24、静态属性与静态方法在类中的使用
需求:在玩CS的时候不停有伙伴加入,那么现在想知道共有多少人在玩,这个时候就可能用静态变量的方法来处理
利用原有的全局变量的方法来解决以上的问题
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); $total = 0; class Game { public $name; public function __construct($name) { $this->name = $name; } public function joinGame() { global $total; echo "{$this->name}小朋友加入了游戏...<br/>"; $total++; } } $child1 = new Game('小明'); $child2 = new Game('小红'); $child3 = new Game('小刚'); $child1->joinGame(); $child2->joinGame(); $child3->joinGame(); echo "现在有{$total}个小朋友在玩游戏"; /** * 输出以下内容 * 小明小朋友加入了游戏... * 小红小朋友加入了游戏... * 小刚小朋友加入了游戏... * 现在有3个小朋友在玩游戏 */ ?>
静态变量是类的静态属性,可以被所有对象共享,利用静态变量的方法来解决以上的问题
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); class Game { public $name; public static $total = 0; public function __construct($name) { $this->name = $name; } private function joinGame() { echo "{$this->name}加入到了游戏中...<br>"; self::$total++; } public function getPersonNum() { echo "现在总共有" . self::$total . "个人加入到游戏中"; } public function __call($class_name, $params) { if (method_exists($this, $class_name)) { return call_user_func_array([$this, $class_name], $params); } return '没有这种方法'; } } $p1 = new Game('小明'); $p2 = new Game('小红'); $p3 = new Game('小刚'); $p1->joinGame(); $p2->joinGame(); $p3->joinGame(); $p1->getPersonNum(); ?>
如何访问静态变量归集
静态变量在类里面的两种表示方法1、self::$静态变量名 2、类名::$静态变量名(::表示范围解析符),如上面的可能表示为:self::$total或者Game::$total这两种方式
在类的外部访问静态变量,可以使用:类名::$静态变量名,但是前提是这个静态属性必需是公开的(public)
self与$this的区别 self是类的范畴(指向类),而$this是对象的实例(指向类的实例)
静态方法
如果程序员在类中需要对静态属性进行操作,那么可以定义静态方法进行操作,换言之静态方法主要是操作静态属性的
在类的外部访问静态方法有三种方式如下例子
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); class Person { public $name; public static $address = '中国'; public function __construct($name) { $this->name = $name; } public static function getAddress() { return self::$address; } } //建议使用第一种方式,不建议使用第二种第三种方式 //方式一 echo Person::getAddress(); //输出 中国 //方式二 $p = new Person('小明'); echo $p::getAddress(); //输出 中国 //方式三 echo '<br>'; echo $p->getAddress(); //输出 中国 ?>
在类的内部访问类的静态方法的三种方式
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); class Person { public $name; public static $address = '中国'; public function __construct($name) { $this->name = $name; } public static function getAddress() { return self::$address; } public function getStaticMethod() { //方式一 echo self::getAddress(); echo '<br>'; //方式二 echo Person::getAddress(); echo '<br>'; //方式三 echo $this->getAddress(); } } $p = new Person('leo'); $p->getStaticMethod(); //输出 中国 中国 中国 ?>
25、利用静态变量或者静态方法来实现单例模式(注意这里还没有规避来自继承的风险)
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); class Person { public $name; public $age; static $pe; /**把构造函数设置为私有的方法,以便更好的进行单例模式 * Person constructor. * @param $name * @param $age */ private function __construct($name, $age) { $this->name = $name; $this->age = $age; } //阻止克隆 private function __clone() { } // /**第一种写法利用静态方法来实例化类 // * @param $name // * @param $age // * @return Person // */ // static function getPerson($name, $age) // { // if (!self::$pe) { // self::$pe = new