1 请求报文和响应报文
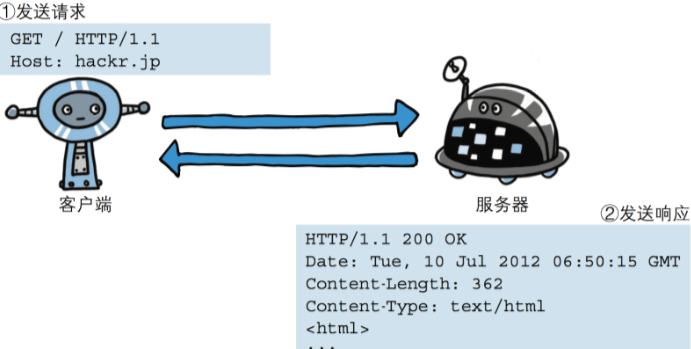
打开浏览器,当我们输入一个url,点击访问的时候会向目标服务器发送一个HTTP请求,请求的的时候会发生什么呢,会经过os七层,这里不赘述os七层通讯原理,可以理解为通过url请求目标服务器的一段具体的资源,可以理解为发送了一个请求,一个请求的本质就是向目标服务器上面发送了一些数据,这种浏览器于服务器之间交互的数据被称为报文。
-
请求报文:请求时浏览器发送的数据称为请求报文
-
响应报文:服务器收到了请求返回给浏览器的数据称为响应报文
提示:这里是BS架构, BS架构就是浏览器和后端服务器的交互,CS架构是客户端和服务端的交互,BS架构可以理解为CS架构的一个具体实现。浏览器就是客户端,后端服务器就是服务端。
报文中的GET请求和POST请求
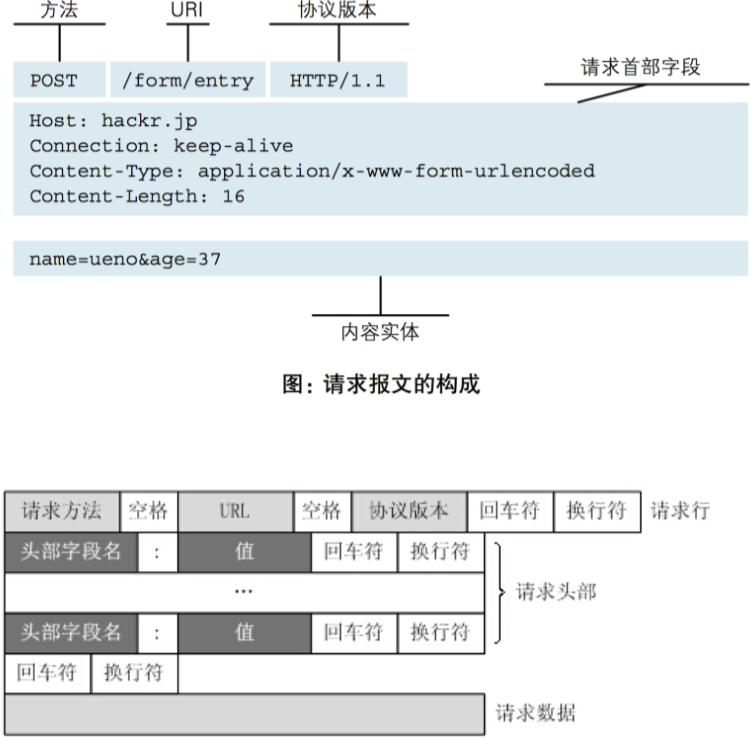
- GET提交的数据会放在URL之后,以?分割URL和传输数据,参数之间以&相连,如EditBook?name=test1&id=123456.
- POST方法是把提交的数据放在HTTP包的请求体中.
