第一步:编写两个pojo,比如一个学生表一个课程表 这里使用注解。
需要
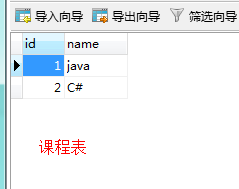
课程表:

1 package com.qcf.pox; 2 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 import java.util.Set; 5 6 import javax.persistence.Entity; 7 import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; 8 import javax.persistence.GenerationType; 9 import javax.persistence.Id; 10 import javax.persistence.ManyToMany; 11 12 @Entity 13 public class Course { 14 @Id 15 @GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.AUTO) 16 private int id; 17 private String name; 18 @ManyToMany(mappedBy="courses") 19 private Set<Student2> student2s=new HashSet<Student2>(); 20 public int getId() { 21 return id; 22 } 23 public void setId(int id) { 24 this.id = id; 25 } 26 public String getName() { 27 return name; 28 } 29 public void setName(String name) { 30 this.name = name; 31 } 32 public Set<Student2> getStudent2s() { 33 return student2s; 34 } 35 public void setStudent2s(Set<Student2> student2s) { 36 this.student2s = student2s; 37 } 38 public Course(int id, String name, Set<Student2> student2s) { 39 super(); 40 this.id = id; 41 this.name = name; 42 this.student2s = student2s; 43 } 44 public Course() { 45 super(); 46 } 47 48 }
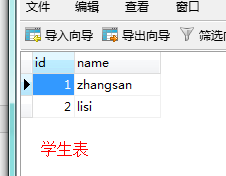
学生表:

1 package com.qcf.pox; 2 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 import java.util.Set; 5 6 import javax.persistence.CascadeType; 7 import javax.persistence.Entity; 8 import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue; 9 import javax.persistence.GenerationType; 10 import javax.persistence.Id; 11 import javax.persistence.ManyToMany; 12 13 @Entity 14 public class Student2 { 15 @Id 16 @GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.AUTO) 17 private int id; 18 private String name; 19 @ManyToMany(cascade=CascadeType.ALL) 20 private Set<Course> courses=new HashSet<Course>(); 21 public int getId() { 22 return id; 23 } 24 public void setId(int id) { 25 this.id = id; 26 } 27 public String getName() { 28 return name; 29 } 30 public void setName(String name) { 31 this.name = name; 32 } 33 public Set<Course> getCourses() { 34 return courses; 35 } 36 public void addCourses(Course courses) { 37 this.courses.add(courses); 38 } 39 public Student2(int id, String name, Set<Course> courses) { 40 super(); 41 this.id = id; 42 this.name = name; 43 this.courses = courses; 44 } 45 public Student2() { 46 super(); 47 } 48 49 }
第二步:在hibernate.cfg.xml文件中引入这两个po类

1 <mapping class="com.qcf.pox.Student2"/> 2 <mapping class="com.qcf.pox.Course"/>
第三步:编写测试代码

1 package com.qcf.test; 2 3 import org.hibernate.Session; 4 import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; 5 import org.hibernate.Transaction; 6 import org.hibernate.cfg.AnnotationConfiguration; 7 import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; 8 9 import com.qcf.pox.Course; 10 import com.qcf.pox.Student2; 11 12 public class TestManyToMany { 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 Configuration configuration=new AnnotationConfiguration().configure(); 15 SessionFactory factory=configuration.buildSessionFactory(); 16 Session session=factory.openSession(); 17 Transaction transaction=session.beginTransaction(); 18 19 //创建两个课程 20 Course course=new Course(); 21 course.setName("java"); 22 Course course2=new Course(); 23 course2.setName("C#"); 24 25 //创建两个学生 26 Student2 student=new Student2(); 27 student.setName("zhangsan"); 28 Student2 student2=new Student2(); 29 student2.setName("lisi"); 30 31 student.addCourses(course); 32 student.addCourses(course2); 33 34 student2.addCourses(course); 35 student2.addCourses(course2); 36 37 session.save(student); 38 session.save(student2); 39 40 transaction.commit(); 41 session.close(); 42 43 } 44 45 }
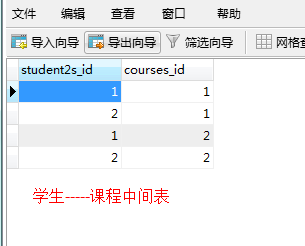
执行成功后的结果: