问题:控制访问频率,在访问的时候加上一定的次数限制
基本实现
views.py
class VisitThrottle(object):
def allow_request(self, request, view):
return True # 可以继续访问
# return False # 访问频率太高, 被限制
def wait(self):
pass
可以进一步的升级,限制 10s 内只能访问3次
import time
VISIT_RECORD = {}
class VisitThrottle(object):
'''
10s内只能访问3次
'''
def allow_request(self, request, view):
# 1. 获取用户IP
remote_addr = request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')
ctime = time.time()
if remote_addr not in VISIT_RECORD:
VISIT_RECORD[remote_addr] = [ctime, ]
return True
history = VISIT_RECORD.get(remote_addr)
while history and history[-1] < ctime - 10:
history.pop()
if len(history) < 3:
history.insert(0, ctime)
return True
# return True # 可以继续访问
# return False # 访问频率太高, 被限制
def wait(self):
'''
还需要等待的时间
'''
ctime = time.time()
return 60 - (ctime - self.history[-1])
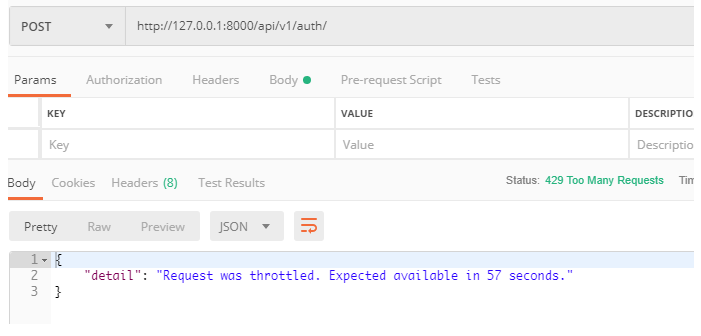
源码流程
和前面一样,也是从 dispatch 开始,到 initial
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# Ensure that the incoming request is permitted
self.perform_authentication(request)
self.check_permissions(request)
# 控制访问频率
self.check_throttles(request)
def check_throttles(self, request):
# get_throttles 里面是一个列表生成式
for throttle in self.get_throttles():
if not throttle.allow_request(request, self):
self.throttled(request, throttle.wait())
def get_throttles(self):
"""
Instantiates and returns the list of throttles that this view uses.
"""
return [throttle() for throttle in self.throttle_classes]
throttle_classes 默认使用配置文件
class APIView(View):
...
throttle_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES
...
可以添加到全局使用,首先在 utils 下新建 throttle.py,将视图文件中的类移至 throttle.py,这里修改了 60s内能访问3次
# throttle.py
import time
VISIT_RECORD = {}
class VisitThrottle(object):
'''
60s内只能访问3次
'''
def __init__(self):
self.history = None
def allow_request(self, request, view):
# 1. 获取用户IP
remote_addr = request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')
ctime = time.time()
if remote_addr not in VISIT_RECORD:
VISIT_RECORD[remote_addr] = [ctime, ]
return True
history = VISIT_RECORD.get(remote_addr)
self.history = history
while history and history[-1] < ctime - 60:
history.pop()
if len(history) < 3:
history.insert(0, ctime)
return True
# return True # 可以继续访问
# return False # 访问频率太高, 被限制
def wait(self):
'''
还需要等待的时间
'''
ctime = time.time()
return 60 - (ctime - self.history[-1])
然后在配置文件 settings.py 中添加路径
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
...
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': ['api.utils.throttle.VisitThrottle']
}
最后将视图中的局部配置删除即可。
回到 check_throttles
def check_throttles(self, request):
for throttle in self.get_throttles():
# throttle.allow_request 为 False,走下一步,throttled 抛出异常,表示访问频率过多
if not throttle.allow_request(request, self):
self.throttled(request, throttle.wait())
def throttled(self, request, wait):
"""
If request is throttled, determine what kind of exception to raise.
