ "_id" : "Homer", "books" : [ "The Odyssey", "Iliad" ] }
{ "_id" : "Dante", "books" : [ "The Banquet", "Divine Comedy", "Eclogues" ] }
3、Group Documents(字段) by author
$$ROOT 系统变量(代表文档自身)
>db.books.aggregate([
{
$group:{
_id:"$author",
books:{$push:"$$ROOT"}
}
}
]).pretty()
结果:
{ "_id" : "Homer",
"books" : [ { "_id" : 7000, "title" : "The Odyssey", "author" : "Homer", "copies" : 10 }, { "_id" : 7020, "title" : "Iliad", "author" : "Homer", "copies" : 10 } ]
}
{ "_id" : "Dante",
"books" : [ { "_id" : 8751, "title" : "The Banquet", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 2 }, { "_id" : 8752, "title" : "Divine Comedy", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 1 }, { "_id" : 8645, "title" : "Eclogues", "author" : "Dante", "copies" : 2 } ]
}
5、$unwind:
1、定义:
将文档中的某一个数组类型字段拆分成多条,每条包含数组中的一个值。
2、两种语法结构
1、指定拆分字段的路径path
{ $unwind: <field path> }
2、指定一个文档格式
{
$unwind:
{
path: <field path>,
includeArrayIndex: <string>,
preserveNullAndEmptyArrays: <boolean>
}
}
3、实例:
插入测试数据:
db.inventory.insert(
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC1", sizes: [ "S", "M", "L"] }
)
使用$unwind进行分组:
>db.inventory.aggregate([
{
$unwind:"$sizes"
}
])
结果:
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC1", "sizes" : "S" }
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC1", "sizes" : "M" }
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC1", "sizes" : "L" }
3、includeArrayIndex and preserveNullAndEmptyArrays:
1、includeArrayIndex:
1、插入测试数据:
db.inventory.insert([
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC", "sizes": [ "S", "M", "L"] },
{ "_id" : 2, "item" : "EFG", "sizes" : [ ] },
{ "_id" : 3, "item" : "IJK", "sizes": "M" },
{ "_id" : 4, "item" : "LMN" },
{ "_id" : 5, "item" : "XYZ", "sizes" : null }
])
2、注意:如果sizes字段不能解析成数组,但又不属于情况(不存在,null,或一个空数组,处理方式:丢弃),$unwind 将视为一个单数组操作
>db.inventory.aggregate([
{
$unwind:"$sizes"
}
])
结果:
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC", "sizes" : "S" }
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC", "sizes" : "M" }
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC", "sizes" : "L" }
{ "_id" : 3, "item" : "IJK", "sizes" : "M" }
3、指定索引号:
>db.inventory.aggregate([
{
$unwind:{path:"$sizes",includeArrayIndex: "arrayIndex" }
}
])
结果:
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC", "sizes" : "S", "arrayIndex" : NumberLong(0) }
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC", "sizes" : "M", "arrayIndex" : NumberLong(1) }
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "ABC", "sizes" : "L", "arrayIndex" : NumberLong(2) }
{ "_id" : 3, "item" : "IJK", "sizes" : "M", "arrayIndex" : null }
注:如果 sizes字段 不能解析成数组,但又不属于情况(不存在,null,或者是空数组)的话,索引值字段为null
2、preserveNullAndEmptyArrays:
1、定义:
数据出现了丢失情况,sizes为不存在,[] 或者null时,数据丢失;$unwind 使用preservenullandemptyarrays选项 可以 输出sizes字段(不存在、null或空数组)的这些文档。
2、语法:
db.inventory.aggregate( [
{ $unwind: { path: "$sizes", preserveNullAndEmptyArrays: true } }
] )
6、$lookup:
1、概念:
执行左连接到一个集合(unsharded),必须在同一个数据库中
2、语法
{
$lookup:
{
from: <collection to join>,
localField: <field from the input documents>,
foreignField: <field from the documents of the "from" collection>,
as: <output array field>
}
}
1、from:右集合,指定在同一数据库中执行连接的集合。此集合不能shared分片。
2、localField:指定左集合(db.collectionname)匹配的字段。如果左集合不包含localField,$lookup 视为null值来匹配。
3、foreignField:指定from集合(右集合)用来匹配的字段。如果集合不包含该字段,$lookup 视为null值来匹配。
4、as:指定要添加到输入文档的新数组字段的名称。新的数组字段包含from集合中匹配的文档。如果在文档中指定的名称已经存在,现有的领域覆盖。
3、实例:
1、插入测试数据:
db.orders.insert([
{ "_id" : 1, "item" : "abc", "price" : 12, "quantity" : 2 },
{ "_id" : 2, "item" : "jkl", "price" : 20, "quantity" : 1 },
{ "_id" : 3 }
])
db.inventory.insert([
{ "_id" : 1, "sku" : "abc", description: "product 1", "instock" : 120 },
{ "_id" : 2, "sku" : "def", description: "product 2", "instock" : 80 },
{ "_id" : 3, "sku" : "ijk", description: "product 3", "instock" : 60 },
{ "_id" : 4, "sku" : "jkl", description: "product 4", "instock" : 70 },
{ "_id" : 5, "sku": null, description: "Incomplete" },
{ "_id" : 6 }
])
2、注意事项:
1、两个集合必须在同一个db。
2、orders是左集合,左连接。
3、item是orders左集合字段。
4、sku是inventory右集合字段。
5、item为null, 左连接, 右集合 sku为null。
3、编写连接:
>db.orders.aggregate([
{
$lookup:
{
from:"inventory",
localField:"item",
foreignField:"sku",
as:"inventroy_docs"
}
}
]).pretty()
结果:
{
"_id" : 1,
"item" : "abc",
"price" : 12,
"quantity" : 2,
"inventroy_docs" : [
{
"_id" : 1,
"sku" : "abc",
"description" : "product 1",
"instock" : 120
}
]
}
{
"_id" : 2,
"item" : "jkl",
"price" : 20,
"quantity" : 1,
"inventroy_docs" : [
{
"_id" : 4,
"sku" : "jkl",
"description" : "product 4",
"instock" : 70
}
]
}
{
"_id" : 3,
"inventroy_docs" : [
{
"_id" : 5,
"sku" : null,
"description" : "Incomplete"
},
{
"_id" : 6
}
]
}