接口隔离原则
用多个专门的接口,而不是使用单一的总接口,
客户端不应该依赖它不需要的接口
一个类对一个类的依赖应该建在最小的接口上
建立单一接口
细化接口,接口的方法尽量少
注意适度原则
符合常说的高内聚低耦合的设计思想,从而使类具有可读性,可扩展性,可维护性
IAnimalAction
1 public interface IAnimalAction { 2 void eat(); 3 void fly(); 4 void swim(); 5 6 }
IEatAnimalAction
1 public interface IEatAnimalAction { 2 3 void eat(); 4 5 }
IFlyAnimalAction
1 public interface IFlyAnimalAction { 2 3 void fly(); 4 }
ISwimAction
public interface ISwimAnimalAction { void swim(); }
Dog
1 public class Dog implements ISwimAnimalAction,IEatAnimalAction { 2 3 @Override 4 public void eat() { 5 6 } 7 8 @Override 9 public void swim() { 10 11 } 12 }
Bird
public class Bird implements IAnimalAction{ @Override public void eat() { } @Override public void fly() { } @Override public void swim() { } }
单一职责原则和接口隔离原则的区别
单一职责指的是类,接口,方法的职责单一,强调职责
接口隔离,对接口依赖的隔离
迪米特原则
定义:一个对象对其他对象保持最少的了解
尽量降低类与类之间的耦合
降低类之间的耦合
强调只和朋友交流,不和陌生人说话
朋友:指的是出现在成员变量,方法的输入,输出参数中的类称为成员朋友类
而出现在方法体内部的类不属于朋友类
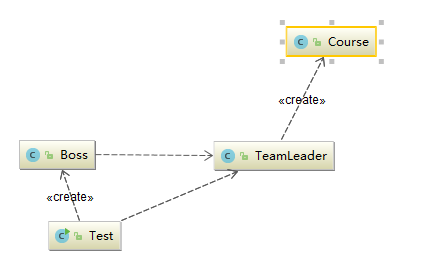
举例:Boss查询课程,交由teamleader完成,不与course产生关联
Boss
public class Boss { public void commandCheckNumber(TeamLeader teamLeader){ teamLeader.checkNumberOfCourse(); } }
TeamLeader
1 public class TeamLeader { 2 3 public void checkNumberOfCourse(){ 4 List<Course> courseList = new ArrayList<Course>(); 5 for (int i = 0;i<20; i++){ 6 courseList.add(new Course()); 7 } 8 System.out.println("在线课程数量有"+courseList.size()); 9 } 10 }
Coures
public class Course{
}
Test
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Boss boss = new Boss(); 4 TeamLeader teamLeader = new TeamLeader(); 5 boss.commandCheckNumber(teamLeader); 6 7 } 8 9 }
Diagram
里氏替换原则
一个软件实体如果适用一个父类的话,那一定适用其子类,
所有引用父类的地方必须能透明地适用其子类的对象,子类对象能够替换父类对象
而程序逻辑不变
子类可以扩展父类的功能,但不能改变父类原有的功能
优点:
约束:约束继承泛滥,开闭原则的一种体现
加强程序的健壮性,同时变更时可以做到更好的兼容性,
提高程序的维护性,扩展性。降低需求变更引入的风险
Rectangle
public class Rectangle { private long width; private long length; public long getWidth() { return width; } public void setWidth(long width) { this.width = width; } public long getLength() { return length; } public void setLength(long length) { this.length = length; } }
Square
public class Square extends Rectangle{ private long sideLength; public long getSideLength() { return sideLength; } public void setSideLength(long sideLength) { this.sideLength = sideLength; } //Override @Override public long getWidth() { return getSideLength(); } @Override public void setWidth(long width) { setSideLength(width); } @Override public long getLength() { return getSideLength(); } @Override public void setLength(long length) { setSideLength(length); } }
Test
public class Test { public static void resize(Rectangle rectangle){ while (rectangle.getWidth() <= rectangle.getLength()){ rectangle.setWidth(rectangle.getWidth()+1); System.out.println(""+rectangle.getWidth()+"length:"+rectangle.getLength()); } System.out.println("resize方法结束"+""+rectangle.getWidth()+"length:"+rectangle.getLength()); } public static void main(String[] args) { Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(); rectangle.setWidth(10); rectangle.setLength(20); resize(rectangle); } }
合成/聚成复用原则
定义:
尽量使用对象组合/聚合,而不是继承关系达到软件复用的目的
聚合 has -A 和 组合contains-A
可以使系统更加灵活,降低类与类之间的耦合度,
一个类的变化对其他类造成的影响较小
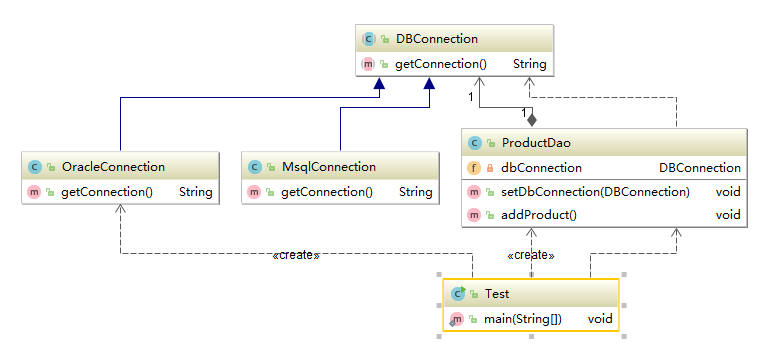
DBConnection
1 public abstract class DBConnection { 2 3 public abstract String getConnection(); 4 }
MysqlConnection
1 public class MsqlConnection extends DBConnection{ 2 3 4 @Override 5 public String getConnection() { 6 return "Mysql数据库连接"; 7 } 8 }
OracleConnection
1 public class OracleConnection extends DBConnection { 2 3 @Override 4 public String getConnection() { 5 return "oracle数据库连接"; 6 } 7 }
ProductDao
public class ProductDao { private DBConnection dbConnection; //setter注入 public void setDbConnection(DBConnection dbConnection) { this.dbConnection = dbConnection; } public void addProduct(){ String conn = dbConnection.getConnection(); System.out.println("使用"+conn+"增加产品"); } }
Test
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 ProductDao productDao = new ProductDao(); 4 productDao.setDbConnection(new OracleConnection()); 5 6 /* 7 productDao.setDbConnection(new MsqlConnection()); 8 ... 9 */ 10 productDao.addProduct(); 11 12 } 13 14 }
Diagram
完