引子
1 def max(a,b): 2 ''' 3 求出a,b中的最大值 4 :return: 最大的一项值 5 ''' 6 return a if a>b else b 7 8 def the_max(x,y,z): 9 ''' 10 求出x,y,x中的最大值 11 :return: 最大的一项值 12 ''' 13 c = max(x,y) 14 return max(c,z) 15 print(the_max(1,2,3))
1:嵌套的定义
1 def outer(): 2 def inner(): 3 print('inner') 4 inner() 5 outer()
1.1 内部函数可以使用外部函数的变量
1 def outer(): 2 a = 1 3 def inner(): 4 b = 2 5 print(a) 6 print('inner') 7 def inner2(): 8 print(a,b) 9 print('inner') 10 inner2() 11 inner() 12 outer() #输出结果:1 13 # inner 14 # 1 2 15 # inner
1.2 在函数内部,不可变数据类型只能查看不能修改
1 def outer(): 2 a = 1 3 def inner(): 4 b = 2 5 print(a) 6 print('inner') 7 def inner2(): 8 a += 1 9 print(a) 10 inner2() 11 inner() 12 outer() #输出结果:UnboundLocalError: local variable 'a' referenced before assignment
1.3若是要修改的话---global(全局变量的修改) nonlocal(局部变量的修改)
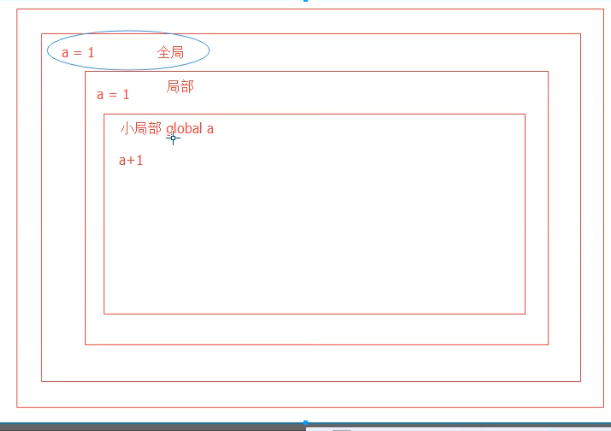
nonlocal:如果局部变量里面没有,但是全局变量里面有,那么则报错,nonlocal只能用于局部变量,找上一层中离当前函数最近的一层的局部变量
1 a = 1 #全局a 2 def outer(): 3 a = 1 #局部a 4 def inner(): 5 b = 2 6 print(a) 7 print('inner') 8 def inner2(): 9 nonlocal a #nonlocal 声明一个局部变量 10 a += 1 11 print('局部',a) 12 inner2() 13 inner() 14 outer() 15 print('全局',a) #输出结果:1 16 # inner 17 # 局部 2 18 # 全局 1
global
1 # 2 a = 1 #全局a 3 def outer(): 4 a = 1 #局部a 5 def inner(): 6 b = 2 7 print(a) 8 print('inner') 9 def inner2(): 10 global a #global 声明一个全局变量 11 a += 1 12 print('小局部:',a) #打印的是全局的a 13 inner2() 14 inner() 15 print('局部:',a) 16 outer() 17 print('全局:',a) #输出结果:1 18 # inner 19 # 小局部: 2 20 # 局部: 1 21 # 全局: 2