"""
raise exceptions.Throttled(wait)
频率的内置类
在自定义频率的时候,为了更加规范,需要继承,并且父类有获取 IP 的方法(可以在 BaseThrottle 中查看),因此这里直接调用父类的方法即可
from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle
import time
VISIT_RECORD = {}
class VisitThrottle(BaseThrottle):
'''
60s内只能访问3次
'''
def __init__(self):
self.history = None
def allow_request(self, request, view):
# 1. 获取用户IP,调用父类的方法
remote_addr = self.get_ident(request)
ctime = time.time()
if remote_addr not in VISIT_RECORD:
VISIT_RECORD[remote_addr] = [ctime, ]
return True
history = VISIT_RECORD.get(remote_addr)
self.history = history
while history and history[-1] < ctime - 60:
history.pop()
if len(history) < 3:
history.insert(0, ctime)
return True
# return True # 可以继续访问
# return False # 访问频率太高, 被限制
def wait(self):
'''
还需要等待的时间
'''
ctime = time.time()
return 60 - (ctime - self.history[-1])
进入 BaseThrottle ,发现在其下方有个 SimpleRateThrottle ,也是继承 BaseThrottle 。首先看 SimpleRateThrottle 的 __init__ 方法
class SimpleRateThrottle(BaseThrottle):
... # 省略的内容
scope = None
THROTTLE_RATES = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES
def __init__(self):
if not getattr(self, 'rate', None):
# 这里执行了 get_rate 方法
self.rate = self.get_rate()
self.num_requests, self.duration = self.parse_rate(self.rate)
def get_rate(self):
"""
Determine the string representation of the allowed request rate.
"""
if not getattr(self, 'scope', None):
msg = ("You must set either `.scope` or `.rate` for '%s' throttle" %
self.__class__.__name__)
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg)
try:
# scope实际上是一个字典的 key,这里在 THROTTLE_RATES 中取值
# 在上面的代码中看到 THROTTLE_RATES 是一个配置项,获取用户自定义的配置
return self.THROTTLE_RATES[self.scope]
except KeyError:
msg = "No default throttle rate set for '%s' scope" % self.scope
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg)
至此,就可以在配置文件中写一个 60s内能访问3次 的程序,让它自动完成,无需自定义写
throttle.py
class VisitThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = "xi" # scope作为key使用
settings.py
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
... # 省略
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': ['api.utils.throttle.VisitThrottle'],
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES' : {
'xi': '3/m' # m是分钟,每分钟访问3次
}
}
这时,配置了访问次数,就会在 return self.THROTTLE_RATES[self.scope] 中获取到,返回给 get_rate 方法,然后 __init__ 中的 rate 拿到的就是 3/m
class SimpleRateThrottle(BaseThrottle):
... # 省略的内容
scope = None
THROTTLE_RATES = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES
def __init__(self):
if not getattr(self, 'rate', None):
# '3/m'
self.rate = self.get_rate()
# 将字符串 '3/m' 当做参数传递给 parse_rate
# 走完 parse_rate,num_requests代表3次,duration代表60s
self.num_requests, self.duration = self.parse_rate(self.rate)
.... # 省略
def parse_rate(self, rate):
"""
Given the request rate string, return a two tuple of:
<allowed number of requests>, <period of time in seconds>
"""
# rate就是 '3/m'
if rate is None:
return (None, None)
num, period = rate.split('/')
num_requests = int(num)
duration = {'s': 1, 'm': 60, 'h': 3600, 'd': 86400}[period[0]]
return (num_requests, duration)
此时,构造函数走完,接着查看 allow_request
def allow_request(self, request, view):
if self.rate is None:
return True
# 内置提供的访问记录放在了缓存中,通过 get_cache_key 实现
self.key = self.get_cache_key(request, view)
if self.key is None:
return True
self.history = self.cache.get(self.key, [])
self.now = self.timer()
# 来到 get_cache_key,源码上并没有写什么,这表示是让我们自己写的
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
raise NotImplementedError('.get_cache_key() must be overridden')
# get_cache_key 实际上是表示能够唯一标识的方法,所以返回值可以是获取IP,用来表示谁的访问记录
# throttle.py
class VisitThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = "xi"
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
return self.get_ident(request) # 获取IP
回到 allow_request
def allow_request(self, request, view):
if self.rate is None:
return True
# 内置提供的访问记录放在了缓存中,通过 get_cache_key 实现
self.key = self.get_cache_key(request, view)
if self.key is None:
return True
# 去缓存中取出所有记录
# cache = default_cache,是django内置的缓存
self.history = self.cache.get(self.key, [])
self.now = self.timer() # timer() = time.time(),获取当前时间
# Drop any requests from the history which have now passed the
# throttle duration
# 这里与上面自定义的相同
while self.history and self.history[-1] <= self.now - self.duration:
self.history.pop()
if len(self.history) >= self.num_requests:
return self.throttle_failure()
return self.throttle_success()
def throttle_success(self):
"""
Inserts the current request's timestamp along with the key
into the cache.
