本周最大的问题:
在上周的安装gmssl后,我发现一台虚拟机突然连不上网,报错网络连接激活失败(如下图所示),起初我以为虚拟机与手机热点突然无法兼容,回到寝室测试仍无法连接,不曾与gmssl联系,打开VMware 使用另一台虚拟机安装gmssl,而后使用过程中发现同样出现此问题。

此后尝试过重置虚拟网络编辑器,和在wins+R中输入service.msc,显示该服务正在使用,重启之后也未果。
后来添加桥连方式也没有成功。
在VB和VMware中分别添加新的虚拟机就可连接网络,说明软件本身没有出现问题,目前尚未找到合适的解决办法。
aes-[128|192|256]-cbc 128/192/256 bit AES in CBC mode
aes[128|192|256] Alias for aes-[128|192|256]-cbc
aes-[128|192|256]-cfb 128/192/256 bit AES in 128 bit CFB mode
一、用法:
aes-128-cbc [options]
二、具体选项:
-help Display this summary
-ciphers List ciphers
-in infile Input file
-out outfile Output file
-pass val Passphrase source
-e Encrypt
-d Decrypt
-p Print the iv/key
-P Print the iv/key and exit
-v Verbose output
-nopad Disable standard block padding
-salt Use salt in the KDF (default)
-nosalt Do not use salt in the KDF
-debug Print debug info
-a Base64 encode/decode, depending on encryption flag
-base64 Same as option -a
-A Used with -[base64|a] to specify base64 buffer as a single line
-bufsize val Buffer size
-k val Passphrase
-kfile infile Read passphrase from file
-K val Raw key, in hex
-S val Salt, in hex
-iv val IV in hex
-md val Use specified digest to create a key from the passphrase
-none Don't encrypt
-* Any supported cipher
-engine val Use engine, possibly a hardware device
-config val A config file
三、实例
1.将要加密的内容输入到plain.txt
echo "1234567890abc" > plain.txt
2.使用openssl加密. -p 表示打印出加密用的salt, key, iv. salt就是所谓的加盐, 防止同样的内容产生同样的加密数据. iv和key是openssl 的cbc模式需要的参数. openssl enc -aes-128-cbc -in plain.txt -out encrypt.txt -iv f123 -K 1223 -p
salt=E0DEB1EAFE7F0000
key=12230000000000000000000000000000
iv =F1230000000000000000000000000000
3.输出加密前和加密后内容的十六进制. 这里使用xxd和hexdump都可以.
xxd plain.txt
00000000: 3132 3334 3536 3738 3930 6162 630a 1234567890abc.
xxd encrypt.txt
00000000: c5af 18cb ddee 9923 0374 6a21 9bb6 3f99 …#.tj!..?.
4.解密加密后的数据
openssl aes-128-cbc -d -in encrypt.txt -out encrypt_decrypt.txt -S E0DEB1EAFE7F0000 -iv F1230000000000000000000000000000 -K 12230000000000000000000000000000
-S salt Salt to use, specified as a hexidecimal string
-salt Use a salt in the key derivation routines (default)
5.查看解密后的数据和原始数据是否一致.
xxd encrypt_decrypt.txt
00000000: 3132 3334 3536 3738 3930 6162 630a 1234567890abc.
一、用法
Usage: aes-128-ecb [options]
二、选项
Valid options are:
-help Display this summary
-ciphers List ciphers
-in infile Input file
-out outfile Output file
-pass val Passphrase source
-e Encrypt
-d Decrypt
-p Print the iv/key
-P Print the iv/key and exit
-v Verbose output
-nopad Disable standard block padding
-salt Use salt in the KDF (default)
-nosalt Do not use salt in the KDF
-debug Print debug info
-a Base64 encode/decode, depending on encryption flag
-base64 Same as option -a
-A Used with -[base64|a] to specify base64 buffer as a single line
-bufsize val Buffer size
-k val Passphrase
-kfile infile Read passphrase from file
-K val Raw key, in hex
-S val Salt, in hex
-iv val IV in hex
-md val Use specified digest to create a key from the passphrase
-none Don't encrypt
-* Any supported cipher
-engine val Use engine, possibly a hardware device
-config val A config file
-in filename:指定要加密的文件存放路径
-out filename:指定加密后的文件存放路径
-salt:自动插入一个随机数作为文件内容加密,默认选项
-e:可以指明一种加密算法,若不指的话将使用默认加密算法
-d:解密,解密时也可以指定算法,若不指定则使用默认算法,但一定要与加密时的算法一致
-a/-base64:使用-base64位编码格式
一、用法
Usage: aes-192-cbc [options]
二、选项
Valid options are:
-help Display this summary
-ciphers List ciphers
-in infile Input file
-out outfile Output file
-pass val Passphrase source
-e Encrypt
-d Decrypt
-p Print the iv/key
-P Print the iv/key and exit
-v Verbose output
-nopad Disable standard block padding
-salt Use salt in the KDF (default)
-nosalt Do not use salt in the KDF
-debug Print debug info
-a Base64 encode/decode, depending on encryption flag
-base64 Same as option -a
-A Used with -[base64|a] to specify base64 buffer as a single line
-bufsize val Buffer size
-k val Passphrase
-kfile infile Read passphrase from file
-K val Raw key, in hex
-S val Salt, in hex
-iv val IV in hex
-md val Use specified digest to create a key from the passphrase
-none Don't encrypt
-* Any supported cipher
-engine val Use engine, possibly a hardware device
-config val A config file
具体例子:
EXAMPLES
Just base64 encode a binary file:
openssl base64 -in file.bin -out file.b64
Decode the same file
openssl base64 -d -in file.b64 -out file.bin
