1.感知机
感知机是二类分类线性分类模型,输出的值为{+1, -1}两种类型;感知机是利用超平面将两类分离的算法。
假设输入空间(特征空间)是X∈Rn,输出空间是Y={+1, -1}。输入x∈X表示实例特征向量。对应于输出空间(特征空间)的点:输出y∈Y表示实例类别,由输入空间到输出空间的如下函数:
f(x) = sign(w*x+b)
线性方程:
w*x+b=0
对应于特征空间Rn 中的一个超平面S,其中w是超平面的法向量,b是超平面的截距。
2.感知机学习策略
单个点x0到超平面S的距离是:
对于误分类来说,-yi(w*xi+b)>0。因此误分类点到超平面S的距离
假设超平面S误分类点集合为M,则总距离:
因此,感知机sign(wx+b)的损失函数可以简写为:
3.感知机原始形式
假设M集合是固定,那么损失函数的梯度为:
随机一个选取一个误分类点(xi, yi)对w和b进行更新。

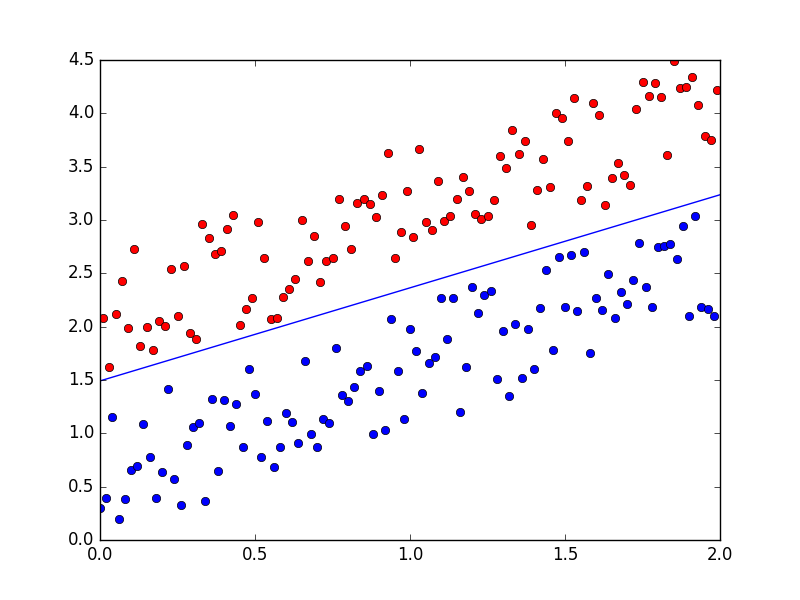
1 # coding:utf-8 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 import numpy as np 4 5 def dataN(length):#生成数据 6 x=[[1,x/100.0,x/100.0+ (x%2)*1.5 + np.random.uniform(0,1.2)] for x in range(length)] 7 y=[(-1)**(y%2-1) for y in range(length)] 8 x=np.mat(x) 9 return x,y 10 11 def percepT(x,y, iter):#感知机原始形式 12 n =np.shape(x)[1] 13 m=len(x) 14 theta=np.ones(n) 15 alpha=0.02 16 for it in range(iter): 17 l=0 18 print it #0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 19 for k in range(m): 20 if (x[k].dot(theta.T))*y[k]<0: 21 l=1 22 theta=np.add(theta,alpha*y[k]*x[k]) 23 if l==0: 24 break 25 return theta 26 27 def showP(x,y,theta):#作图 28 plt.figure(1) 29 color=['','or','ob'] 30 for i in xrange(length): 31 plt.plot(x[i, 1], x[i, 2],color[int(y[i])]) 32 theta=theta.getA() 33 plt.plot([0,length/100],[-theta[0][0],-theta[0][0]-theta[0][1]*length/100]/theta[0][2]) 34 plt.show() 35 36 length=200 37 iter=200 38 x,y=dataN(length) 39 theta=percepT(x,y,iter) 40 print theta #[[-0.38 -0.2464 0.25287193]] 41 showP(x,y,theta)
4.感知机对偶形式
对偶形似的基本想法是:将w和b表示实例xi和标记yi的线性组合形式,通过求解器系数的到w和b。在原始形式中,通过
逐步修改w和b,假设修改了n次,则w和b关于(xi, yi)的增量分别是aixiyi和aiyi,这里的ai=niη。最后学习到的w和b是:
1 # coding:utf-8 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 import numpy as np 4 5 def dataN(length):#生成数据 6 x=[[x/100.0,x/100.0+ (x%2)*1.5 + np.random.uniform(0,1.2)] for x in range(length)] 7 y=[(-1)**(y%2-1) for y in range(length)] 8 x=np.mat(x) 9 return x,y 10 11 def percepTG(x,y, iter):#感知机对偶形式 12 m=len(x) 13 theta=np.zeros(m) 14 b=0 15 alpha=0.1 16 for it in range(iter): 17 l=0 18 print it #0 1 2 19 for k in range(m): 20 if y[k]*(np.sum([theta[j]*y[j]*x[j]*x[k].T for j in range(m)])+b)<=0: 21 l=1 22 theta[k]+=alpha 23 b+=alpha*y[k] 24 if l==0: 25 break 26 return theta,b 27 28 def showP(x,y,theta,b):#作图 29 plt.figure(1) 30 color=['','or','ob'] 31 for i in xrange(len(x)): 32 plt.plot(x[i, 0], x[i, 1],color[int(y[i])]) 33 c= np.zeros(2) 34 for j in range(len(x)): 35 c=np.add(c,theta[j]*y[j]*x[j]) 36 c=c.getA() 37 print c,b #[[-0.351 0.402276]] -0.6 38 plt.plot([0,length/100],[-b,-b-c[0][0]*length/100]/c[0][1]) 39 plt.show() 40 41 length=200 42 iter=5 43 x,y=dataN(length) 44 theta,b=percepTG(x,y,iter) 45 showP(x,y,theta,b)