"""
# 如果成功,加到历史记录中
self.history.insert(0, self.now)
self.cache.set(self.key, self.history, self.duration)
return True
def throttle_failure(self):
"""
Called when a request to the API has failed due to throttling.
"""
return False
def wait(self):
"""
Returns the recommended next request time in seconds.
"""
if self.history:
remaining_duration = self.duration - (self.now - self.history[-1])
else:
remaining_duration = self.duration
available_requests = self.num_requests - len(self.history) + 1
if available_requests <= 0:
return None
return remaining_duration / float(available_requests)
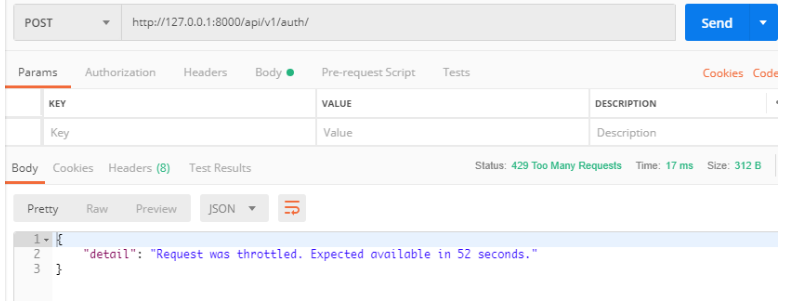
照样是前三次可以访问,后面再访问需要等一分钟,这是对匿名用户的控制
也可以对登录的用户进行控制,但在全局的设置中,不能既有匿名的,还有登录的。这时,就可以将登录用户的访问控制设为全局,匿名用户使用局部的设置。
settings.py
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': ['api.utils.auth.FirstAuthentication', 'api.utils.auth.Authentication'],
# 'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': ['api.utils.auth.FirstAuthentication', ],
'UNAUTHENTICATED_USER': None,
'UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN': None,
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': ['api.utils.permission.SVIPPermission'],
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES': ['api.utils.throttle.UserThrottle'], # 登录用户
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES' : {
'xi': '3/m',
'xiUser': '10/m'
}
}
throttle.py
# 匿名用户
class VisitThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = "xi"
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
return self.get_ident(request)
# 登录用户
class UserThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = "xiUser"
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
return request.user.username
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render, HttpResponse
from django.http import JsonResponse
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from api import models
from api.utils.permission import SVIPPermission, MyPermission
from api.utils.throttle import VisitThrottle
ORDER_DICT = {
1: {
'name': 'qiu',
'age': 18,
'gender': '男',
'content': '...'
},
2: {
'name': 'xi',
'age': 19,
'gender': '男',
'content': '.....'
}
}
def md5(user):
import hashlib
import time
ctime = str(time.time())
m = hashlib.md5(bytes(user, encoding='utf-8'))
m.update(bytes(ctime, encoding='utf-8'))
return m.hexdigest()
class AuthView(APIView):
authentication_classes = []
permission_classes = []
throttle_classes = [VisitThrottle] # 为匿名用户设置频率控制
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
ret = {'code': 1000, 'msg': None}
try:
user = request._request.POST.get('username')
pwd = request._request.POST.get('password')
obj = models.UerInfo.objects.filter(username=user, password=pwd).first()
if not obj:
ret['code'] = 1001
ret['msg'] = '用户名或密码错误'
# 为登录用户创建token
else:
token = md5(user)
# 存在就更新, 不存在就创建
models.UserToken.objects.update_or_create(user=obj, defaults={'token': token})
ret['token'] = token
except Exception as e:
ret['code'] = 1002
ret['msg'] = '请求异常'
return JsonResponse(ret)
class OrderView(APIView):
'''
订单相关业务(只有SVIP用户有权限)
'''
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
ret = {'code': 1000, 'msg': None, 'data': None}
try:
ret['data'] = ORDER_DICT
except Exception as e:
pass
return JsonResponse(ret)
class UserInfoView(APIView):
'''
用户中心(普通用户、VIP有权限)
'''
permission_classes = [MyPermission]
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return HttpResponse('用户信息')
总结
使用
-
类,继承
BaseThrottle,实现allow_request、wait -
类,继承
SimpleRateThrottle,实现get_cache_key、scope = "xi"(配置文件中的key) -
局部:
throttle_classes = [VisitThrottle] -
全局:配置
settings.py