Encrypt a file using AES-128 using a prompted password and PBKDF2 key
derivation:
openssl enc -aes128 -pbkdf2 -in file.txt -out file.aes128
Decrypt a file using a supplied password:
openssl enc -aes128 -pbkdf2 -d -in file.aes128 -out file.txt
-pass pass:<password>
Encrypt a file then base64 encode it (so it can be sent via mail for
example) using AES-256 in CTR mode and PBKDF2 key derivation:
openssl enc -aes-256-ctr -pbkdf2 -a -in file.txt -out file.aes256
使用OpenSSL搭建CA
信息安全防护的目标
- 保密性 Confidentiality
- 完整性 Integrity
- 可用性 Usability
- 可控制性Controlability
- 不可否认性 Non-repudiation
安全防护环节
- 物理安全:各种设备/主机、机房环境
- 系统安全:主机或设备的操作系统
- 应用安全:各种网络服务、应用程序
- 网络安全:对网络访问的控制、防火墙规则
- 数据安全:信息的备份与恢复、加密解密
- 管理安全:各种保障性的规范、流程、方法安全
安全攻击: STRIDE
- Spoofing 假冒
- Tampering 篡改
- Repudiation 否认
- Information Disclosure 信息泄漏
- Denial of Service 拒绝服务
- Elevation of Privilege 提升权限
5安全设计基本原则
- 使用成熟的安全系统
- 以小人之心度输入数据
- 外部系统是不安全的
- 最小授权
- 减少外部接口
- 缺省使用安全模式
- 安全不是似是而非
- 从STRIDE思考
- 在入口处检查
- 从管理上保护好你的系统
安全算法
- 认证
- 授权
- 审计
- 安全通信
- 对称加密
- 公钥加密
- 单向加密
