Description
Write a program that takes as input a rooted tree and a list of pairs of vertices. For each pair (u,v) the program determines the closest common ancestor of u and v in the tree. The closest common ancestor of two nodes u and v is the node w that is an ancestor of both u and v and has the greatest depth in the tree. A node can be its own ancestor (for example in Figure 1 the ancestors of node 2 are 2 and 5)
Input
The data set, which is read from a the std input, starts with the tree descri_ption, in the form:
nr_of_vertices
vertex:(nr_of_successors) successor1 successor2 ... successorn
...
where vertices are represented as integers from 1 to n ( n <= 900 ). The tree descri_ption is followed by a list of pairs of vertices, in the form:
nr_of_pairs
(u v) (x y) ...
The input file contents several data sets (at least one).
Note that white-spaces (tabs, spaces and line breaks) can be used freely in the input.
nr_of_vertices
vertex:(nr_of_successors) successor1 successor2 ... successorn
...
where vertices are represented as integers from 1 to n ( n <= 900 ). The tree descri_ption is followed by a list of pairs of vertices, in the form:
nr_of_pairs
(u v) (x y) ...
The input file contents several data sets (at least one).
Note that white-spaces (tabs, spaces and line breaks) can be used freely in the input.
Output
For
each common ancestor the program prints the ancestor and the number of
pair for which it is an ancestor. The results are printed on the
standard output on separate lines, in to the ascending order of the
vertices, in the format: ancestor:times
For example, for the following tree:
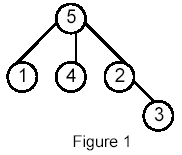
For example, for the following tree:

Sample Input
5
5:(3) 1 4 2
1:(0)
4:(0)
2:(1) 3
3:(0)
6
(1 5) (1 4) (4 2)
(2 3)
(1 3) (4 3)
Sample Output
2:1 5:5
Hint
Huge input, scanf is recommended.
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
#define N 999
using namespace std;
bool vis[N],root[N];
vector<int> nod[N];
int fa[N],q[N][N],cnt[N],n;
void ini(){
memset(root,0,sizeof(root));
memset(q,0,sizeof(q));
memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(unsigned int i=0;i<N;i++) nod[i].clear();
}
int father(int x){return x==fa[x] ? x : (fa[x]=father(fa[x]));}
void dfs(int x){
fa[x]=x;
unsigned int i;
for(i=0;i<nod[x].size();i++){
dfs(nod[x][i]);
fa[nod[x][i]]=x;
}
vis[x]=true;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(vis[i]&&q[i][x]) cnt[father(i)]+=q[i][x];
}
int main(){
int i,j,tf,ns,tn,m;
while(cin>>n){
ini();
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d:(%d)",&tf,&ns);
for(j=1;j<=ns;j++){
scanf("%d",&tn);
nod[tf].push_back(tn);
root[tn]=true;
}
}
char ch1,ch2;
scanf(" %d",&m);
while(m--){
scanf(" %c %d %d %c",&ch1,&tn,&tf,&ch2);
q[tf][tn]++;
q[tn][tf]++;
}
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(!root[i]){
dfs(i);
break;
}
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(cnt[i]) printf("%d:%d
",i,cnt[i]);
}
return 0;
}