昨晚在群裏無意間看到一個朋友有一個需求。他是在C裏面將兩個結構體(HeadStruct,BodyStruct)的内存數據直接通過socket send發給C#寫的服務端來處理。當然他之前所使用的需求基本都是從C到C之間進行通信,然後把内存二進制數據再還原到結構上就行。但是C與C#之間可不能簡單就這麽弄。
後來想了一下,大家暫且想出了兩種方案。
1.還是用C寫一個DLL,直接用C# DllImport這個C的DLL,把Socket接收到的字節數據傳給這個Dll,用這個Dll處理。
2.使用C#的 unsafe。這種方式是我提出的,因爲之前雖然沒用過unsafe但是感覺應該可行的樣子,下面就是對這种方式測試一下C#裏unsafe struct的内存結構與C的内存結構比較。
(1)首先我們定義C的結構和程序:
#include <stdio.h>
//定義結構類型
typedef struct
{
int x;
int y;
char cs[10];
int z;
} TestStruct;
int main()
{
//結構對象
TestStruct ts = { 0 };
ts.x = 10;
ts.y = 20;
ts.z = 30;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
*(ts.cs + i) = i + 10;
}
//打印内存數據
printf(" C Data(%d):
",sizeof(ts));
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(ts); ++i)
{
printf("%d ", *((char*)&ts + i));
}
return 0;
}
(2)然後我們定義C#的結構和程序:
using System;
namespace ConsoleApplication
{
/// <summary>
/// 測試結構
/// </summary>
public unsafe struct TestStruct
{
public int x;
public int y;
public fixed byte cs[10];
public int z;
}
class Program
{
unsafe static void Main(string[] args)
{
//定義結構對象
TestStruct ts = new TestStruct()
{
x = 10
,
y = 20
,
z = 30
};
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
*(ts.cs + i) = (byte)(i + 10);
}
byte[] bs = new byte[sizeof(TestStruct)];
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(TestStruct); ++i)
{
bs[i] = *(((byte*)&ts) + i);
}
//打印結構數據
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("C# Data({0}):", sizeof(TestStruct)));
for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(TestStruct); ++i)
{
Console.Write(*(((byte*)&ts) + i));
Console.Write(" ");
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
(3)接下來就是看結果的時候了,呵呵(兩張圖):
C 結果:
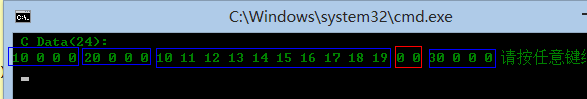
C# 結果:

結果: 可以看到兩個結構的内存大小都是24字節,並且字段的位置分佈也一致。藍色區域表示兩個結構字段的内存。紅色區域便是内存對齊數據了。總之此次測試還是有收穫的。