转载请注明出处!
一、概念
平衡二叉树是一种特殊的二叉搜索树,关于二叉搜索树,请查看上一篇博客二叉搜索树的java实现,那它有什么特别的地方呢,了解二叉搜索树的基本都清楚,在按顺序向插入二叉搜索树中插入值,最后会形成一个类似链表形式的树,而我们设计二叉搜索树的初衷,显然是看中了它的查找速度与它的高度成正比,如果每一颗二叉树都像链表一样,那就没什么意思了,所以就设计出来了平衡二叉树,相对于二叉搜索树,平衡二叉树的一个特点就是,在该树中,任意一个节点,它的左右子树的差的绝对值一定小于2。关于它的演变什么的,请自行网上搜索答案。在本文中,为了方便,也是采用了int型值插入。
二、平衡二叉树的构建
它的类相对于二叉搜索树也并没有什么特殊之处,不做过多讲解,直接上代码
1 static class Node{ 2 Node parent; 3 Node leftChild; 4 Node rightChild; 5 int val; 6 public Node(Node parent, Node leftChild, Node rightChild,int val) { 7 super(); 8 this.parent = parent; 9 this.leftChild = leftChild; 10 this.rightChild = rightChild; 11 this.val = val; 12 } 13 14 public Node(int val){ 15 this(null,null,null,val); 16 } 17 18 public Node(Node node,int val){ 19 this(node,null,null,val); 20 } 21 22 }
三、增加
在谈及平衡二叉树的增加,先来考虑什么样的情况会打破这个平衡,假如A树已经是一颗平衡二叉树,但现在要往里面插入一个元素,有这两种结果,一、平衡未打破,这种肯定皆大欢喜,二、平衡被打破了。那一般要考虑三个问题
一、平衡被打破之前是什么状态?
二、被打破之后又是一个什么样的状态?
三、平衡被打破了,该怎么调整,使它又重新成为一个平衡二叉树呢?
这里截取打破平衡后左子树的高度比右子树高度高2的所有可能情况(若右子树高,情况一样,这里只选取一种分析),下面的图,只是代表着那个被打破平衡的点的子树(被打破平衡的点就是这个节点的左右子树高度差的绝对值大于或等于2,当然,这里只能等于2),不代表整棵树。
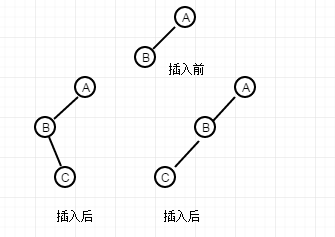
这是第一种情况,其中A节点和B节点只是平衡二叉树的某一个子集合,要想打破这个平衡,那么插入的节点C必然在B的子节点上,即左右子节点,调整后面一起说
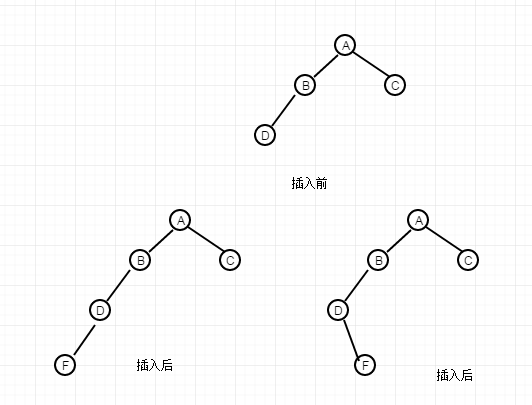
这是第二种情况,其中A、B、C、D四个节点也是该平衡树的某个子集合,同样要打破这个平衡,那么,插入的节点F必然在D节点上。
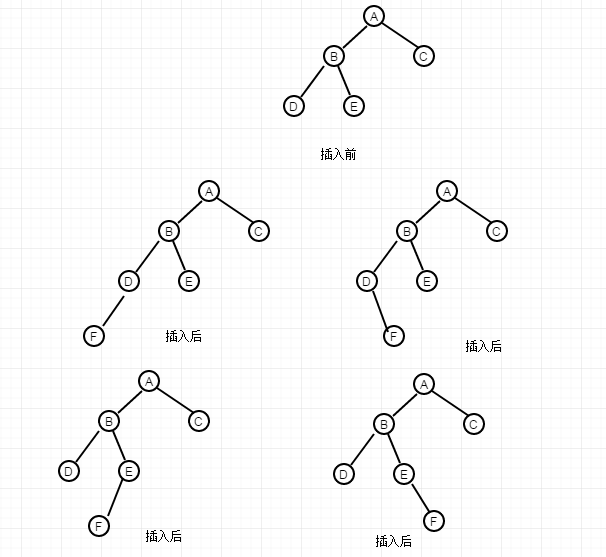
第三种情况,其中A、B、C、D、E五个节点也是该平衡树的某个子集合,同样要打破这个平衡,那么,插入的节点F必然在D节点和E节点上。
(我个人所想到的所有可能情况,若还有其他情况,请在评论中指出,谢谢!)