Person($name, $age); // } // return self::$pe; // } /**第二种写法利用静态方法来实例化类(常用的方法) * @param $name * @param $age * @return Person */ static function getPerson($name, $age) { if (!self::$pe instanceof self) { self::$pe = new self($name, $age); } return self::$pe; } } $p1 = Person::getPerson('小明', 30); $p2 = Person::getPerson('小红', 30); $p3 = Person::getPerson('小刚', 30); var_dump($p1, $p2, $p3); //输出三个对象,都是一个变量 object(Person)#1 (2) { ["name"]=> string(6) "小明" ["age"]=> int(30) } object(Person)#1 (2) { ["name"]=> string(6) "小明" ["age"]=> int(30) } object(Person)#1 (2) { ["name"]=> string(6) "小明" ["age"]=> int(30) } ?>
26、oop编程的三大特征
oop编程的三大特征:封装性,继承,多态,说明一下,在Php的面向对象编程中,多态提及的不多,因为Php天生就是多态的语言
封装性细节普通属性要定义成public,protected,private三者之一,否则会报错,如果用var(php4添加的定义方法)定义,则视为Public,静态属性可以不写这个修辞符,但是默认为public。
封装性的重点---对象连用祥见以下例子
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); class Student { public $name; private $class_name; public function __construct($name, $class) { $this->name = $name; $this->class_name = $class; } /**获取班级的函数 * @return mixed */ public function getClass() { return $this->class_name; } /**设置班级的函数 * @param $new_class */ public function setClass($new_class) { $this->class_name = $new_class; } } class ClassName { public $name; private $school_name; public function __construct($name, $school) { $this->name = $name; $this->school_name = $school; } /**获取学校的函数 * @return mixed */ public function getSchool() { return $this->school_name; } /**设置学校的函数 * @param $new_school */ public function setSchool($new_school) { $this->school_name = $new_school; } } class School { public $name; public function __construct($name) { $this->name = $name; } } $school = new School('精英学院'); //把school这个对象作为一个参数传入函数 $className = new ClassName('精英一班', $school); //把班级这个对象作为一个参数传入函数 $stu = new Student('Leo', $className); //注意这种连续调用的情况 var_dump($stu->getClass()->getSchool()); ?>
oop编程的继承
为了解决代码的冗余,实现代码的复用,oop编程可以实现继承(基类,扩展类=》父类,子类)用关键字extends来实现继承
注意:如果在子类里覆盖了父类的方法那么要用关键字parent::方法名(调用的是类里面的方法,而不是实例化后的方法)或者用父类名::方法名来调用(可以是静态方法,也可以是普通方法),但是如果子类里面没有覆盖父类里面的方法,那么可能用$this->方法名来调用;parent::属性名可以访问父类的静态属性,但是不能访问父类里的属性因为那个是要实例化后才有的属性祥见例子
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); class Student { public $name; public $classNum; protected $score; protected $isTest; public function __construct($name, $classNum) { $this->name = $name; $this->classNum = $classNum; } public function testing() { echo '现在正在测试...'; $this->isTest = true; $this->score = mt_rand(10, 100); } public function getScore() { return $this->score; } } class PrimaryStudent extends Student { public $addFood; public function __construct($name, $className, $food) { parent::__construct($name, $className); $this->addFood = $food; } public function getAll() { return [ 'score' => parent::getScore(), 'food' => $this->addFood ]; } } $p = new PrimaryStudent('leo', 20, 'brake'); $p->testing(); echo '<br/>'; var_dump($p->getAll()); //输出 现在正在测试... //array(2) { ["score"]=> int(52) ["food"]=> string(5) "brake" } ?>
子类对父类方法的重写,属性保证方法名和参数是一致的,否则会报错,如果参数添加了类型约束,那么,子类的类型约束必需和父类是一致的,否则也是会报错的
