函数式编程只需要关注实现的功能,而不需要关注实现的细节
举例:
1 public class DemoMain { 2 3 /** 4 * 求最小值 5 * 6 */ 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 int[] nums = {33,23,34,89}; 9 10 int min = IntStream.of(nums).min().getAsInt(); 11 System.out.println(min); 12 13 14 } 15 }
创建线程
1 public class ThreadDemo { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 new Thread(new Runnable() { 5 6 @Override 7 public void run() { 8 System.out.println("aaa"); 9 } 10 }).start(); 11 12 //jdk1.8 13 new Thread(()->System.out.println("aaa")).start(); 14 15 } 16 }
lamba表达式就是返回了一个实现指定接口的对象实例
jdk8 新增的接口默认方法
1 /**注为FunctionalInterface的接口被称为函数式接口,该接口只能有一个自定义方法,但是可以包括从object类继承而来的方法。如果一个接口只有一个方法,则编译器会认为这就是一个函数式接口 2 * (单一职责原则) 3 */ 4 @FunctionalInterface 5 interface inter { 6 int doubleNum(int i); 7 8 /** 9 * 新增接口默认方法 10 */ 11 default int add(int x,int y) { 12 return x+y; 13 } 14 } 15 16 17 @FunctionalInterface 18 interface inter2 { 19 int doubleNum(int i); 20 21 /** 22 * 新增接口默认方法 23 */ 24 default int add(int x,int y) { 25 return x+y; 26 } 27 } 28 29 30 @FunctionalInterface 31 interface inter3 extends inter,inter2 { 32 /** 33 * 指明重复的默认方法 34 */ 35 @Override 36 default int add(int x, int y) { 37 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 38 return inter2.super.add(x, y); 39 } 40 41 } 42 43 44 45 46 public class LambdaDemo { 47 48 49 public static void main(String[] args) { 50 51 inter i1 = (i) -> i*2; //1 52 53 System.out.println(i1.doubleNum(20)); 54 55 System.out.println(i1.add(10,20)); 56 57 inter i2 = i->i*2; //2 58 59 inter i3 = (int i)->i*2; //3 60 61 inter i4 = (int i)->{ 62 System.out.println("aaa"); 63 return i*2; 64 }; //4 67 } 68 69 }
函数接口
1 /** 2 * 函数接口好处 3 * 1.不用定义多的接口 4 * 2.支持链式的操作 5 * @author 11658 6 */ 7 8 9 /** 10 *定义输入类型int,输出类型String 11 */ 12 //interface IMoneyFormot{ 13 // String format(int i); 14 //} 15 16 17 class MyMoney{ 18 private final int money; 19 20 public MyMoney(int money) { 21 this.money = money; 22 } 23 24 public void printMoney(Function<Integer,String> iMoneyFormot) { 25 // System.out.println("我的存款:"+ iMoneyFormot.format(this.money)); 26 System.out.println("我的存款:"+ iMoneyFormot.apply(this.money)); 27 28 } 29 30 } 31 32 public class InterDemo { 33 34 public static void main(String[] args) { 35 36 37 MyMoney me = new MyMoney(1000); 38 39 Function<Integer, String> iMoneyFormot = i -> new DecimalFormat().format(i); 40 //链式操作 41 me.printMoney(iMoneyFormot.andThen(s->"$"+s)); 42 43 44 } 45 46 }
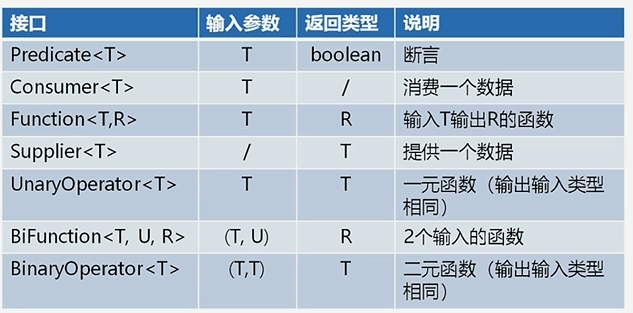
举例:
1 public class FunctionDemo { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 //断言函数 5 //IntPredicate predicate = i -> i >0; 6 Predicate<Integer> predicate = i -> i >0; 7 System.out.println(predicate.test(-9)); 8 9 10 //消费函数接口 11 Consumer<String> consumer = s -> System.out.println(s); 12 consumer.accept("aaaa"); 13 14 } 15 }
方法引用
1.静态方法引用
2.使用对象实例方法引用
3.使用类名来引用
4.构造函数方法引用
1 class Dog{ 2 private String name = "金毛"; 3 4 private int food = 10; 5 6 public static void bark(Dog dog) { 7 System.out.println(dog+"在叫"); 8 } 9 10 /** 11 *吃狗粮 12 *输入 int 输出 int 13 */ 14 public int eat(int num) { 15 System.out.println("吃了"+num+"斤"); 16 this.food -= num; 17 return this.food; 18 } 19 20 21 @Override 22 public String toString() { 23 return this.name; 24 } 25 } 26 27 28 29 public class MethodDemo { 30 31 public static void main(String[] args) { 32 /** 33 * lambda表达式实际是匿名函数 34 * 函数左边是函数参数,右边是函数执行体 35 * 当函数执行体只有一个函数调用时,函数的参数和箭头左边一样,就可以缩写成方法引用的方式 36 */ 37 38 //Consumer<String> consumer = s->System.out.println(s); 39 40 Consumer<String> consumer = System.out::print; 41 42 consumer.accept("aaa"); 43 44 45 46 //1.