[LeetCode] Subsets 子集合
非递归法:
以数组长度作为划分,从长度1开始,逐个处理每个元素.
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>()); for(int num: nums) { int n = res.size(); for(int i = 0;i<n;i++) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(res.get(i)); list.add(num); res.add(list); } } return res; } }
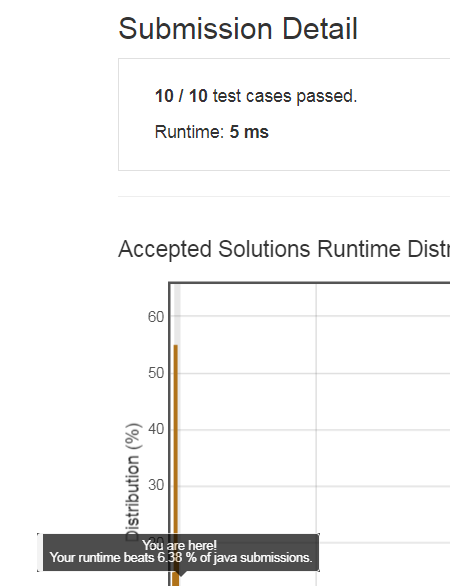
递归的解法:
相当于一种深度优先搜索,参见网友JustDoIt的博客,由于原集合每一个数字只有两种状态,要么存在,要么不存在,那么在构造子集时就有选择和不选择两种情况,所以可以构造一棵二叉树,左子树表示选择该层处理的节点,右子树表示不选择,最终的叶节点就是所有子集合,树的结构如下:
[]
/
/
/
[1] []
/ /
/ /
[1 2] [1] [2] []
/ / / /
[1 2 3] [1 2] [1 3] [1] [2 3] [2] [3] []
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); dfs(res,list,nums,0); return res; } public void dfs(List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> list, int[] nums, int x) { if(x==nums.length) { res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(list)); return; } dfs(res,list,nums,x+1); list.add(nums[x]); dfs(res,list,nums,x+1); list.remove(list.size()-1); } }
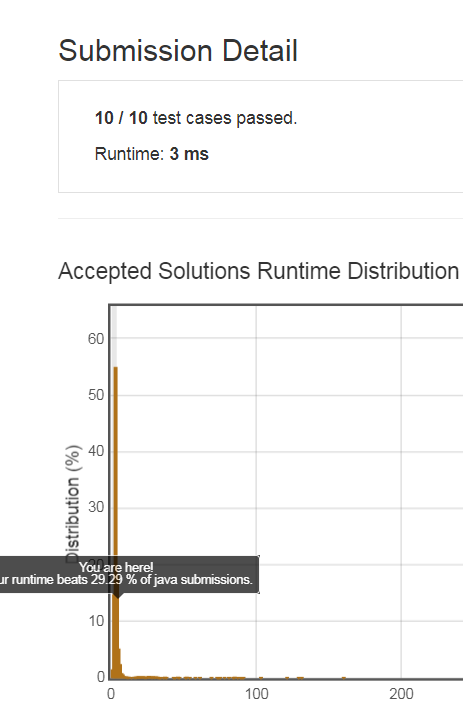
最后我们再来看一种解法,这种解法是CareerCup书上给的一种解法,想法也比较巧妙,把数组中所有的数分配一个状态,true表示这个数在子集中出现,false表示在子集中不出现,那么对于一个长度为n的数组,每个数字都有出现与不出现两种情况,所以共有2n中情况,那么我们把每种情况都转换出来就是子集了,我们还是用题目中的例子, [1 2 3]这个数组共有8个子集,每个子集的序号的二进制表示,把是1的位对应原数组中的数字取出来就是一个子集,八种情况都取出来就是所有的子集了,参见代码如下:
| 1 | 2 | 3 | Subset | |
| 0 | F | F | F | [] |
| 1 | F | F | T | 3 |
| 2 | F | T | F | 2 |
| 3 | F | T | T | 23 |
| 4 | T | F | F | 1 |
| 5 | T | F | T | 13 |
| 6 | T | T | F | 12 |
| 7 | T | T | T | 123 |
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); int mx = 1<<nums.length; for(int i =0;i<mx;i++) { List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); changeToSet(list,i,nums); res.add(list); } return res; } public void changeToSet(List<Integer> list, int k,int[] nums) { int x =0; for(int i = k;i>0;i>>=1) { if((i&1)==1) list.add(nums[x]); x++; } } }
有重复项时,上一项与这一项相同时,不含有上一项的分支就不用进行下去了
class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) { List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); Arrays.sort(nums); dfs(0,nums,res,list,false); return res; } public void dfs(int x,int[] nums, List<List<Integer>> res, List<Integer> list, boolean has) { if(x == nums.length) { res.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(list)); return; } dfs(x+1,nums,res,list,false); if(x!=0 && nums[x]==nums[x-1] && !has) return; list.add(nums[x]); dfs(x+1,nums,res,list,true); list.remove(list.size()-1); } }