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); class Person { public $name; public function __construct($name) { $this->name = $name; } public function sayHello(string $str) { echo 'hello' . $str; } } class Student extends Person { //重写方法的时候,函数名和参数必需和父类的一致,否则会报错 public function sayHello(string $str) { echo 'are you ok???' . $str; } } $p = new Student('leo'); $p->sayHello('haha'); //输出 are you ok???haha ?>
子类对父类进行重写的时候,函数的修饰符可以放大,但是不能缩小,比如protected可以变成public但是不能变成private,并且在子类调用父类的方法中,子类继承了父类的属性,那么会输出子类的属性值,当子类没有调用父类的属性时,那么会输出父类的值
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); class A { public $num1 = 999; protected $num2; private $num3 = 888; public function __construct(int $num) { $this->num2 = $num; } public function showNum1() { return $this->num1; } public function showNum2() { return $this->num2; } public function showNum3() { return $this->num3; } public function setNum3() { $this->num3 = 888666; } } class B extends A { public $num1 = 333; public $num2 = 666; public $num3 = 777; } class C extends A { } $t = new B(111); $f = new C(789); echo $t->showNum1() . '<br>'; //输出 333 echo $t->showNum2() . '<br>'; //输出 111 $f->setNum3(); //改变的是自己继承的父类,不会改变其他类的父类 echo $t->showNum3() . '<br>'; //输出 888 子类没有继承父类的属性,输出的是父类的属性值 echo $f->showNum3(); //输出 888666 子类没有继承父类的属性,输出的是父类的属性值 ?>
27、抽象类
抽象类的存在的价值是,让其他类来继承他,并实现它写的抽象方法,它的价值在于设计
抽象类的6个细节
1、抽象类不能被实例化,如果里面的静态方法不是抽象的,那么是可以调用静态方法的
2、抽象类可以没有抽象方法
3、抽象类中可以有普通的成员方法,属性和常量
4、如果一个类中有了抽象方法,则这个类必需声明为abstract
5、抽象方法不能有方法体,即不能有{}
6、如果一个类,继承了某个抽象类,则该类,必须把这个抽象类所有的抽象方法全部实现(除非,该类自已也声明为abstract类);并且实现的过程中,如果基类里的抽象方法里有形参,那么继承的方法里面也需要有形参,不能省略。
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); /**抽象类,实现两个方法 * Class Person */ abstract class Person { public $name; public $age; abstract public function cry(); abstract public function run(); } class student extends Person{ public function __construct($name, $age) { $this->name = $name; $this->age = $age; } public function cry() { return "my name is {$this->name}"; } public function run() { return "I can run"; } } $student1 = new student('leo', 30); var_dump($student1); //输出 object(student)#1 (2) { ["name"]=> string(3) "leo" ["age"]=> int(30) } echo $student1->cry(); //输出 my name is leo echo $student1->run(); //输出 I can run ?>
28、接口
接口的细节:注意接口的命名规则是第一个字母小写,一般以i开头,其他的按照驼峰命名规则进行命名
1、接口不能实例化
2、接口中的所有方法,都不能实现,即不能有方法体
3、一个类可以实现多个接口,并且需要把所有接口的方法都实现
4、一个接口中,可以有属性,但是必需是常量,并且这个常量的访问方法与静态变量的方法一样
5、接口中的所有方法都是Public,默认即Public;
6、一个接口可以继承其他接口,可以多继承,中间用逗号隔开,但是接口是不能继承类的(注意:php是继承的,即一个类只能有一个父类,不能有多个父类,但接口就不一样了);
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); /**人类的接口 * Interface Person */ interface Person{ const STATUS = true; public function run(); public function cry(); } /**动物的接口 * Interface Animal */ interface Animal { public function eating(); } /**实现人类的接口与动物的接口 * Class Student */ class Student implements Person, Animal { public $name; public $age; public function __construct($name, $age){ $this->name = $name; $this->age = $age; } public function