静态方法的方法引用 47 //类名::静态方法名 48 Consumer<Dog> consumer2 = Dog::bark; 49 Dog dog = new Dog(); 50 51 consumer2.accept(dog); 52 53 //非静态方法引用 54 //2.使用对象实例方法引用 55 //实例::方法名 56 Function<Integer,Integer> function = dog::eat; 57 //方法的输入和输出类型一样,可改为一元函数接口 58 // UnaryOperator<Integer> function = dog::eat; 59 60 System.out.println("还剩"+function.apply(2)+"斤"); 61 62 } 63 }
aaa金毛在叫
吃了2斤
还剩8斤
1 class Cat{ 2 private String name = "小猫"; 3 4 private int food = 10; 5 6 /** 7 * 创建构造函数 8 */ 9 public Cat() { 10 11 } 12 13 //分析:输入String,输出当前类的实例 14 public Cat(String name) { 15 this.name = name; 16 } 17 18 /** 19 * eat 方法, 20 * jdk 默认会把当前实例传入到非静态方法,参数名是this,位置是第一个 21 * 用类名对非静态方法做引用的时候,实际上是有两个输入,一个输出 22 * 23 */ 24 public int eat(Cat this,int num) { 25 System.out.println("吃了"+num+"斤"); 26 this.food -= num; 27 return this.food; 28 } 29 30 31 @Override 32 public String toString() { 33 return this.name; 34 } 35 } 36 37 38 39 public class MethodDemo2 { 40 41 public static void main(String[] args) { 42 43 Cat cat = new Cat(); 44 cat.eat(2); 45 46 47 Function<Integer,Integer> function = cat::eat; 48 49 System.out.println("还剩"+function.apply(2)+"斤"); 50 51 //Cat::eat 52 //3.使用类名来引用方法 53 BiFunction<Cat,Integer,Integer> eatFunction = Cat::eat; 54 System.out.println("还剩"+eatFunction.apply(cat, 2)+"斤"); 55 56 57 //4.构造方法的引用 ,没有参数时,没有输入只有输出 58 //类名::new 59 Supplier<Cat> supplier = Cat::new; 60 System.out.println(supplier.get()); 61 62 63 64 /** 带参数的构造函数方法的引用 65 * 分析:输入String,输出当前类的实例 66 * public Cat(String name) { 67 * this.name = name; 68 } 69 */ 70 Function<String,Cat> function2 = Cat::new; 71 System.out.println(function2.apply("大橘")); 72 73 } 74 75 }
吃了2斤
还剩4斤
小猫
大橘
类型推断
1 /** 2 * 类型推断 3 * lambda表达式实际上是匿名函数,返回了一个指定接口的对象,究竟实现那个接口,否则就报错 4 * 这就是类型推断 5 */ 6 7 @FunctionalInterface 8 interface IMath{ 9 int add(int x,int y); 10 } 11 12 13 14 15 public class TypeDemo { 16 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 19 //变量类型定义 20 IMath math = (x,y) ->x+y; 21 22 //数组里 23 IMath[] math2 = {(x,y) -> x+y}; 24 25 //强转 26 Object math3 = (IMath)(x,y) -> x+y; 27 28 //通过返回类型 29 IMath createLambda = createLambda(); 30 31 TypeDemo demo = new TypeDemo(); 32 //指定方法 33 //当有二义性时,使用强转对应的接口解决 34 demo.test((x,y) -> x+y); 35 36 } 37 38 //通过方法指定接口,进行匹配 39 public void test(IMath math) {} 40 41 42 private static IMath createLambda() { 43 44 return (x,y) ->x+y; 45 46 } 47 48 }
变量引用
1 /** 2 * 变量引用 3 * @author 11658 4 * 5 */ 6 public class VarDemo { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 /** 10 * 匿名类引用外部变量必须为final ? 保证里面的变量和外部的变量指向同一个对象 11 * 传参的形式是传值而不是传引用, 12 */ 13 final String str = "aaa"; 14 Consumer<String> consumer = s -> System.out.println(s+str); 15 16 consumer.accept("1222"); 17 } 18 19 }
1222aaa
级联表达式和柯里化
1 /** 2 * 级联表达式和柯里化 3 * 柯里化:把多个参数的函数转换为只有一个参数的函数 4 * 目的:函数标准化 5 */ 6 public class CurryDemo { 7 8 9 10 public static void main(String[] args) { 11 12 Function<Integer, Function<Integer,Integer>> fun= x -> y-> x+y; 13 14 System.out.println(fun.apply(2).apply(3)); 15 16 17 //函数标准化,进行统一处理 18 Function<Integer, Function<Integer,Function<Integer,Integer>>> fun2= x->y->z->x+y+z; 19 20 System.out.println(fun2.apply(2).apply(3).apply(4)); 21 22 23 } 24 25 26 27 }
完