- 框架与框架要解决的核心问题
- 我们做房子卖给用户住,用于用户自己安装门窗和空调,我做的房子就是框架,用户需要使用我的框架,把门窗插入进我提供的框架中。框架与工具类有区别,工具类被用户的类调用,而框架则是调用用户提供的类。
- 框架要解决的核心问题
- 我在写框架(房子)时,你这个用户可能还在上小学,还不会写程序呢?我写的框架程序怎样能调用到你以后写的类呢?
Class.forName(classNameStr).getMethod(methodName).invoke(obj,Class)
- 因为在写程序时无法知道要被调用的类名,所以,在程序中无法直接new某个类的实例对象了,而要用反射方式来做。
- 综合案例
- 先直接用new语句创建ArrayList和HashSet的实例对象,演示用eclipse自动生成ReflectPoint类的equals和hashCode方法,
比较两个集合的运行结果差异。
- 然后改为采用配置文件加载反射的方式创建ArrayList和HashSet的实例对象,比较观察运行结果差异。
- 引入了eclpse对资源文件的管理方式的讲解。
- Properties类
- Properties对象就等效于一个HashMap,内存里装的是<key,value><key,value><key,value>
- 在HashMap的基础上扩展了一些功能,
- ①可以把内存里的键值对存到硬盘里面
- ② 可以在初始化时把文件里的键值对加载进properties对象里来。
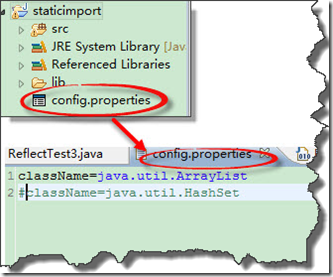
package com.itcast.day1; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.ArrayList; public class ReflectTest3 { public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { InputStream ips = new FileInputStream("config.properties"); Properties props=new Properties(); props.load(ips);//1 硬盘加载到内存 ,2从内存中加载到props对象中 ips.close();//关闭是指释放ips加载的资源,ips对象不会随着close方法的执行而被JVM回收如果不关闭,则有小小的内存泄露 。 String className= props.getProperty("className"); System.out.println(className); Collection collections=(Collection)Class.forName(className).newInstance(); ReflectPoint pt1=new ReflectPoint(3,3); collections.add(pt1);//放入 } }
config.properties文件放在哪里呢?
相对当前工作路径,在实际项目中,几乎没有这么干的!
实际项目一定要用绝对路径,但绝对路径不是硬编码!
实际项目中应当:
config.properties文件在硬盘上的存放位置由用户指定,用户可配置“主目录”/config.properties。
getRealPath();// 主目录/config.properties
- 类加载器--ClassLoader
类加载器通常用来加载 *.class文件,既然 .class文件都可以加载进来(强大!),那么加载其他配置文件,岂不是小菜一碟!就看愿不愿意加载了。
RefectTest3.class.geteClassLoader().getResourceAsStream()//适用于只读配置文件时
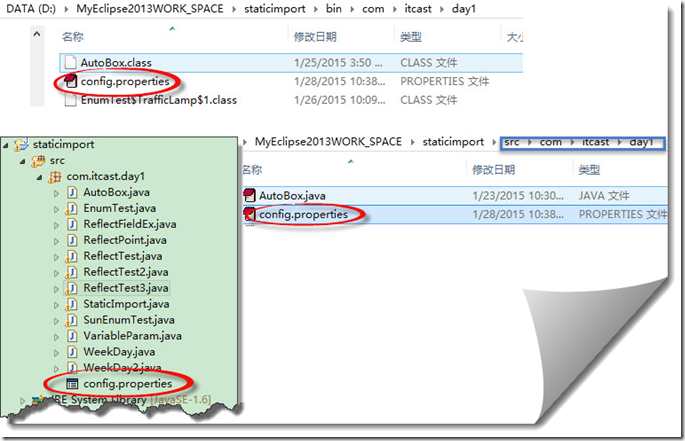
框架的配置文件都放在类路径下,原因是框架内部读取配置文件都是在采用类加载器加载方式,而类加载器加载文件时会从类路径下查找。
- 类加载器加载config.properties其中config.propertis存放在类路径下
package com.itcast.day1; import java.io.File; import java.io.InputStream; import java.net.URL; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Properties; public class ReflectTest3 { public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { //在类路径下找文件,转换成输入流 InputStream ips=null; // ips=ReflectTest3.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream // ("com"+File.separator+"itcast"+File.separator+"day1"+File.separator+"config.properties"); // ips=ReflectTest3.class.getResourceAsStream("config.properties");//在本包下找 //Class提供了一种更简洁的方式来加载配置文件(和class.newInstance方法省略了得到构造器类似),在类路径的根目录下开始找 ips=ReflectTest3.class.getResourceAsStream ("/"+"com"+File.separator+"itcast"+File.separator+"day1"+File.separator+"config.properties"); Properties props=new Properties(); props.load(ips);//1 硬盘加载到内存 ,2从内存中加载到props对象中 ips.close();//关闭是指释放ips加载的资源,ips对象不会随着close方法的执行而被JVM回收如果不关闭,则有小小的内存泄露 。 String className= props.getProperty("className"); System.out.println(className); Collection collections=(Collection)Class.forName(className).newInstance(); ReflectPoint pt1=new ReflectPoint(3,3); collections.add(pt1);//放入 System.out.println(collections.size()); } }