run() { echo "{$this->name} can run<br>"; } public function cry() { echo "he is {$this->age} year old, but also cry <br/>"; } public function eating() { echo "{$this->name} can eating"; } } class Ask { public $person; public function __construct(Student $st){ $this->person = $st; } public function init() { $this->person->cry(); $this->person->run(); $this->person->eating(); } } $s=new Student('leo',3); $t=new Ask($s); $t->init(); /** * 输出 * he is 3 year old, but also cry * leo can run * leo can eating */ ?>
29、关键字 final在类中的使用
A、当程序员不希望某个成员方法被子类重写时,我们可以将该方法修饰为final方法。
B、当程序员不希望某个类被继承,我们可以将该类修饰为final类
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); final class A { public $name; public $age; public function __construct($name, $age) { $this->name = $name; $this->age = $age; } } class B extends A { } //会报错,因为final类是不允许被继承的 class A { public $name; public $age; public function __construct($name, $age) { $this->name = $name; $this->age = $age; } final public function init() { echo "my name is {$this->name} I'm {$this->age} year old"; } } class B extends A { public function init() { echo 'are you ok???'; } } //会报错,因为有final修饰的方法是不能被重写的 ?>
final关键字的使用细节说明
a、final 不能够修饰成员属性(变量);
b、final 方法不能被重写,但可以被继承;
c、一般来说,final类中不会出现final方法,因为final类都不能被继承,也就不会去重写final方法
d、final类是可以被实例化的
30、类常量
类中的常量的定义示例
class 类名 {
const 常量名 = 常量值
}
常量的命名规范:全部大写,并且用下划线隔开
常量不能是对象,也不能是资源,其他类型的可以
常量的访问参考静态变量的访问
31、类的其他知识点的学习
a、类的遍历 ,在类的外部对类进行遍历,那么可以遍历到所有public修饰的属性值,但是在类的内部对类进行遍历,那么可以遍历所有的属性值(不含方法)即Public,protected,private三种属性值
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); class A { public $name; public $age; protected $sex; private $salary; public function __construct($name, $age, $sex, $salary) { $this->name = $name; $this->age = $age; $this->sex = $sex; $this->salary = $salary; } public function count() { foreach ($this as $key => $val) { echo "{$key} => {$val}<br/>"; } } } $a = new A('leo', 33, 'man', 20000); foreach ($a as $key => $val) { echo "{$key} => {$val}<br/>"; } //输出 //name => leo //age => 33 $a->count(); //输出 //name => leo //age => 33 //sex => man //salary => 20000 ?>
b、内置标准类
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); $a = new stdClass(); var_dump($a); //输出 object(stdClass)#1 (0) { } //如果有这个需求,那么可以往里面填充数据 $a->name = 'are you ok???'; $a->age = 24; var_dump($a); //输出 object(stdClass)#1 (2) { ["name"]=> string(13) "are you ok???" ["age"]=> int(24) } ?>
c、类与数组或者其他形式的值进行互相转换
当类转成数组时,私有的变量仍然不能访问
数组或者其他形式的变量转成类时,会转成标准类
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); $array = [ 'name' => 'aaa', 'age' => 30, 'say' => function () { echo 'are you ok???'; } ]; var_dump($array); echo '<br>'; //输出 array(3) { ["name"]=> string(3) "aaa" ["age"]=> int(30) ["say"]=> object(Closure)#1 (0) { } } $array['say'](); //输出 are you ok??? $obj=(object) $array; echo '<br>'; var_dump($obj); //输出 object(stdClass)#2 (3) { ["name"]=> string(3) "aaa" ["age"]=> int(30) ["say"]=> object(Closure)#1 (0) { } } ?>
d、类的序列化与类的反序列化
如果需要把实例化后的类存储起来,那么可以把类序列化成字符串进行存储(要用到关键函数 serialize);