或许细心的人已经发现,第二种和第三种情况就是由第一种情况变化而来的,如分别在A节点的右孩子和B节点的右孩子上添加子节点,就变化成了第二种和第三种情况(这里并不是说第一种情况直接加上这些节点就变成了第二或第三种情况)
这里只详细分析第一种情况
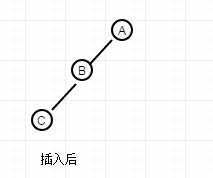
要使A节点的左右子树差的绝对值小于2,此时只需将B节点来替换A节点,A节点成为B节点的右孩子。若A节点有父节点,则A的父节点的子节点要去指向B节点,而A节点的父节点要去指向B节点,先看这段代码吧。这段操作也就是右旋操作
1 /** 2 * 在这种情况,因为A和B节点均没有右孩子节点, 3 * 所以不用考虑太多 4 * @param aNode 代表A节点 5 * @return 6 */ 7 public Node leftRotation(Node aNode){ 8 if(aNode != null){ 9 Node bNode = aNode.leftChild;// 先用一个变量来存储B节点 10 bNode.parent = aNode.parent;// 重新分配A节点的父节点指向 11 //判断A节点的父节点是否存在 12 if(aNode.parent != null){// A节点不是根节点 13 /** 14 * 分两种情况 15 * 1、A节点位于其父节点左边,则B节点也要位于左边 16 * 2、A节点位于其父节点右边,则B节点也要位于右边 17 */ 18 if(aNode.parent.leftChild == aNode){ 19 aNode.parent.leftChild = bNode; 20 }else{ 21 aNode.parent.rightChild = bNode; 22 } 23 }else{// 说明A节点是根节点,直接将B节点置为根节点 24 this.root = bNode; 25 } 26 bNode.rightChild = aNode;// 将B节点的右孩子置为A节点 27 aNode.parent = bNode;// 将A节点的父节点置为B节点 28 return bNode;// 返回旋转的节点 29 } 30 return null; 31 }
而对于第一种情况的这个图
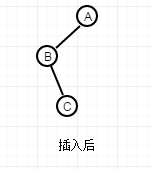
涉及的情况又不一样,假如按照上面那种情况一样去右旋,那么得到的图是或许是这样的
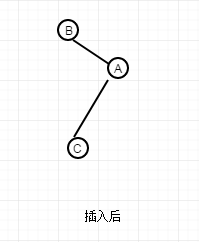
这好像又不平衡,似乎和原图是一个对称的。不太行的通。如果将C节点替换B节点位置,而B节点成为C节点的左节点,这样就成为了上一段代码的那种情况。这段B节点替换成为C节点的代码如下,这里操作也就是,先左旋后右旋
1 /** 2 * 3 * @param bNode 代表B节点 4 * @return 5 */ 6 public Node rightRotation(Node bNode){ 7 if(bNode != null){ 8 Node cNode = bNode.rightChild;// 用临时变量存储C节点 9 cNode.parent = bNode.parent; 10 // 这里因为bNode节点父节点存在,所以不需要判断。加判断也行, 11 if(bNode.parent.rightChild == bNode){ 12 bNode.parent.rightChild = cNode; 13 }else{ 14 bNode.parent.leftChild = cNode; 15 } 16 cNode.leftChild = bNode; 17 bNode.parent = cNode; 18 return cNode; 19 } 20 return null; 21 }
代码逻辑和上一段代码一样。变换过来后,再按照上面的右旋再操作一次,就变成了平衡树了。
对于第二种和第三种情况的分析和第一种类似,再把代码修改一下,适合三种情况,即可。完整代码如下。
1 public Node rightRotation(Node node){ 2 if(node != null){ 3 Node leftChild = node.leftChild;// 用变量存储node节点的左子节点 4 node.leftChild = leftChild.rightChild;// 将leftChild节点的右子节点赋值给node节点的左节点 5 if(leftChild.rightChild != null){// 如果leftChild的右节点存在,则需将该右节点的父节点指给node节点 6 leftChild.rightChild.parent = node; 7 } 8 leftChild.parent = node.parent; 9 if(node.parent == null){// 即表明node节点为根节点 10 this.root = leftChild; 11 }else if(node.parent.rightChild == node){// 即node节点在它原父节点的右子树中 12 node.parent.rightChild = leftChild; 13 }else if(node.parent.leftChild == node){ 14 node.parent.leftChild = leftChild; 15 } 16 leftChild.rightChild = node; 17 node.parent = leftChild; 18 return leftChild; 19 } 20 return null; 21 }
以上是右旋代码。逻辑参考以上分析