- 认证协议
- 密码/数据嗅探
- 数据操作
- 验证操作
- 相当于邮寄明信片
- telnet、FTP、POP3等等;不安全密码
- http、smtp、NFS等等;不安全信息
- Ldap、NIS、rsh等等;不安全验证
对称加密算法
- 加密、解密使用同一个密钥,效率高
- 将原始数据分割成固定大小的块,逐个进行加密
- 密钥过多
- 密钥分发
- 数据来源无法确认10
非对称加密算法
- 用公钥加密数据,只能使用与之配对的私钥解密;反之亦然
- 数字签名:主要在于让接收方确认发送方身份
- 对称密钥交换:发送方用对方的公钥加密一个对称密钥后发送给对方
- 数据加密:适合加密较小数据
- 密钥长,加密解密效率低下
- RSA(加密,数字签名),DSA(数字签名),ELGamal
非对称加密
- 生成公钥/密钥对:P和S
- 公开公钥P,保密密钥S
- 使用接收者的公钥来加密消息M
- 将P(M)发送给接收者
- 使用密钥S来解密:M=S(P(M))
- 生成公钥/密钥对:P和S
- 公开公钥P,保密密钥S
- 使用密钥S来加密消息M
- 发送给接收者S(M)
- 使用发送者的公钥来解密M=P(S(M))
- 结合签名和加密
- 分离签名
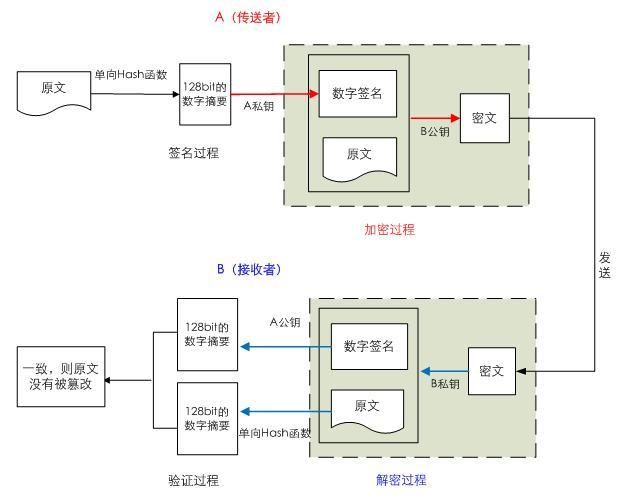
CA和证书
PKI: Public Key Infrastructure
- 签证机构:CA(Certificate Authority)
- 注册机构:RA
- 证书吊销列表:CRL
- 证书存取库
X.509:定义了证书的结构以及认证协议标准
- 版本号
- 序列号
- 签名算法
- 颁发者
- 有效期限
- 主体名称
- 主体公钥
- CRL分发点
- 扩展信息
- 发行者签名
证书获取
证书类型:
- 证书授权机构的证书
- 服务器
- 用户证书
- 使用证书授权机构
- 生成签名请求(csr)
- 将csr发送给CA
- 从CA处接收签名
- 自已签发自己的公钥
安全协议
- SSL: Secure Socket Layer
- TLS: Transport Layer Security
-
- 1995:SSL 2.0 Netscape
- 1996: SSL 3.0
- 1999: TLS 1.0
- 2006: TLS 1.1 IETF(Internet工程任务组) RFC 4346
- 2008:TLS 1.2 当前使用