当需要把序列化好的类进行返序列化使用那么可以进行反序列化(要用关键函数 unserialize);
注意在使用反序列化好的类时,要把原有的类的方法引入到当前文件,直接用require_once或者include_once即可
魔术方法__sleep和__wakeup
__sleep 方法定义在需要被系列化的类里,并且本方法返回的是一个数组,该数组是指定哪些变量需要被序列化,静态变量不能被指定,是给程序员一个机会在序列化前改变一些变量
__wakeup方法也是定义在需要被系列化的类里,是给程序员一个机会在反序列化前改变一些变量
定义类的文件
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); class A { public $name; public $age; static $salary; public function __construct($name, $age, $salary) { $this->name = $name; $this->age = $age; self::$salary = $salary; } public function introduce() { echo "hello , my name is {$this->name},I'm {$this->age} years old"; } public function __sleep() { //改变序列化前name的值为aaa $this->name = 'aaa'; //指定两个变量需要被序列化,返回值一定要是一个数组 return ['name', 'age']; } public function __wakeup() { //改变返序列化前age的值为40; $this->age = 40; } } $a = new A('leo', 30, 10000); //进行序列化 $_a = serialize($a); //把序列化后的字符串写入文件 file_put_contents('./yftest.txt', $_a); ?>
引用类的文件
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); //注意一定要引入原本的类,否则无法引用已经实例化后的数据; require_once './index.php'; $str = file_get_contents('./yftest.txt'); //进行反序列化操作 $a = unserialize($str); var_dump($a); //输出 object(A)#2 (2) { ["name"]=> string(3) "aaa" ["age"]=> int(40) } var_dump($a::$salary); //输出 10000; $a->introduce(); //输出 hello , my name is aaa,I'm 40 years old ?>
E、traits的讲解(重点)
如果有个些类根据定制按需要决定是否拥有指定的方法,那么不能用继承,这个时候就需要用到traits技术了
使用时用关键字use 类名(traits类名);
注意:
1、默认时traits里的修饰是Public,如果是private 或者是 protected,那么就没有办法引用。
2、如果trait里面的方法与类的父类的名字重合,相当于对类的方法的重写,那么就必需遵循类重写的规则(规定的参数和类型必需一致)。
3、trait类里可以使用类里的方法及静态方法,及变量,静态变量,类里同时也可以访问以上的变量和方法。
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); class A { public $name; public $age; public function __construct($name, $age) { $this->name = $name; $this->age = $age; } public function introduce() { echo "this is A's method"; } } trait Common { static $ask = 'are you ok???'; public function introduce() { echo "你好啊,我的名字啊{$this->name},我今年{$this->age}岁了<br/>"; //输出 你好啊,我的名字啊leo,我今年28岁了 var_dump($this); //输出 object(B)#1 (2) { ["name"]=> string(3) "leo" ["age"]=> int(28) } echo self::$cry; //输出 www echo self::$ask; //输出 are you ok??? } } class B extends A { use Common; //引用trait类 static $cry = 'www'; public function test() { echo self::$ask; } } class C extends A { } $b = new B('leo', 28); //C类里没有引用,所以C的实例没有那个方法 $c = new C('john', 50); $b->introduce(); $b->test(); //输出 are you ok??? ?>
F、反射类
所以的类都是一个对象,可能通过建立反射类来返回所有类的信息
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); class A { public $name; public $age; public function __construct($name, $age) { $this->name = $name; $this->age = $age; } public function __toString() { $ref = new ReflectionClass($this); echo $ref->getName(), '<br/>'; //输出 A var_dump($ref->getMethods()); //获取所有的方法 //输出 array(2) { [0]=> object(ReflectionMethod)#3 (2) { ["name"]=> string(11) "__construct" ["class"]=> string(1) "A" } [1]=> object(ReflectionMethod)#4 (2) { ["name"]=> string(10) "__toString" ["class"]=> string(1) "A" } } var_dump($ref->getProperties()); //获取所有的属性 //输出 array(2) { [0]=> object(ReflectionProperty)#4 (2) { ["name"]=> string(4) "name" ["class"]=> string(1) "A" } [1]=> object(ReflectionProperty)#3 (2) { ["name"]=> string(3) "age" ["class"]=> string(1) "A" } } return ''; } } $a = new A('LEO', 23); echo $a; ?>