2:函数名的几个小用法
2.1 函数名可以赋值
def func(): print('123') #func 函数名就是变量地址 func2 = func func2() #输出结果:123
2.2 函数名可以作为容器类型的元素
1 l = [func,func2] 2 print(l) 3 for i in l: 4 i() #输出结果:[<function func at 0x036B9810>, <function func at 0x036B9810>] 5 # 123 6 # 123
2.3 函数名可以作为函数的参数
1 def func(): 2 print(123) 3 4 def func2(f): 5 f() 6 func2(func) #输出结果:123
2.4 函数名可以作为返回值
1 def func(): 2 print(123) 3 4 def func2(f): 5 return f 6 7 res = func2(func) 8 res() #输出结果:123
3:闭包:嵌套函数,内部函数调用外部函数的变量
1 def outer(): 2 a = 1 3 def inner(): 4 print(a)
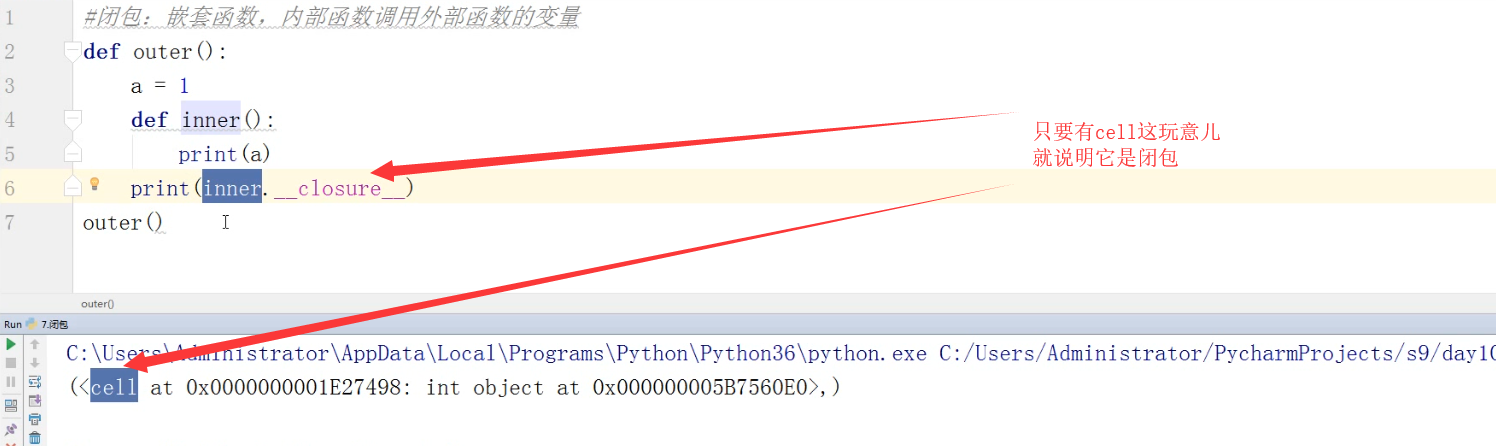
闭包的判断:
1 def outer(): 2 a = 1 3 def inner(): 4 print(a) 5 print(inner.__closure__) 6 outer() # 输出结果:(<cell at 0x03DAEF50: int object at 0x54ED3900>,) 7 # 只要有cell这玩意儿,就说明是闭包
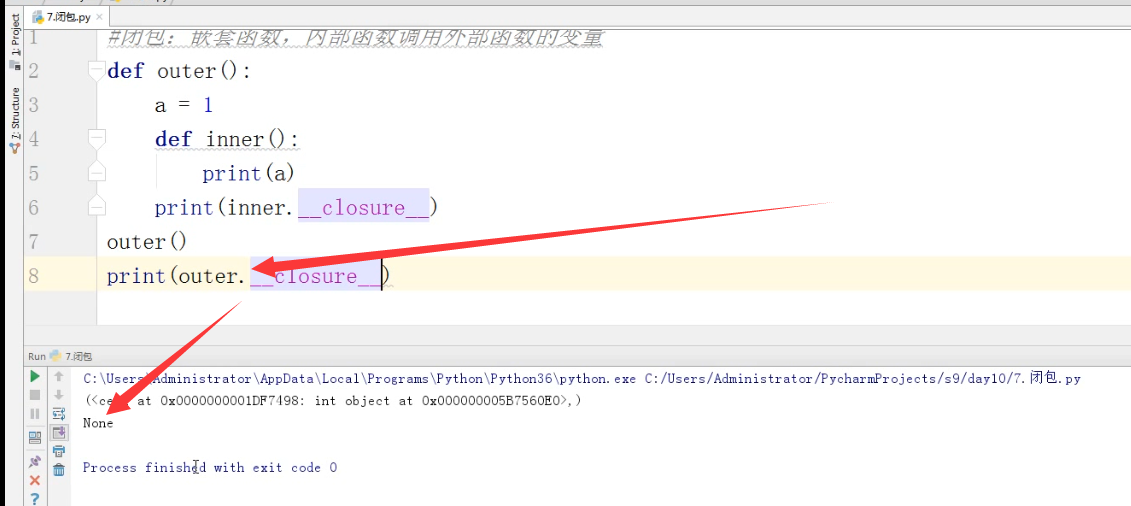
1 def outer(): 2 a = 1 3 def inner(): 4 print(a) 5 print(inner.__closure__) 6 outer() 7 print(outer.__closure__) # 输出结果:(<cell at 0x03DAEF50: int object at 0x54ED3900>,) 8 # 输出结果:None (outer函数非闭包)
闭包常见的调用方法:在一个函数外部使用它函数内部的函数(重要)
1 def outer(): 2 a = 1 3 def inner(): 4 print(a) 5 return inner 6 inn = outer() 7 inn() 8 #只要后面有对inn()函数的引用,则outer内inner外的进程不会立马结束, 9 # 好处是没必要每次调用outer都重新生成
闭包的应用举例:
1 from urllib.request import urlopen 2 3 def get_url(): 4 url = 'https://y.qq.com' 5 def get(): 6 ret = urlopen(url).read() 7 print(ret) 8 return get 9 10 get_func = get_url() 11 get_func() 12 #没必要每次使用时都在重新生成变量url,这样的话,可以节约资源