- 2015: TLS 1.3
- 机密性,认证,完整性,重放保护
- 握手阶段(协商阶段):客户端和服务器端认证对方身份(依赖于PKI体系,利用数字证书进行身份认证),并协商通信中使用的安全参数、密码套件以及主密钥。后续通信使用的所有密钥都是通过MasterSecret生成。
- 应用阶段:在握手阶段完成后进入,在应用阶段通信双方使用握手阶段协商好的密钥进行安全通信
SSL/TLS
- Handshake协议:包括协商安全参数和密码套件、服务器身份认证(客户端身份认证可选)、密钥交换
- ChangeCipherSpec 协议:一条消息表明握手协议已经完成
- Alert 协议:对握手协议中一些异常的错误提醒,分为fatal和warning两个级别,fatal类型错误会直接中断SSL链接,而warning级别的错误SSL链接仍可继续,只是会给出错误警告
- Record 协议:包括对消息的分段、压缩、消息认证和完整性保护、加密等
- HTTPS 协议:就是“HTTP 协议”和“SSL/TLS 协议”的组合。HTTP over SSL”或“HTTP over TLS”,对http协议的文本数据进行加密处理后,成为二进制形式传输
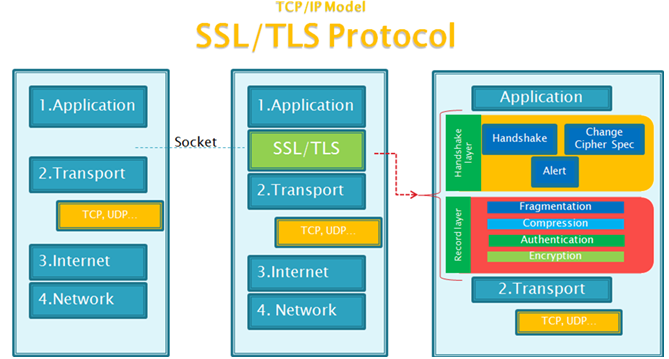
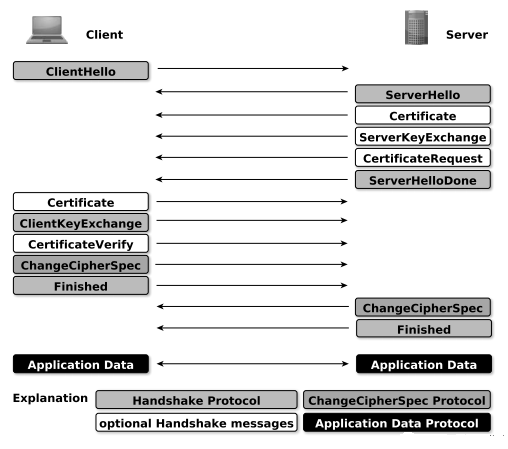
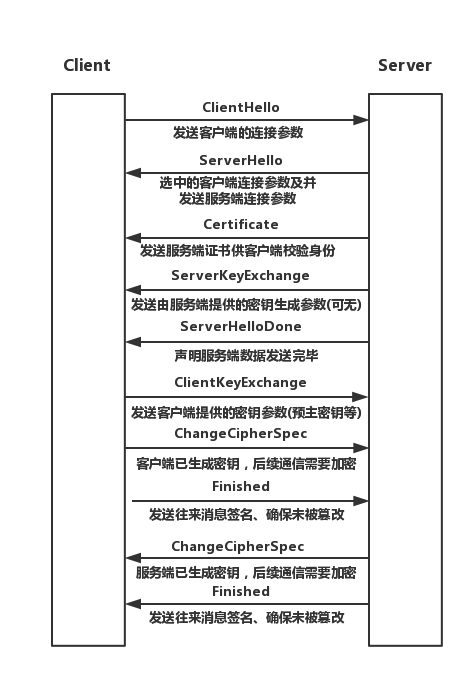
OpenSSL
- openssl: 多用途的命令行工具,包openssl
- libcrypto: 加密算法库,包openssl-libs
- libssl:加密模块应用库,实现了ssl及tls,包nss
SSH
- OpenSSH: ssh协议的开源实现,CentOS默认安装
- dropbear:另一个开源实现
- v1: 基于CRC-32做MAC,不安全;man-in-middle
- v2:双方主机协议选择安全的MAC方式
- 基于DH算法做密钥交换,基于RSA或DSA实现身份认证
- 基于password
- 基于key
本测试实现内容:
1、创建CA
生成一对用于制作自签证书的密钥
生成自签证书
2、客户端(相对于CA而言的客户端)
生成一对用于申请CA证书密钥
生成证书颁发请求;
将请求发给CA
3、CA端
签署证书
将签署完成的证书传送给客户端
说明:
