- CSS 到 DOM的抽象
- 通过操作 CSS 对应的 DOM对象来更新CSS样式
- 换肤操作
- 如何获取实际的样式(不仅有行内,更有页面和外联样式表中定义的样式)
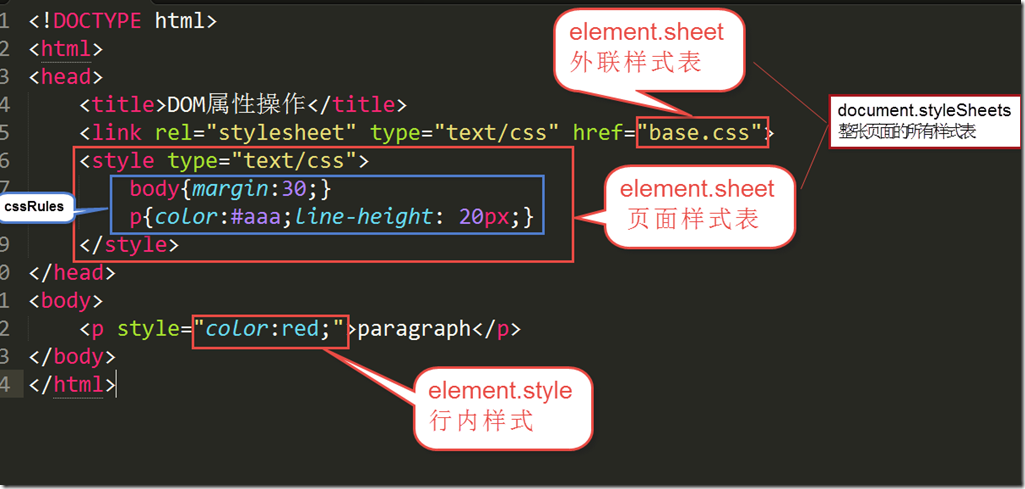
样式表分为三类: 外联,页面,行内
内部样式表
<style type="text/css"> body{margin:30;} p{color:#aaa;line-height: 20px;} </style>
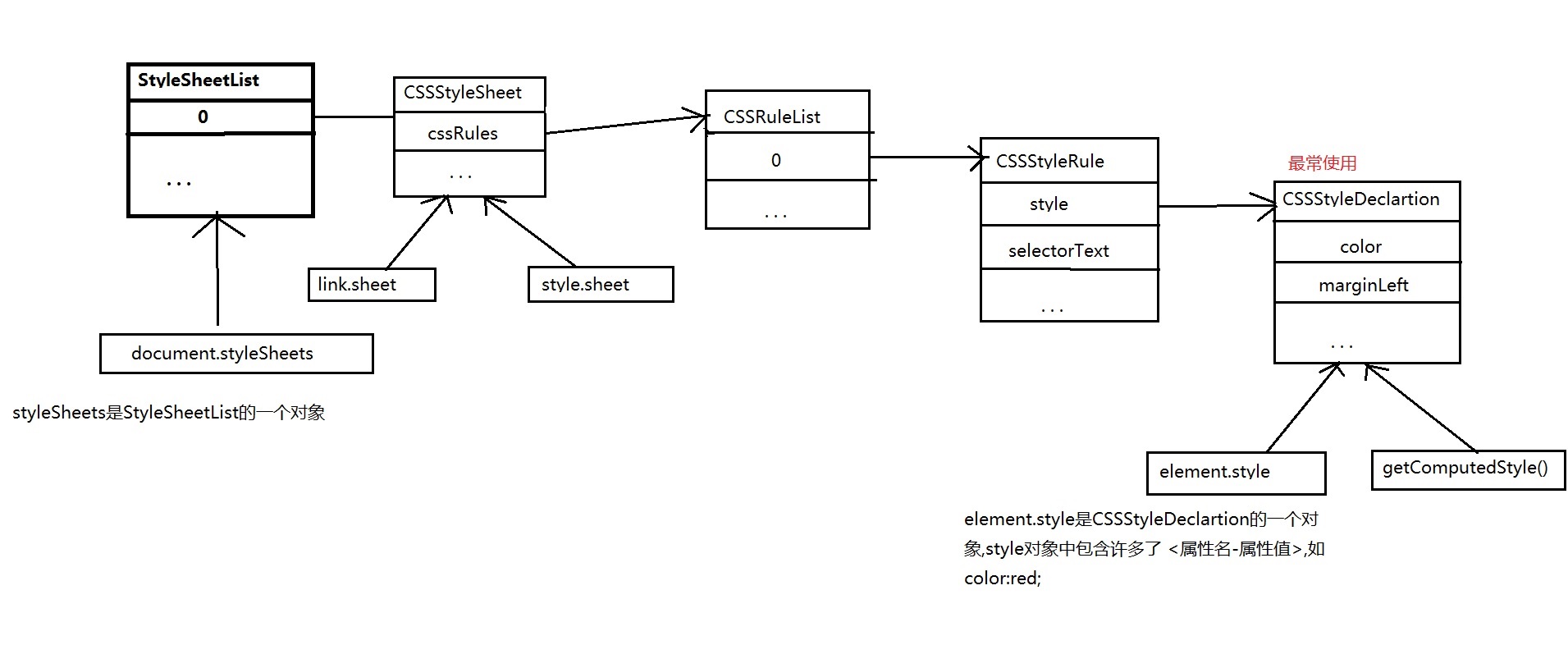
element.sheet.cssRules
element.sheet.cssRules[1] <---> p{color:#aaa;line-height: 20px;} //cssRules中的『第二条rule』
.style <---> color:#aaa;line-height: 20px; //rule的『css声明(属性名和属性值的键值对)』
.lineHeight //通过『属性名』获得『属性值』
.selectorText <---> p //这条rule的选择器
我们可以通过这种方式查询,修改,删除css样式。
style,是CSSStyleDeclaration类的一个对象,CSSStyleDeclaration是一个键值对列表
样式属性--行内样式
<p style="color:red;">paragraph</p>
element.style <---> color:red
element.style.color <--->red
更新样式
element.style
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>css行内样式操作</title> </head> <body> <input type="text" name="phone" id="phone"> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var input=document.getElementsByTagName('input'); //DOM写法 input[0].style.borderColor='red'; input[0].style.color='red'; //css写法 input[0].style.cssText = 'border-color:red;color:red;'; </script> </html>
上面DOM写法 和 CSS写法 效果是相同的。
缺点: 样式混在js的逻辑当中。为了解决这个维护成本,改为了下面的 『更新class』
更新class
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>css行内样式操作</title> <style type="text/css"> .invalid{ border-color:red; color: red; } </style> </head> <body> <input type="text" name="phone" id="phone"> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var input=document.getElementsByTagName('input'); input[0].className+='invalid'; //将元素的className替换成 css样式 invalid </script> </html>
通过 javascript操作 元素的className DOM属性,增加了invalid样式。
缺点: 遇到『换肤』这种需要替换大量样式替换操作的时候,更新class方式也显得太繁琐。 所以应该考虑【一次性更新很多元素的样式--更新样式表】
一次性更新很多元素的样式--更新样式表
