Problem subset: CircutsSequential LogicFinite State Machines.
Simple FSM 1 (asynchronous reset)
URL:Fsm1
Description
This is a Moore state machine with two states, one input, and one output. Implement this state machine. Notice that the reset state is B.
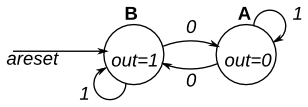
solution
- determine "next state" by input
in. - determine the sequential logic.
ref answer
module top_module (
input clk,
input in,
input areset,
output out
);
// Give state names and assignments. I'm lazy, so I like to use decimal numbers.
// It doesn't really matter what assignment is used, as long as they're unique.
parameter A=0, B=1;
reg state; // Ensure state and next are big enough to hold the state encoding.
reg next;
// A finite state machine is usually coded in three parts:
// State transition logic
// State flip-flops
// Output logic
// It is sometimes possible to combine one or more of these blobs of code
// together, but be careful: Some blobs are combinational circuits, while some
// are clocked (DFFs).
// Combinational always block for state transition logic. Given the current state and inputs,
// what should be next state be?
// Combinational always block: Use blocking assignments.
always@(*) begin
case (state)
A: next = in ? A : B;
B: next = in ? B : A;
endcase
end
// Edge-triggered always block (DFFs) for state flip-flops. Asynchronous reset.
always @(posedge clk, posedge areset) begin
if (areset) state <= B; // Reset to state B
else state <= next; // Otherwise, cause the state to transition
end
// Combinational output logic. In this problem, an assign statement is the simplest.
// In more complex circuits, a combinational always block may be more suitable.
assign out = (state==B);
endmodule
my answer
module top_module(
input clk,
input areset, // Asynchronous reset to state B
input in,
output out);//
parameter A=0, B=1;
reg state, next_state;
always @(*) begin // This is a combinational always block
// State transition logic
case(in)
1: next_state <= state; /* non-blocking is not appropriate here */
0: next_state <= ~state;
endcase
end
always @(posedge clk, posedge areset) begin // This is a sequential always block
// State flip-flops with asynchronous reset
if(areset)begin
state = B;
end else begin
state <= next_state;
end
end
// Output logic
// assign out = (state == ...);
assign out = state;
endmodule
Warning (10230): Verilog HDL assignment warning at top_module.v(22): truncated value with size 32 to match size of target (1) File: /var/www/verilog/work/vlgVSQ7KV_dir/top_module.v Line: 22
Truncating values occur when the right side of an assignment is wider than the left side and the upper bits are cut off. This can indicate a bug if there is a truncation you didn't expect, so check these carefully. The most common case where this isn't a bug is when you're using literals without a width (32 bits is implied), e.g., using assign a[1:0] = 1; instead of assign a[1:0] = 2'd1;.
Simple FSM 1 (synchronous reset)
URL:Fsm1s
description
This is a Moore state machine with two states, one input, and one output. Implement this state machine. Notice that the reset state is B.
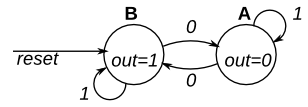
solution
- reset
- not reset: next_state; out.
ref answer
null.
my answer
// Note the Verilog-1995 module declaration syntax here:
module top_module(clk, reset, in, out);
input clk;
input reset; // Synchronous reset to state B
input in;
output out;//
reg out;
// Fill in state name declarations
reg present_state, next_state;
always @(posedge clk) begin
if (reset) begin
present_state <= 1;
out <= 1; /* mind the 'if'! I forget the out in 'if...' at first */
end else begin
case (present_state)
// Fill in state transition logic
1: next_state = in ? 1 : 0;
0: next_state = in ? 0 : 1;
endcase
// State flip-flops
present_state = next_state;
case (present_state)
// Fill in output logic
1: out = 1;
0: out = 0;
endcase
end
end
endmodule
Warning(for width.)
Simple FSM 2 (asynchronous reset)
URL:Fsm2
description
This is a Moore state machine with two states, two inputs, and one output. Implement this state machine.
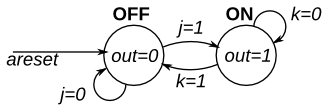
solution
- rst / switch to the next_state
- what is the next_state in the j-k ff?
ref answer
null
my answer
module top_module(
input clk,
input areset, // Asynchronous reset to OFF
input j,
input k,
output out); //
parameter OFF=0, ON=1;
reg state, next_state;
always @(*) begin
// State transition logic
case(state)
OFF:next_state=j;
ON:next_state=~k;
endcase
end
always @(posedge clk, posedge areset) begin
// State flip-flops with asynchronous reset
if(areset)begin
state = OFF;
end else begin
state = next_state;
end
end
// Output logic
assign out = (state == ON);
endmodule
Simple FSM 2 (synchronous reset)
URL:Fsm2s
description
This is a Moore state machine with two states, two inputs, and one output. Implement this state machine.
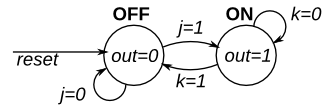
solution
similar to the previous one.
ref answer
null
my answer
module top_module(
input clk,
input reset, // Synchronous reset to OFF
input j,
input k,
output out); //
parameter OFF=0, ON=1;
reg state, next_state;
always @(*) begin
// State transition logic
case(state)
OFF: next_state = j;
ON : next_state = ~k;
endcase
end
always @(posedge clk) begin
// State flip-flops with synchronous reset
if(reset)begin
state <= OFF;
end else begin
state <= next_state;
end
end
// Output logic
assign out = (state == ON);
endmodule