1 public Node leftRotation(Node node){ 2 if(node != null){ 3 Node rightChild = node.rightChild; 4 node.rightChild = rightChild.leftChild; 5 if(rightChild.leftChild != null){ 6 rightChild.leftChild.parent = node; 7 } 8 rightChild.parent = node.parent; 9 if(node.parent == null){ 10 this.root = rightChild; 11 }else if(node.parent.rightChild == node){ 12 node.parent.rightChild = rightChild; 13 }else if(node.parent.leftChild == node){ 14 node.parent.leftChild = rightChild; 15 } 16 rightChild.leftChild = node; 17 node.parent = rightChild; 18 19 } 20 return null; 21 }
至此,打破平衡后,经过一系列操作达到平衡,由以上可知,大致有以下四种操作情况
一、只需要经过一次右旋即可达到平衡
二、只需要经过一次左旋即可达到平衡
三、需先经过左旋,再经过右旋也可达到平衡
四、需先经过右旋,再经过左旋也可达到平衡
那问题就来了,怎么判断被打破的平衡要经历哪种操作才能达到平衡呢?
经过了解,这四种情况,还可大致分为两大类,如下(以下的A节点就是被打破平衡的那个节点)
第一大类,A节点的左子树高度比右子树高度高2,最终需要经过右旋操作(可能需要先左后右)
第二大类,A节点的左子树高度比右子树高度低2,最终需要经过左旋操作(可能需要先右后左)
所以很容易想到,在插入节点后,判断插入的节点是在A节点的左子树还是右子树(因为插入之前已经是平衡二叉树)再决定采用哪个大类操作,在大类操作里再去细分要不要经历两步操作。
插入元素代码如下
1 public boolean put(int val){ 2 return putVal(root,val); 3 } 4 private boolean putVal(Node node,int val){ 5 if(node == null){// 初始化根节点 6 node = new Node(val); 7 root = node; 8 size++; 9 return true; 10 } 11 Node temp = node; 12 Node p; 13 int t; 14 /** 15 * 通过do while循环迭代获取最佳节点, 16 */ 17 do{ 18 p = temp; 19 t = temp.val-val; 20 if(t > 0){ 21 temp = temp.leftChild; 22 }else if(t < 0){ 23 temp = temp.rightChild; 24 }else{ 25 temp.val = val; 26 return false; 27 } 28 }while(temp != null); 29 Node newNode = new Node(p, val); 30 if(t > 0){ 31 p.leftChild = newNode; 32 }else if(t < 0){ 33 p.rightChild = newNode; 34 } 35 rebuild(p);// 使二叉树平衡的方法 36 size++; 37 return true; 38 }
这部分代码,详细分析可看上一篇博客,二叉搜索树的java实现。继续看rebuild方法的代码,这段代码采用了从插入节点父节点进行向上回溯去查找失去平衡的节点
1 private void rebuild(Node p){ 2 while(p != null){ 3 if(calcNodeBalanceValue(p) == 2){// 说明左子树高,需要右旋或者 先左旋后右旋 4 fixAfterInsertion(p,LEFT);// 调整操作 5 }else if(calcNodeBalanceValue(p) == -2){ 6 fixAfterInsertion(p,RIGHT); 7 } 8 p = p.parent; 9 } 10 }
那个calcNodeBalanceValue方法就是计算该参数的左右子树高度之差的方法。fixAfterInsertion方法是根据不同类型进行不同调整的方法,代码如下
1 private int calcNodeBalanceValue(Node node){ 2 if(node != null){ 3 return getHeightByNode(node); 4 } 5 return 0; 6 } 7 // 计算node节点的高度 8 public int getChildDepth(Node node){ 9 if(node == null){ 10 return 0; 11 } 12 return 1+Math.max(getChildDepth(node.leftChild),getChildDepth(node.rightChild)); 13 } 14 public int getHeightByNode(Node node){ 15 if(node == null){ 16 return 0; 17 } 18 return getChildDepth(node.leftChild)-getChildDepth(node.rightChild); 19 }
1 /** 2 * 调整树结构 ,该方法有瑕疵,本想直接修改,但为了起参考作用就留在这,正解见评论。修改与2019-08-03 12:13 3 * @param p 4 * @param type 5 */ 6 private void fixAfterInsertion(Node p, int type) { 7 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 8 if(type == LEFT){ 9 final Node leftChild = p.leftChild;