本流程均在VMware实现

1、创建根CA
(1)创建CA所需要的文件
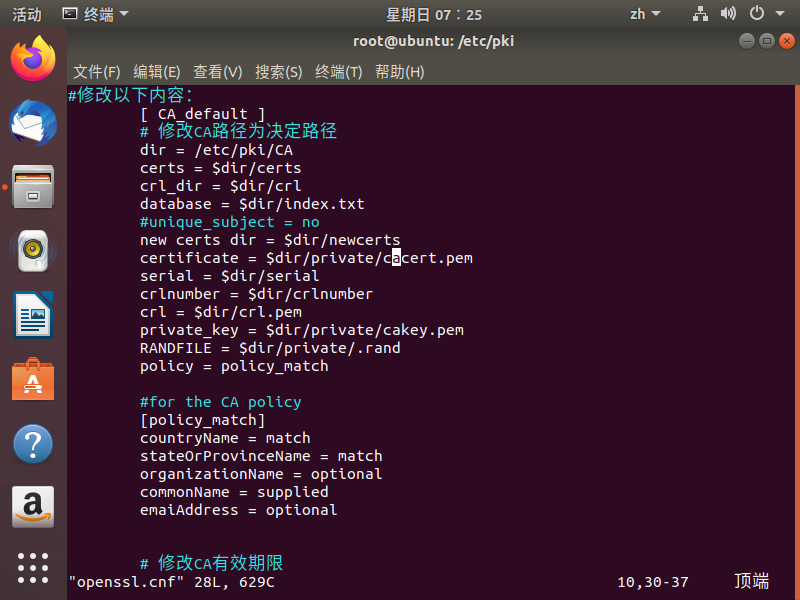
使用openssl工具创建CA证书和申请证书时,需要先查看配置文件,因为配置文件中对证书的名称和存放位置等相关信息都做了定义,具体可以参考

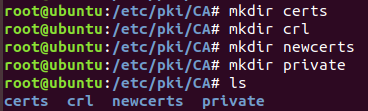
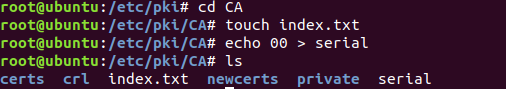
(2)生成私钥,私钥的文件名与存放位置都要和配置文件的设置相匹配



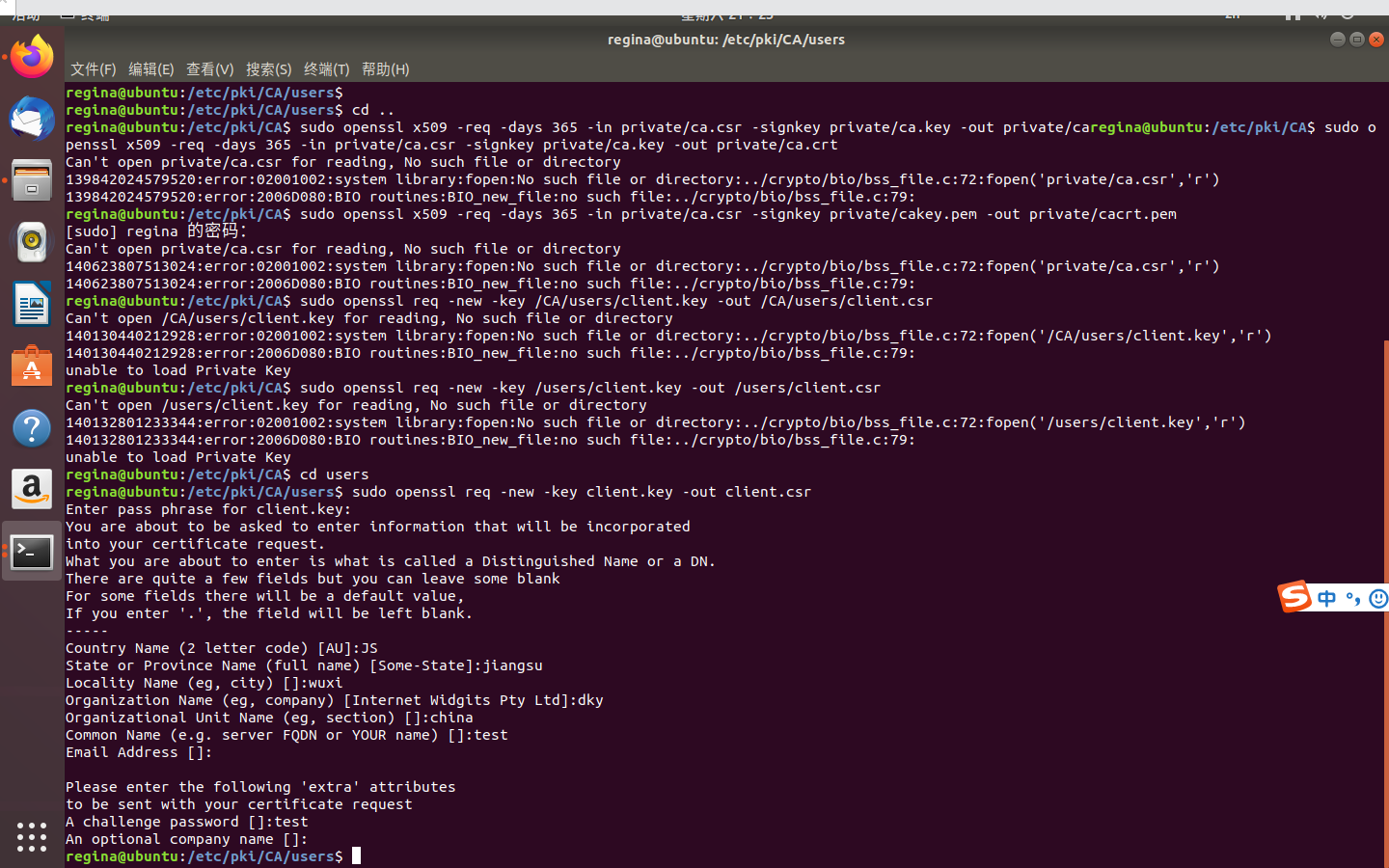

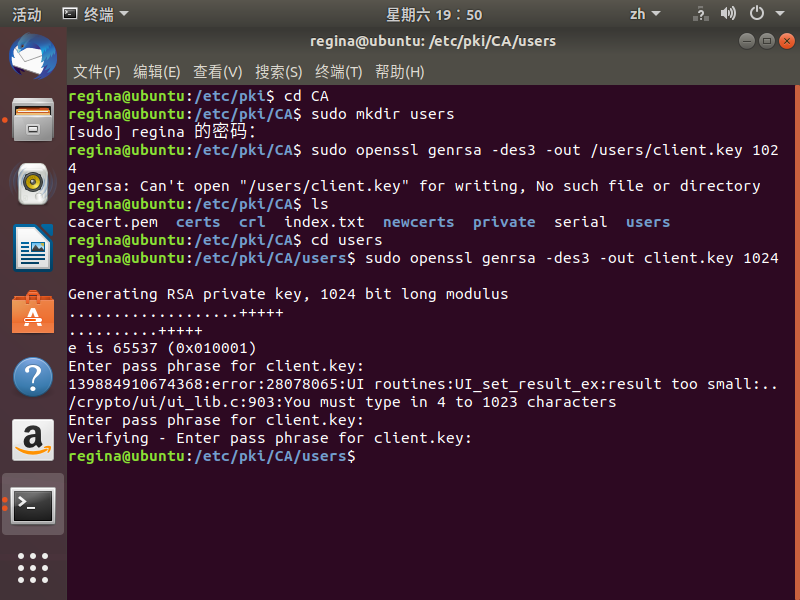
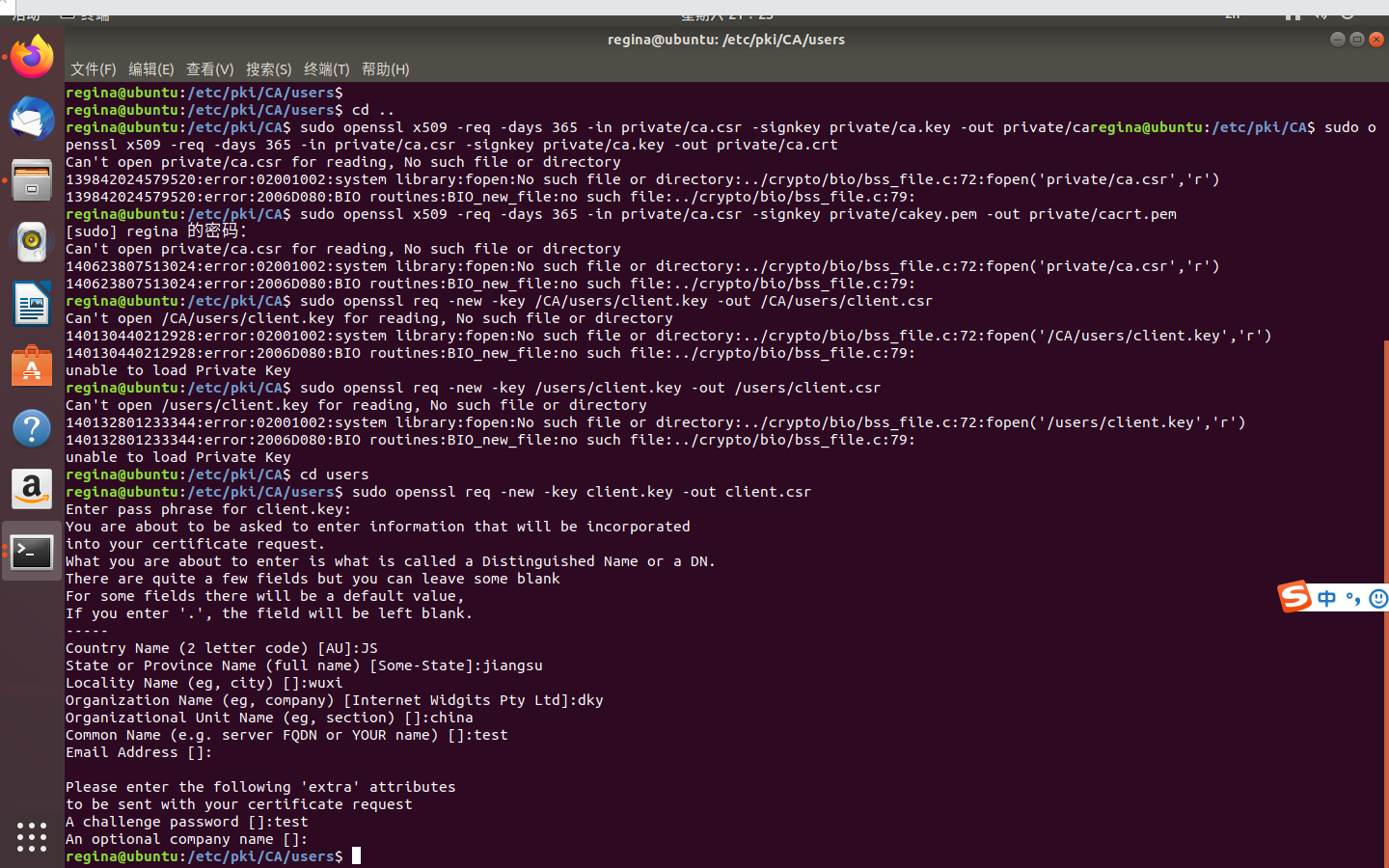
出现的问题

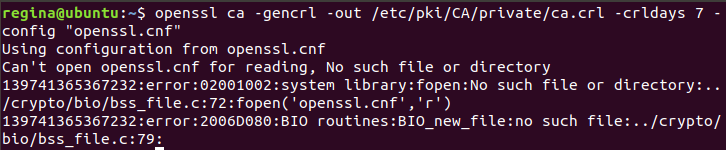
一开始在OpenSSL.cnf的调用时,发现无法打开OpenSSL.cnf,以为路径错误,随后修改为绝对路径
ca: Error on line 9 of config file "openssl.cnf"打开openssl.cnf文件,发现少了下划线

无法打开文件阅读,随后修改为管理员权限
sudo -s
后来反复尝试,在最后的使用CA证书的key为客户端key签名出现问题
sudo openssl ca -in /etc/pki/ca/users/client.csr -cert /etc/pki/ca/private/ca.crt -keyfile /etc/pki/ca/private/ca.key -out /etc/pki/ca/users/client.crt -config "/etc/pki/openssl.conf"
即如上命令,各种报错,由于反复尝试,我害怕虚拟机过于混乱就停止了。
本周总结:
相对于上周进展较快,开始时在重装虚拟机上花费较多时间,由于无法解决网络连接问题,最终选择再装一台虚拟机,经过此事情,告诫自己养成及时拍快照,能够恢复,减少安装的时间。我初步接触使用OpenSSL搭建CA,在网络上大量浏览资料,其实与我们的情况相适宜的很少,需要多尝试,多比较发现问题。虽然最后在为客户端证书签名的过程中,使用CA证书的key为客户端key签名出现问题,但是取得进展。