- GET提交的数据大小有限制(因为浏览器对URL的长度有限制)
- POST方法提交的数据没有限制。
- GET与POST请求在服务端获取请求数据方式不同。
报文实例:
'''
GET请求报文
# 请求首行
GET / HTTP/1.1
# get请求后面的参数
GET /?name=lqz&age=18 HTTP/1.1
# 请求头
Host: 127.0.0.1:8008
Connection: keep-alive
Cache-Control: max-age=0
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/65.0.3325.181 Safari/537.36
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9
Cookie: csrftoken=7xx6BxQDJ6KB0PM7qS8uTA892ACtooNbnnF4LDwlYk1Y7S7nTS81FBqwruizHsxF
'
# 请求体(get请求,请求体为空)
'''
'''
POST请求报文
# 请求首行
POST /?name=lqz&age=18 HTTP/1.1
# 请求头
Host: 127.0.0.1:8008
Connection: keep-alive
Content-Length: 21
Cache-Control: max-age=0
Origin: http://127.0.0.1:8008
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/65.0.3325.181 Safari/537.36
Accept:text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8
Referer: http://127.0.0.1:8008/?name=lqz&age=18
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9
Cookie: csrftoken=7xx6BxQDJ6KB0PM7qS8uTA892ACtooNbnnF4LDwlYk1Y7S7nTS81FBqwruizHsxF
# 请求体
name=lqz&password=123'
'''
2 request对象
2.1什么是request对象?
request对象封装解析了请求报文中的数据,其大部分功能是由依赖包werkzeug完成的,并且每个request对象都是线程隔离的,保证了数据的安全性。
2.2为什么要有request对象?
request对象解决了很多问题,各种请求的方法以及请求参数的格式都不一致,所以flask帮我们做了一个request对象,专门去解析各种方法以及各种格式的请求,以便于去开发使用。
2.3 requst对象的常用方法
request对象使用需要从flask模块中导入
from flask import Flask, request
2.3.1 使用request属性获取url
访问: http://127.0.0.1:5000/student_list/?name=mark :
表2-1 使用request的属性获取url
| 属性 | 解析值 | 属性 | 解析值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| path | u‘/student_list/’ | base_url | u'http://127.0.0.1:5000/student_list/' |
| full_path | u‘/student_list/?name=mark’ | url | u'http://127.0.0.1:5000/student_list/?name=mark' |
| host | u'127.0.0.1:5000' | url_root | u'http://127.0.0.1:5000/' |
| host_url | u'http://127.0.0.1:5000/' |
request的解析结果如下。
@app.route('/student_list/')
def student_list():
print(request.path) # 输出 /student_list/
print(request.full_path) # 输出 /student_list/?name=mark
print(request.host) # 输出 127.0.0.1:5000
print(request.host_url) # 输出 http://127.0.0.1:5000/
print(request.base_url) # 输出 http://127.0.0.1:5000/student_list/