10 if(leftChild.leftChild != null){//右旋 11 rightRotation(p); 12 }else if(leftChild.rightChild != null){// 先左旋后右旋 13 leftRotation(leftChild); 14 rightRotation(p); 15 } 16 }else{ 17 final Node rightChild = p.rightChild; 18 if(rightChild.rightChild != null){// 左旋 19 leftRotation(p); 20 }else if(rightChild.leftChild != null){// 先右旋,后左旋 21 rightRotation(p); 22 leftRotation(rightChild); 23 } 24 } 25 }
在对每个大类再具体分析,我这里采用了 左右子树是否为空的判断来决定它是单旋还是双旋,我思考的原因:如果代码执行到了这个方法,那么肯定平衡被打破了,就暂且拿第一个大类来说 ,A的左子树高度要比右子树高2,意味平衡被打破了,再去结合上面分析的第一种情况,当插入元素后树结构是以下结构,那肯定是单旋
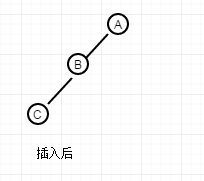
如果是以下结构,那肯定是这种结构,由上面分析,这种结构必须的双旋。
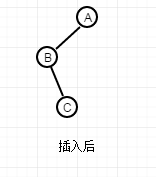
除了这两种情况,并没有其他旋转情况了。所以,我这里是根据插入的节点是位于B节点的左右方来决定是单旋还是双旋,(在这里,不保证结论完全正确,若有错误,还望大家指正)。
以上就是平衡二叉树的插入操作,以及后续的调整操作代码
四、删除
先来上一段二叉树的删除代码,关于具体的删除逻辑,请查看上一篇博客,这里只讨论重调整操作
1 p); 2 }else if(rightChild.leftChild != null){// 先右旋,后左旋 3 rightRotation(p); 4 leftRotation(rightChild); 5 } 6 } 7 } 8 private int calcNodeBalanceValue(Node node){ 9 if(node != null){ 10 return getHeightByNode(node); 11 } 12 return 0; 13 } 14 public void print(){ 15 print(this.root); 16 } 17 public Node getNode(int val){ 18 Node temp = root; 19 int t; 20 do{ 21 t = temp.val-val; 22 if(t > 0){ 23 temp = temp.leftChild; 24 }else if(t < 0){ 25 temp = temp.rightChild; 26 }else{ 27 return temp; 28 } 29 }while(temp != null); 30 return null; 31 } 32 public boolean delete(int val){ 33 Node node = getNode(val); 34 if(node == null){ 35 return false; 36 } 37 boolean flag = false; 38 Node p = null; 39 Node parent = node.parent; 40 Node leftChild = node.leftChild; 41 Node rightChild = node.rightChild; 42 //以下所有父节点为空的情况,则表明删除的节点是根节点 43 if(leftChild == null && rightChild == null){//没有子节点 44 if(parent != null){ 45 if(parent.leftChild == node){ 46 parent.leftChild = null; 47 }else if(parent.rightChild == node){ 48 parent.rightChild = null; 49 } 50 }else{//不存在父节点,则表明删除节点为根节点 51 root = null; 52 } 53 p = parent; 54 node = null; 55 flag = true; 56 }else if(leftChild == null && rightChild != null){// 只有右节点 57 if(parent != null && parent.val > val){// 存在父节点,且node位置为父节点的左边 58 parent.leftChild = rightChild; 59 }else if(parent != null && parent.val < val){// 存在父节点,且node位置为父节点的右边 60 parent.rightChild = rightChild; 61 }else{ 62 root = rightChild; 63 } 64 p = parent; 65 node = null; 66 flag = true; 67 }else if(leftChild != null && rightChild == null){// 只有左节点 68 if(parent != null && parent.val > val){// 存在父节点,且node位置为父节点的左边 69 parent.leftChild = leftChild; 70 }else if(parent != null && parent.val < val){// 存在父节点,且node位置为父节点的右边 71 parent.rightChild = leftChild; 72 }else{ 73 root = leftChild; 74 } 75 p = parent; 