C语言的基本概念
第一个C程序例子。
1 /* pun.c */ 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 4 int main(void) 5 { 6 printf("To C, or not to C: that is the question. "); 7 return 0; 8 }
其中,main函数的参数列表完整形式可以写成:
1 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 2 {
//用户代码
}
编译和链接(更多资料建议查阅GCC文档)
预处理:首先程序会被送交给预处理器(preprocessor)。预处理器执行行以#开头的命令(通常称为指令)。预处理器有点类似于编辑器,它可以给程序增加内容,也可以对程序进行修改。
编译 :预处理器修改后的程序现在可以进入编译器(compiler)了。编译器会把程序翻译成机器指令(即目标代码)。然而,这样的程序还是不可以运行的。
链接 :在最后一个步骤中,链接器(linker)把由编译器产生的目标代码和所需的其他附加代码整合在一起,这样才最终产生了完全可执行的程序。
扩展:Linux下C程序的编译于调试。
简单的C程序一般具有以下形式:
1 指令 2 3 int main(void) 4 { 5 语句 6 }
C语言极其依赖缩写词和特殊符号,这是C语言非常简洁(或者不客气地说含义模糊)的一个原因。即使最简单的C程序也依赖3个关键语言特性:指令(在编译前修改程序的编辑指令)、函数(被命名的可执行代码块,如main函数)、语句(程序运行时执行的命令)。
类型,用来说明变量所存储的数据的种类,它决定了分配的内存空间、取值范围以及可以对其进行的操作。
float型变量的缺陷:①进行算术运算时float型变量通常比int型变量慢;②float型变量所存储的数值往往只是实际数值的一个近似值。
变量必须先声明,后使用。
小技巧:当我们把一个包含小数点的常量赋值给float变量时,最好在该常量后面添加一个字母f(代表float)。
计算箱子的空间重量
1 /* dweight.c */ 2 /* Computes the dimensional weight of a 12" x 10" x 8" box */ 3 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 6 int main(void) 7 { 8 int height, length, width, volume, weight; 9 10 height = 8; 11 length = 12; 12 width = 10; 13 volume = height * length * width; 14 weight = (volume + 165) / 166; 15 16 printf("Dimensions: %dx%dx%d ", length, width, height); 17 printf("Volume(cubic inches): %d ", volume); 18 printf("Dimensional weight (pounds): %d ", weight); 19 20 return 0; 21 }
运行结果如下:

计算箱子的空间重量(改进版)
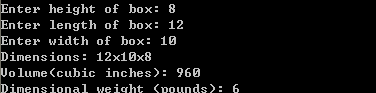
1 /* dweight2.c */ 2 /* Computes the dimensional weight of a box 3 from input provided by the user 4 */ 5 6 #include <stdio.h> 7 8 int main(void) 9 { 10 int height, length, width, volume, weight; 11 12 printf("Enter height of box: "); 13 scanf("%d", &height); 14 printf("Enter length of box: "); 15 scanf("%d", &length); 16 printf("Enter width of box: "); 17 scanf("%d", &width); 18 volume = height * length * width; 19 weight = (volume + 165) / 166; 20 21 printf("Dimensions: %dx%dx%d ", length, width, height); 22 printf("Volume(cubic inches): %d ", volume); 23 printf("Dimensional weight (pounds): %d ", weight); 24 25 return 0; 26 }
运行结果如下:
华氏温度转换为摄氏温度
1 /* celsius.c */ 2 /* Converts a Fahrenheit temperature to Celsius */ 3 4 #include <stdio.h> 5 6 #define FREEZING_PT 32.0f 7 #define SCALE_FACTOR (5.0f / 9.0f) 8 9 int main(void) 10 { 11 float fahrenheit, celsius; 12 13 printf("Enter Fahrenheit temperature: "); 14 scanf("%f", &fahrenheit); 15 celsius = (fahrenheit - FREEZING_PT) * SCALE_FACTOR; 16 printf("Celsius equivalent: %.1f ", celsius); 17 18 return 0; 19 }
运行结果如下:

标识符:在C语言中,标识符可以含有字母、下划线和数字,但是必须以字母或者下划线开头。C语言是区分大小写的,对标识符的最大长度没有限制。
练习题:
6 为什么说在标识符中使用多个相邻的下划线(如current___balance)不太合适?
因为人们不太能够准确判断下划线的个数,因此容易出错。