print(request.url) # 输出 http://127.0.0.1:5000/student_list/?name=mark
print(request.url_root) # 输出 http://127.0.0.1:5000/
return 'request.urldemo测试'
2.3.2 其他request对象常用的属性和方法。
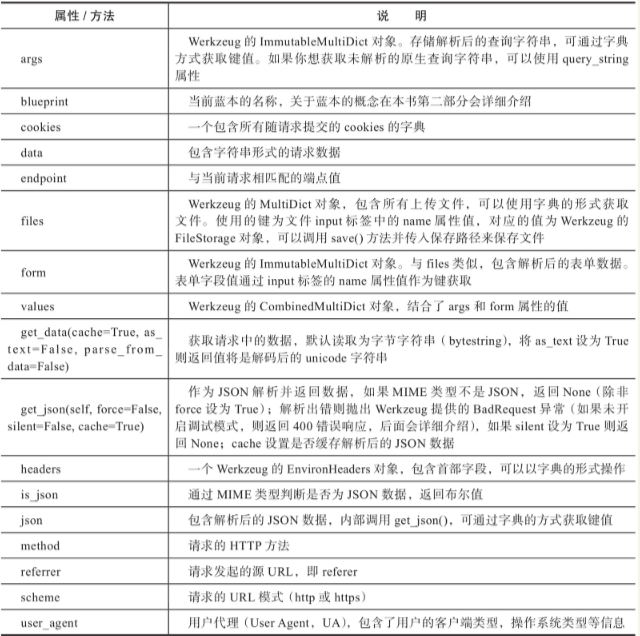
request里面有诸多的方法,先对requests这些方法有个初步印象,随着学习会慢慢接触到这些request常用的方法。
3 GET和post的实例:
3.1 常见的HTTP方法见下表:
| 请求 | 说明 | 请求 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | 获取服务器资源 | DELETE | 删除服务器资源 |
| POST | 处理服务器资源 | PATCH | 在服务器更新资源(客户端提供改变的属性) |
| PUT | 在服务器更新资源(客户端提供改变后的完整资源) |
一般常用的请求为GET和POST
3.2 GET请求:
GET请求一般用于在服务器上获取资源,不会更改服务器的状态。
GET实例:
@app.route('/', methods=['GET']) # 不写methods也可以 默认就接收get请求
def demo_get():
print(request.args.get('name')) # 输出 mark
return '{}请求'.format(request.method)
结合request对象,使用request.args属性获取get传来的参数,关于args我们在上一章已经论述过了。
关键词:
- 使用request.args属性获取get传来的参数,关于args在上一章已经论述过了。
- @app.route('/', methods=['GET']) 指定浏览器只能以GET方法访问服务端。
3.3 POST请求:
POST 请求: 会给服务器提交一些数据或者文件,会对服务器的状态产生影响。
在了解POST请求之前我们先了解一下render_termplate
3.3.1 render_template的简单使用
from flask import Flask, request, render_template
暂时只简单的理解render_template模块可以把html文件返回给浏览器并渲染。
如:
server.py
from flask import Flask, request, render_template
...
@app.route('/login/',methods=['GET'])
def login():
return render_template('login.html')
...
注意:render_template()会去flask根目录下的templates里面寻找文件,所以给的参数路径是相对路径。
关键词:render_template()中放的文件路径是与templates文件夹相对的路径
templates/login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>登录界面</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/login_request/" method="POST">
用户:<input type="text" name="username">
密码:<input type="text" name="password">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
关键词
-
form标签的
action指定的是跳转的页面。并且会自动拼接成http://127.0.0.1:5000/login_request/也就是本项目的: ip地址+端口+/login_request/
-
form标签的
method指定的是以什么方法请求服务端,此案例中请求的方法为POST方法。
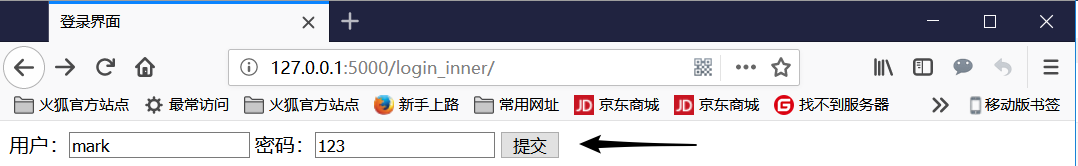
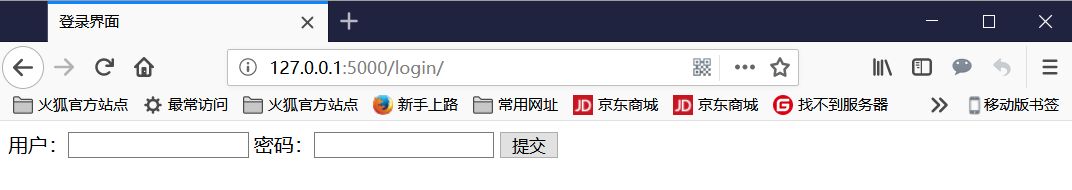
访问127.0.0.1:5000/login/ 后如下图
3.3.2 正式开始POST案例:
项目目录:
server.py
from flask import Flask, request, render_template
import config
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/login_request/',methods=['POST'])
