文章更新时间:2020/04/06
一、一个例子
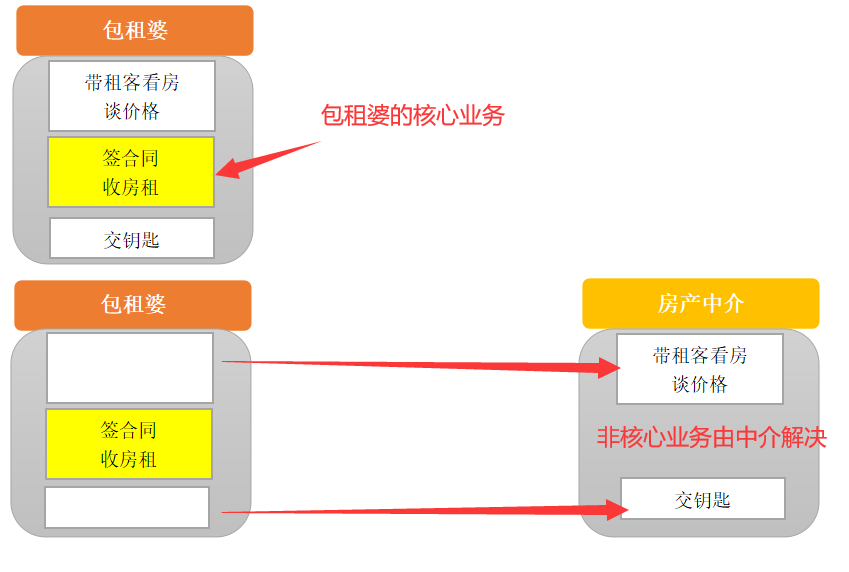
在上面的例子中,包租婆的核心业务就是签合同,收房租,那么这就够了,灰色框起来的部分都是重复且边缘的事,交给中介商就好了,这就是 AOP 的一个思想:让关注点代码与业务代码分离!
例子解析:
1.在 Package【service】下新建一个【LandlordService】类(核心业务)
/** * 包租婆关心的业务~(模拟核心业务) */ @Component("landlord") public class LandlordService { public void service() { // 仅仅只是实现了核心的业务功能 System.out.println("签合同"); System.out.println("收房租"); } }
2.在 Package【aspect】下新建一个中介商【BrokerAspect】类(周边功能)
/** * 包租婆不关心~ * 中介关心的业务~(模拟周边功能) */ @Component @Aspect class BrokerAspect { @Before("execution(* service.LandlordService.service())") public void before() { System.out.println("带租客看房"); System.out.println("谈价格"); } @After("execution(* service.LandlordService.service())") public void after() { System.out.println("交钥匙"); } }
3.在 applicationContext.xml 中配置自动注入,并告诉 Spring IoC 容器去哪里扫描这两个 Bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="aspect"/> <context:component-scan base-package="service"/> <!--声明自动为spring容器中那些配置@Aspect切面的bean创建代理,织入切面。--> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> </beans>
4.编写测试类
public class TestSpring { @Test public void test() { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); LandlordService landlord = (LandlordService) context.getBean("landlord", LandlordService.class); landlord.service(); } }
5.查看执行结果

二、使用注解来开发 Spring AOP
第一步:选择连接点
Spring 是方法级别的 AOP 框架,我们主要也是以某个类额某个方法作为连接点,另一种说法就是:选择哪一个类的哪一方法用以增强功能。
.... public void service() { // 仅仅只是实现了核心的业务功能 System.out.println("签合同"); System.out.println("收房租"); } ....