76 flag = true; 77 }else if(leftChild != null && rightChild != null){// 两个子节点都存在 78 Node successor = getSuccessor(node);// 这种情况,一定存在后继节点 79 int temp = successor.val; 80 boolean delete = delete(temp); 81 if(delete){ 82 node.val = temp; 83 } 84 p = successor; 85 successor = null; 86 flag = true; 87 } 88 if(flag){ 89 rebuild(p); 90 } 91 return flag; 92 } 93 94 /** 95 * 找到node节点的后继节点 96 * 1、先判断该节点有没有右子树,如果有,则从右节点的左子树中寻找后继节点,没有则进行下一步 97 * 2、查找该节点的父节点,若该父节点的右节点等于该节点,则继续寻找父节点, 98 * 直至父节点为Null或找到不等于该节点的右节点。 99 * 理由,后继节点一定比该节点大,若存在右子树,则后继节点一定存在右子树中,这是第一步的理由 100 * 若不存在右子树,则也可能存在该节点的某个祖父节点(即该节点的父节点,或更上层父节点)的右子树中, 101 * 对其迭代查找,若有,则返回该节点,没有则返回null 102 * @param node 103 * @return 104 */ 105 private Node getSuccessor(Node node){ 106 if(node.rightChild != null){ 107 Node rightChild = node.rightChild; 108 while(rightChild.leftChild != null){ 109 rightChild = rightChild.leftChild; 110 } 111 return rightChild; 112 } 113 Node parent = node.parent; 114 while(parent != null && (node == parent.rightChild)){ 115 node = parent; 116 parent = parent.parent; 117 } 118 return parent; 119 }
这里也采用了插入操作的调整平衡代码。不做过多分析
五、遍历
这里采用了两种遍历,一种是中序遍历打印数据,第二种是层次遍历,以便查看调整后的数据是否正确
中序遍历
1 public void print(){ 2 print(this.root); 3 } 4 private void print(Node node){ 5 if(node != null){ 6 print(node.leftChild); 7 System.out.println(node.val+","); 8 print(node.rightChild); 9 } 10 }
层次遍历
1 /** 2 * 层次遍历 3 */ 4 public void printLeft(){ 5 if(this.root == null){ 6 return; 7 } 8 Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>(); 9 Node temp = null; 10 queue.add(root); 11 while(!queue.isEmpty()){ 12 temp = queue.poll(); 13 System.out.print("节点值:"+temp.val+",平衡值:"+calcNodeBalanceValue(temp)+" "); 14 if(temp.leftChild != null){ 15 queue.add(temp.leftChild); 16 } 17 if(temp.rightChild != null){ 18 queue.add(temp.rightChild); 19 } 20 } 21 }
六、测试
测试代码如下
1 @Test 2 public void test_balanceTree(){ 3 BalanceBinaryTree bbt = new BalanceBinaryTree(); 4 bbt.put(10); 5 bbt.put(9); 6 bbt.put(11); 7 bbt.put(7); 8 bbt.put(12); 9 bbt.put(8); 10 bbt.put(38); 11 bbt.put(24); 12 bbt.put(17); 13 bbt.put(4); 14 bbt.put(3); 15 System.out.println("----删除前的层次遍历-----"); 16 bbt.printLeft(); 17 System.out.println("------中序遍历---------"); 18 bbt.print(); 19 System.out.println(); 20 bbt.delete(9); 21 System.out.println("----删除后的层次遍历-----"); 22 bbt.printLeft(); 23 System.out.println("------中序遍历---------"); 24 bbt.print(); 25 }
运行结果
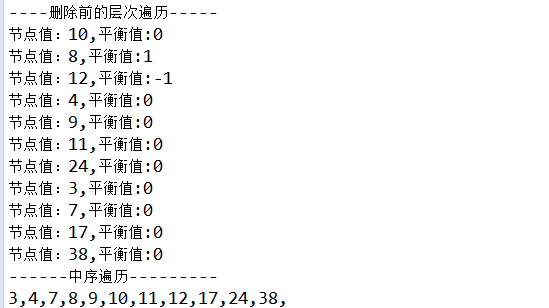
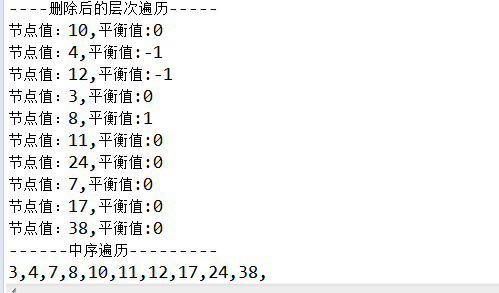
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------分界线----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
以上就是我对平衡二叉树的了解,若有不足或错误之处,还望指正,谢谢!