def login_request():
print(request.form.get('username')) # 'mark'
print(request.form.get('password')) # '123'
if request.form.get('username') == 'mark' and request.form.get('password') == '123':
return 'success'
else:
return 'error'
@app.route('/login/',methods=['GET'])
def login():
return render_template('login.html')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
关键词:
- request.form是专门用来针对表单取数据的,在这里如果前端是以表单的形式提交的,可以使用request.form来取值
- @app.route() 中的 methods=['POST'] 代表只接收浏览器的POST请求
templates/login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>登录界面</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/login_request/" method="POST">
用户:<input type="text" name="username">
密码:<input type="text" name="password">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
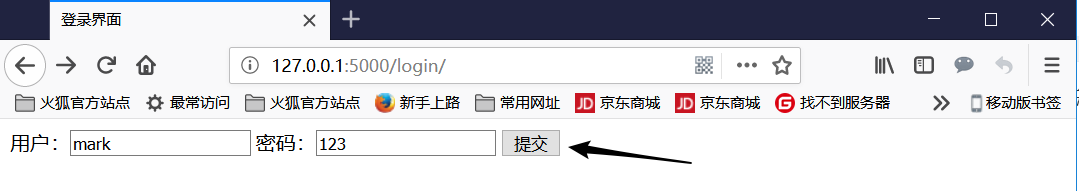
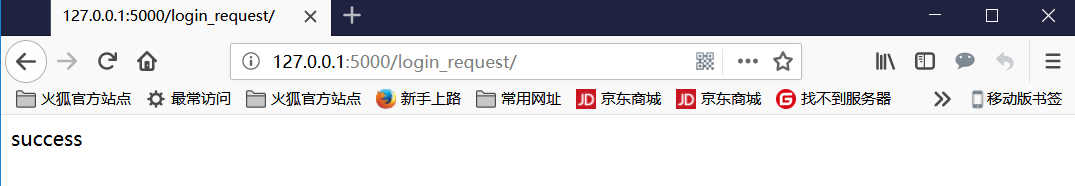
总体的逻辑是 :
- 首先访问127.0.0.1:5000/login/,默认是get请求。
- 然后
return render_template('login.html')返回给浏览器页面。 - 然后填写内容点击提交,以post方式请求 http://127.0.0.1:5000/login_request/。
- 然后进入
def login_request()视图函数 进行逻辑判断返回成功与否。
3.4 一个视图函数同时可以接收GET和POST请求
案例和3.3.2案例完成的业务逻辑是一样的,相当于简化了3.3.2的案例,把两个视图函数合并到一起,利用request.method属性可以获取字符串格式的请求方法。来区分本次请求是GET还是POST
实例:
server.py:
from flask import Flask, request, render_template
import config
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/login_inner/',methods=['POST','GET'])
def login_inner():
if request.method == 'GET': #判断本次请求是否为get请求
return render_template('login.html')
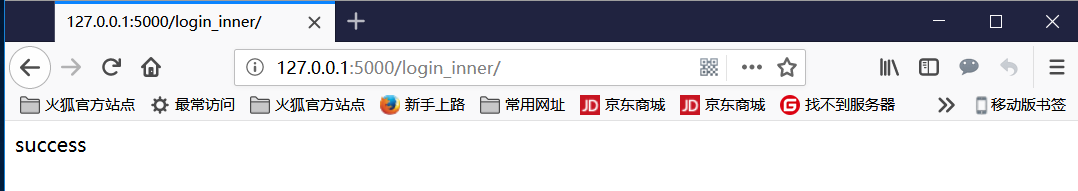
if request.form.get('username') == 'mark' and request.form.get('password') == '123':
return 'success'
return 'error'
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
关键词:
@app.route()的methods方法 指定该视图函数接收浏览器传过来的请求方法,可以指定多个。request.method获取字符串格式的请求方法
templates/login.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>登录界面</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="" method="POST">
用户:<input type="text" name="username">
密码:<input type="text" name="password">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
展示效果