通过反射机制来实例化类,并且调用方法
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); class A { public $name; public $age; public function __construct($name, $age) { $this->name = $name; $this->age = $age; } public function sayHello($name) { echo "hello {$name}, my name is {$this->name} I'm {$this->age} years old"; } } //创建反射机制对象 $reflect_obj = new ReflectionClass('A'); //通过反射机制创建实例 $reflect_instance = $reflect_obj->newInstance('leo', 30); //得到返射方法,这个时候框架就可以通过这个对象做中间处理,比如判断是否是公有的,私有的等等 $reflect_method_sayHello = $reflect_obj->getMethod('sayHello'); //进行返射调用该方法 $reflect_method_sayHello->invoke($reflect_instance, 'jim'); ?>
模拟TP的控制器原理
<?php header('content-type:text/html;charset=utf8'); ini_set('display_errors', true); class IndexAction { public function Index() { echo 'this is index method<br/>'; } public function beforeIndex() { echo 'this is beforeIndex method<br/>'; } public function afterIndex() { echo 'this is afterIndex method<br/>'; } public function test() { echo 'this is test method<br/>'; } } if (class_exists('IndexAction')) { $reflect_obj = new ReflectionClass('IndexAction'); $reflect_instance = $reflect_obj->newInstance(); if ($reflect_obj->hasMethod('Index')) { $reflect_obj_index = $reflect_obj->getMethod('Index'); if ($reflect_obj_index->isPublic()) { if ($reflect_obj->hasMethod('beforeIndex')) { $reflect_obj_before_index = $reflect_obj->getMethod('beforeIndex'); $reflect_obj_before_index->isPublic() && $reflect_obj_before_index->invoke($reflect_instance); } $reflect_obj_index->invoke($reflect_instance); if ($reflect_obj->hasMethod('afterIndex')) { $reflect_obj_after_index = $reflect_obj->getMethod('afterIndex'); $reflect_obj_after_index->isPublic() && $reflect_obj_after_index->invoke($reflect_instance); } $reflect_obj->getMethod('test')->invoke($reflect_instance); } else { echo 'Index 方法不是公有的,不能调用'; } } else { echo '没有index方法,不允许调用'; } } else { echo '这个类不存在,不允许调用'; } //输出 //this is beforeIndex method //this is index method //this is afterIndex method //this is test method ?>
32、简单实现view的render功能
public function renderPhpFile($_file_, $_params_ = []) { ob_start(); ob_implicit_flush(false); extract($_params_, EXTR_OVERWRITE); require($_file_); return ob_get_clean(); //如果需要输出,可以把return 改成 echo; }
33、实现多层级菜单
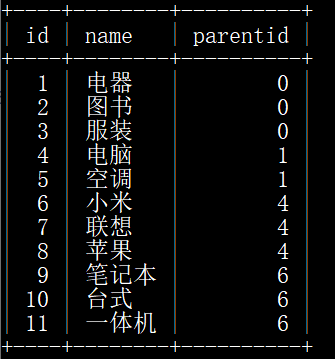
/** * @param $list表示列表 * @param int $pid 表示parentid * @param int $level 表示层级 * @return array */ public function getFilterList($list, $pid = 0, $level = 0) { $arr = []; array_walk($list, function($value)use(&$arr, $list, $pid, &$level) { if($value['parentid'] == $pid) { $value['name'] = sprintf("%s%s%s", $value['parentid'] == 0?'':'|', str_repeat('___', $level), $value['name']); array_push($arr, $value); $arr = array_merge($arr, $this->getFilterList($list, $value['id'], $level+1)); } }); return $arr; }