换肤.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <title>DOM属性操作</title> <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="base.css"> <link id="skin" rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="skin.spring.css"> <style type="text/css"> body{margin:30;} p{color:#aaa;line-height: 20px;} </style> </head> <body> <p>paragraph</p> <input type="button" name="" value="换肤" id="changeSkin"> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var changeSkin_btn=document.getElementById('changeSkin'); changeSkin_btn.onclick=function (){ var skinStyle=document.getElementById('skin'); skinStyle.href='skin.summer.css'; } </script> </html>
skin.spring.css
body{ background: green; } p{ color:yellow; }
skin.summer.css
body{ background: orange; } p{ color:blue; }
获取样式
element.style---只能获得行内样式,而外联、页面样式表中的样式通过element.style是无法获取的。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>获取样式</title> </head> <body> <input type="text" > </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var input = document.getElementsByTagName('input')[0]; var color=input.style.color; //element.style 针对的是内嵌(行内)的样式表 console.log(color); // “” </script> </html>
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>获取样式</title> </head> <body> <input type="text" style="color: red;"> </body> <script type="text/javascript"> var input = document.getElementsByTagName('input')[0]; var color=input.style.color; //element.style 针对的是内嵌(行内)的样式表,所以获取到的为 "" console.log(color); //red //所以说element.style获取到的不一定是实际样式(实际样式可能来自外联样式、页面样式),而外联样式表、页面样式表中的样式无法通过element.style获取, element.style只能获得行内样式 </script> </html>
缺点:无法获取实际的样式(无法获取外联、页面样式表中的样式)。 为了获得实际样式,需要使用『window.getComputedStyle()』
var style=window.getComputedStyle(element[,pseudoElt]);----获取实际样式
<input type="text" >
var input = document.getElementsByTagName('input')[0]; color=window.getComputedStyle(input).color console.log(color);//rgb(0, 0, 0) 获得实际样式 console.log(input); //打印出input.style对象(element.style是CSSStyleDeclaration类的一个对象)
CSSStyleDeclaration
注意:IE9—使用element.currentStyle
在文章最末尾补充一张 CSS 在DOM中的类结构图
学习资料:网易前端微专业课程