这里就选择上述 LandlordService 类中的 service() 方法作为连接点。
第二步:创建切面
选择好了连接点就可以创建切面了,我们可以把切面理解为一个拦截器,当程序运行到连接点的时候,被拦截下来,在开头加入了初始化的方法,在结尾也加入了销毁的方法而已,在 Spring 中只要使用 @Aspect 注解一个类,那么 Spring IoC 容器就会认为这是一个切面了:
/** * 包租婆不关心~ * 中介关心的业务~(模拟周边功能) */ @Component @Aspect class BrokerAspect { @Before("execution(* service.LandlordService.service())") public void before() { System.out.println("带租客看房"); System.out.println("谈价格"); } @After("execution(* service.LandlordService.service())") public void after() { System.out.println("交钥匙"); } }
PS: 被定义为切面的类仍然是一个 Bean ,需要 @Component 注解标注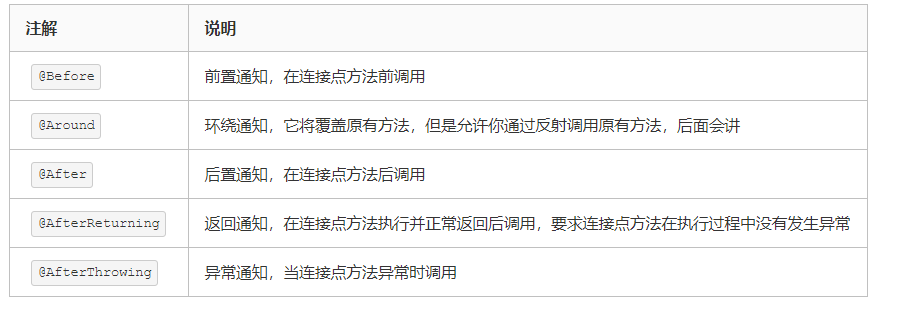
第三步:定义切点
在上面的注解中定义了 execution 的正则表达式,Spring 通过这个正则表达式判断具体要拦截的是哪一个类的哪一个方法:
execution(* service.LandlordService.service())
依次对这个表达式作出分析:
- execution:代表执行方法的时候会触发
- * :代表任意返回类型的方法
- service.LandlordService:代表类的全限定名
- service():被拦截的方法名称
第四步:测试 AOP
我们来探讨一下环绕通知,这是 Spring AOP 中最强大的通知,因为它集成了前置通知和后置通知,它保留了连接点原有的方法的功能,所以它及强大又灵活,让我们来看看:
/** * 包租婆不关心~ * 中介关心的业务~(模拟周边功能) */ @Component @Aspect class BrokerAspect { // 注释掉之前的 @Before 和 @After 注解以及对应的方法 // @Before("execution(* service.LandlordService.service())") // public void before() { // System.out.println("带租客看房"); // System.out.println("谈价格"); // } // // @After("execution(* service.LandlordService.service())") // public void after() { // System.out.println("交钥匙"); // } // 使用 @Around 注解来同时完成前置和后置通知 @Around("execution(* service.LandlordService.service())") public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) { System.out.println("带租客看房"); System.out.println("谈价格"); try { joinPoint.proceed(); } catch (Throwable throwable) { throwable.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("交钥匙"); } }
运行测试代码,结果仍然正确:
三、使用 XML 配置开发 Spring AOP
注解是很强大的东西,但基于 XML 的开发我们仍然需要了解,我们先来了解一下 AOP 中可以配置的元素:

有了之前通过注解来编写的经验,并且有了上面的表,我们将上面的例子改写成 XML 配置很容易(去掉所有的注解):
<!-- 装配 Bean--> <bean name="landlord" class="pojo.Landlord"/> <bean id="broker" class="aspect.Broker"/> <!-- 配置AOP --> <aop:config> <!-- where:在哪些地方(包.类.方法)做增加 --> <aop:pointcut id="landlordPoint" expression="execution(* pojo.Landlord.service())"/> <!-- what:做什么增强 --> <aop:aspect id="logAspect" ref="broker"> <!-- when:在什么时机(方法前/后/前后) --> <aop:around pointcut-ref="landlordPoint" method="around"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config>
运行测试程序,看到正确结果:
