Windmill Animation
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 147 Accepted Submission(s): 75
Problem Description
A windmill animation works as follows:
A two-dimensional set of points, no three of which lie on a line is chosen. Then one of the points is chosen (as the first pivot) and a line is drawn through the chosen point at some initial angle. The animation proceeds by rotating the line counter-clockwise about the pivot at a constant rate. When the line hits another of the points, that point becomes the new pivot point. In the two examples below, the points are (-1,1), (1,1), (0,0), (-1,-2) and (1,-2).
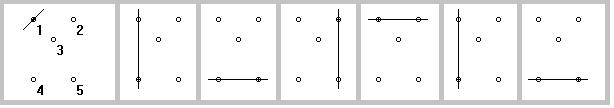
Example 1
In Example 1, the start point is point 1 and the line starts rotated 45 degrees from horizontal. When the line rotates to 90 degrees, point 4 is hit and becomes the new pivot. Then point 5 becomes the new pivot, then point 2 then point 1.
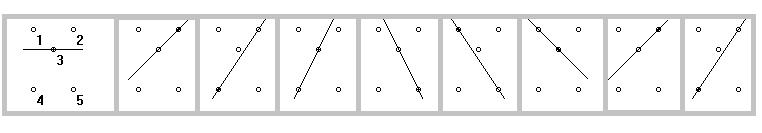
Example 2
In Example 2, the initial point is point 3 and the line starts horizontal. At 45 degrees, point 2 becomes the pivot, then at about 56 degrees, point 4 becomes the pivot. At about 63 degrees, point 3 becomes the pivot again, then point 5, point 1 and back to 3 as at the start.
Write a program, which takes as input the points of the set, the initial point and the initial line angle and outputs the sequence of pivot points.
A two-dimensional set of points, no three of which lie on a line is chosen. Then one of the points is chosen (as the first pivot) and a line is drawn through the chosen point at some initial angle. The animation proceeds by rotating the line counter-clockwise about the pivot at a constant rate. When the line hits another of the points, that point becomes the new pivot point. In the two examples below, the points are (-1,1), (1,1), (0,0), (-1,-2) and (1,-2).

In Example 1, the start point is point 1 and the line starts rotated 45 degrees from horizontal. When the line rotates to 90 degrees, point 4 is hit and becomes the new pivot. Then point 5 becomes the new pivot, then point 2 then point 1.

In Example 2, the initial point is point 3 and the line starts horizontal. At 45 degrees, point 2 becomes the pivot, then at about 56 degrees, point 4 becomes the pivot. At about 63 degrees, point 3 becomes the pivot again, then point 5, point 1 and back to 3 as at the start.
Write a program, which takes as input the points of the set, the initial point and the initial line angle and outputs the sequence of pivot points.
Input
The first line of input contains a single integer P, (1<= P <= 1000), which is the number of data sets that follow. Each data set should be processed identically and independently.
Each data set consists of multiple lines of input. The first line of each data set consists of four space- separated decimal integers followed by a single floating-point value. The first integer is the data set number. The second integer is the number of points M to follow (3 <= M <= 20). The third integer gives the number, s , of the pivot points to output (3 <= s <= 20) and the fourth integer gives the index, I, of the initial point (1 <= I <= M). The floating-point value is the angle, A, in degrees, that the initial line is rotated counter-clockwise from horizontal (0 <= A < 180).
The remaining M lines in the data set contain the coordinates of the set of points. Each line consists of an integer, the point.s index, I, and two floating-point values, the X and Y coordinates of the point respectively.
Each data set consists of multiple lines of input. The first line of each data set consists of four space- separated decimal integers followed by a single floating-point value. The first integer is the data set number. The second integer is the number of points M to follow (3 <= M <= 20). The third integer gives the number, s , of the pivot points to output (3 <= s <= 20) and the fourth integer gives the index, I, of the initial point (1 <= I <= M). The floating-point value is the angle, A, in degrees, that the initial line is rotated counter-clockwise from horizontal (0 <= A < 180).
The remaining M lines in the data set contain the coordinates of the set of points. Each line consists of an integer, the point.s index, I, and two floating-point values, the X and Y coordinates of the point respectively.
Output
For each data set there is a single line of output. It contains the data set number, followed by s space separated point indices (excluding the initial point index).
Sample Input
2
1 5 5 1 45
1 -1 1
2 1 1
3 0 0
4 -1 -2
5 1 -2
2 5 7 3 0
1 -1 1
2 1 1
3 0 0
4 -1 -2
5 1 -2
Sample Output
1 4 5 2 1 4
2 2 4 3 5 1 3 2
Source
方法:把题目中给出的任意两点连成的直线的斜率算出来并求得与x轴正向夹角并保存下来,以后每次找倾斜角角比当前直线倾斜角大的与其作差an[j][k]-a,如果倾斜角角比当前直线的小就+PI-当前的直线倾斜角an[j][k]+PI-a,这样找出最小的差值对应的点即为需要输出的点miny,然后更新旋转的那个店j,k1是与旋转点组成当前直线的另一个点,a是当前直线与x轴的夹角
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
struct map
{
double x,y;
}s[50];
double an[50][50],PI=acos(-1.0);
int main()
{
int i,j,k,p,m,ss,no,I,minx,miny,k1;
double a,temp,mina;
scanf("%d",&p);
while(p--)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d%lf",&no,&m,&ss,&I,&a);
a=a/180.0*PI;
for(i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&j);
scanf("%lf%lf",&s[j].x,&s[j].y);//这里写马虎了写成了%d,导致我耽误了好久来查错
}
printf("%d ",no);
for(i=1;i<m;i++)
{
for(j=i+1;j<=m;j++)
{
if(i!=j)
{
if(s[i].x-s[j].x)
{
temp=atan((s[i].y-s[j].y)/(s[i].x-s[j].x));
if(temp>=0)
an[i][j]=an[j][i]=temp;
else
an[i][j]=an[j][i]=temp+PI;
}
else
an[i][j]=an[j][i]=PI/2;
}
}
}
for(i=0,j=I,k1=I;i<ss;i++)//这里把j和k初始化为I,因为第一次直线上只有一个点
{
mina=PI;
for(k=1;k<=m;k++)
{
if(k!=j&&k!=k1)//保证不会取到直线上的两个点
{
if(an[j][k]>a)//角度比当前直线大
{
if(an[j][k]-a<mina)
{
mina=an[j][k]-a;
miny=k;
}
}
else//如果角度比当前直线小
{
if(an[j][k]+PI-a<mina)
{
mina=an[j][k]+PI-a;
miny=k;
}
}
}
}
if(i<ss-1)
printf("%d ",miny);
a=an[j][miny];//更新当前直线与x轴的夹角
k1=j;//更新组成当前直线的非旋转点
j=miny;
}
printf("%d
",miny);
}
return 0;
}