内存分配
原则:
优先分配到eden
大对象直接分配到老年代
长期存活的对象分配到老年代
空间分配担保
动态对象年龄判断
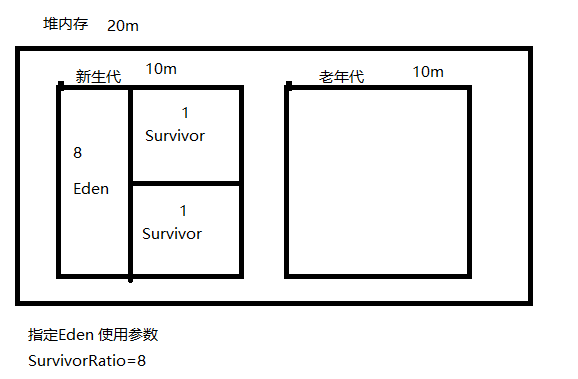
验证优先分配到eden
1 public class Main { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 byte [] b1 = new byte[4 * 1024 * 1024]; 6 7 8 } 9 10 11 }
1 Heap 2 PSYoungGen total 37888K, used 6717K [0x00000000d6200000, 0x00000000d8c00000, 0x0000000100000000) 3 eden space 32768K, 20% used [0x00000000d6200000,0x00000000d688f7c8,0x00000000d8200000) 4 from space 5120K, 0% used [0x00000000d8700000,0x00000000d8700000,0x00000000d8c00000) 5 to space 5120K, 0% used [0x00000000d8200000,0x00000000d8200000,0x00000000d8700000) 6 ParOldGen total 86016K, used 0K [0x0000000082600000, 0x0000000087a00000, 0x00000000d6200000) 7 object space 86016K, 0% used [0x0000000082600000,0x0000000082600000,0x0000000087a00000) 8 Metaspace used 2793K, capacity 4486K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K 9 class space used 298K, capacity 386K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K
验证空间分配担保
VM arguments: -verbose:gc -XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+UseSerialGC -Xms20M -Xmx20M -Xmn10M -XX:SurvivorRatio=8
1 public class Main { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 5 byte [] b1 = new byte[2 * 1024 * 1024]; 6 byte [] b2 = new byte[2 * 1024 * 1024]; 7 byte [] b3 = new byte[2 * 1024 * 1024]; 8 byte [] b4 = new byte[4 * 1024 * 1024]; 9 10 System.gc(); 11 12 13 } 14 15 16 }
[GC (Allocation Failure) [DefNew: 7295K->629K(9216K), 0.0062550 secs] 7295K->6773K(19456K), 0.0063211 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.01 secs] [Full GC (System.gc()) [Tenured: 6144K->6144K(10240K), 0.0033827 secs] 11029K->10868K(19456K), [Metaspace: 2786K->2786K(1056768K)], 0.0034518 secs] [Times: user=0.00 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] Heap def new generation total 9216K, used 4888K [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000ff600000, 0x00000000ff600000) eden space 8192K, 59% used [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000ff0c62b8, 0x00000000ff400000) from space 1024K, 0% used [0x00000000ff500000, 0x00000000ff500000, 0x00000000ff600000) to space 1024K, 0% used [0x00000000ff400000, 0x00000000ff400000, 0x00000000ff500000) tenured generation total 10240K, used 6144K [0x00000000ff600000, 0x0000000100000000, 0x0000000100000000) the space 10240K, 60% used [0x00000000ff600000, 0x00000000ffc00030, 0x00000000ffc00200, 0x0000000100000000) Metaspace used 2793K, capacity 4486K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K class space used 298K, capacity 386K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K
eden 约占4m, b4所占空间, 老年代约占6m,为b1,b2,b3所占空间,b1,b2,b3原所在eden区,因survivor区内存不足,直接存入老年代,接着新的对象b4存入eden区。
大对象直接进入老年代
参数:-XX:PretenureSizeThreshold ,如果大于这个值直接进入老年代中。
为何大对象直接分配到老年代中?
大对象一般是字符串或数组,存活时间较长,如依然分到eden中,复制算法会移动大的对象,影响性能,而相对,老年代垃圾回收次数相对较低,性能较好。
VM arguments: -verbose:gc -XX:+PrintGCDetails -XX:+UseSerialGC -Xms20M -Xmx20M -Xmn10M -XX:SurvivorRatio=8 -XX:PretenureSizeThreshold=6M
1 public class Main { 2 3 private static final int M = 1024 * 1024; 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 7 byte[] b1 = new byte[7 * M]; 8 9 10 } 11 }
直接分配到老年代
1 Heap 2 def new generation total 9216K, used 1315K [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000ff600000, 0x00000000ff600000) 3 eden space 8192K, 16% used [0x00000000fec00000, 0x00000000fed48e18, 0x00000000ff400000) 4 from space 1024K, 0% used [0x00000000ff400000, 0x00000000ff400000, 0x00000000ff500000) 5 to space 1024K, 0% used [0x00000000ff500000, 0x00000000ff500000, 0x00000000ff600000) 6 tenured generation total 10240K, used 7168K [0x00000000ff600000, 0x0000000100000000, 0x0000000100000000) 7 the space 10240K, 70% used [0x00000000ff600000, 0x00000000ffd00010, 0x00000000ffd00200, 0x0000000100000000) 8 Metaspace used 2791K, capacity 4486K, committed 4864K, reserved 1056768K 9 class space used 298K, capacity 386K, committed 512K, reserved 1048576K
长期存活的对象将进入老年代
-XX:MaxTenuringThreshold
空间分配担保:
-XX:+HandlePromotionFailure
1.如何禁用状态,不担保,如果为启用状态,进行担保,
2.验证老年代最大的可用的连续空间是否大于历次晋升到老年代对象的平均大小,如果大于平均值,可以启用担保,如果小于,不能分配空间,即分配失败。
逃逸分析与栈上分配
堆不再是内存分配的唯一选择,栈上分配,根据方法的执行而进行分配和释放,不需要垃圾回收器进行回收,性能得到提高。
逃逸分析主要分析对象的作用域,筛选出没有逃逸的对象在栈上进行分配,
只有在方法体内部有效的才会认为对象没有发生逃逸,反之逃逸。
1 public class StackAllocation { 2 3 public StackAllocation obj; 4 5 /** 6 * 方法返回StackAllocation对象,发生逃逸 7 */ 8 public StackAllocation getInstance() { 9 return obj == null?new StackAllocation() :obj; 10 11 } 12 13 14 /** 15 * 为成员属性赋值,发生逃逸 16 */ 17 public void setObj() { 18 this.obj = new StackAllocation(); 19 } 20 21 /** 22 * 对象的作用域仅在当前方法中有效,没有发生逃逸 23 */ 24 public void useStackAllocation() { 25 StackAllocation s = new StackAllocation(); 26 } 27 28 /** 29 * 引用成员变量的值,发生逃逸 30 */ 31 public void useStackAllocation2() { 32 StackAllocation s = getInstance(); 33 } 34 35 36 37 38 }