[leetcode]1379. Find a Corresponding Node of a Binary Tree in a Clone of That Tree
链接
描述
Given two binary trees original and cloned and given a reference to a node target in the original tree.
The cloned tree is a copy of the original tree.
Return a reference to the same node in the cloned tree.
Note that you are not allowed to change any of the two trees or the target node and the answer must be a reference to a node in the cloned tree.
Follow up: Solve the problem if repeated values on the tree are allowed.
Example 1:
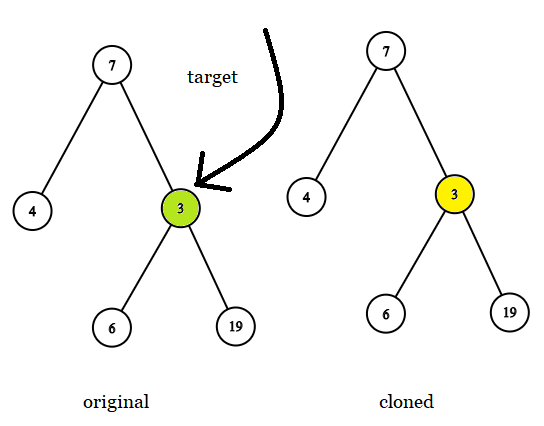
Input: tree = [7,4,3,null,null,6,19], target = 3
Output: 3
Explanation: In all examples the original and cloned trees are shown. The target node is a green node from the original tree. The answer is the yellow node from the cloned tree.
Example 2:
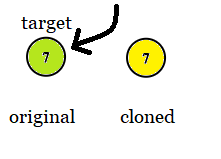
Input: tree = [7], target = 7
Output: 7
Example 3:
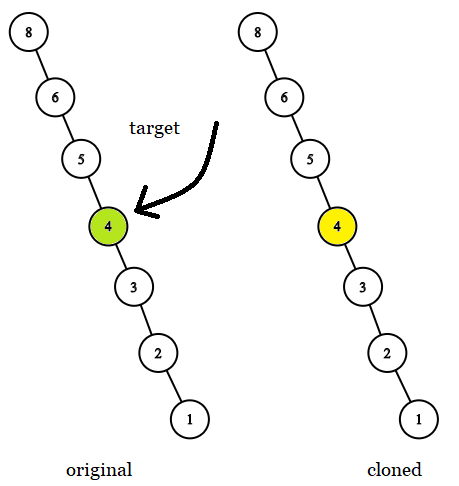
Input: tree = [8,null,6,null,5,null,4,null,3,null,2,null,1], target = 4
Output: 4
Example 4:
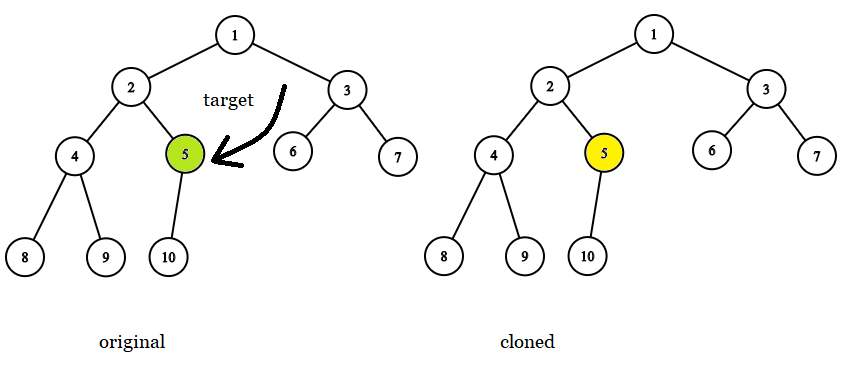
Input: tree = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10], target = 5
Output: 5
Example 5:
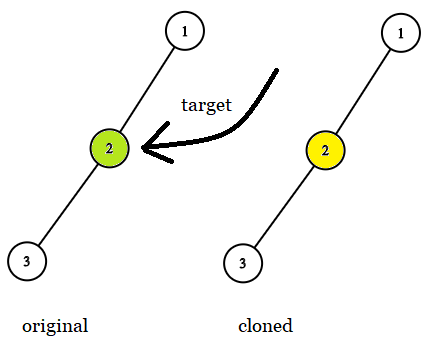
Input: tree = [1,2,null,3], target = 2
Output: 2
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 10^4].
The values of the nodes of the tree are unique.
target node is a node from the original tree and is not null.
solution
采用最朴素的BFS(广度优先遍历)即可;
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* getTargetCopy(TreeNode* original, TreeNode* cloned, TreeNode* target) {
queue<TreeNode*> oq, cq;
if (original == NULL)
return NULL;
oq.push(original);
cq.push(cloned);
while (!oq.empty())
{
TreeNode *tmp = oq.front();
TreeNode *tmpC = cq.front();
oq.pop();
cq.pop();
if (tmp == target)
return tmpC;
if (tmp->left)
{
oq.push(tmp->left);
cq.push(tmpC->left);
}
if (tmp->right)
{
oq.push(tmp->right);
cq.push(tmpC->right);
}
}
return NULL;
}
};
分析
时间复杂度 O(n);n是二叉树中节点的个数,树种的每一个节点只会被遍历一次;
空间复杂度O(1)