责任链模式是一种对象的行为模式【GOF95】。在责任链模式里,很多对象由每一个对象对其下家的引用而连接起来形成一条链。请求在这个链上传递, 直到链上的某一个对象决定处理此请求。发出这个请求的客户端并不知道链上的哪一个对象最终处理这个请求,这使得系统可以在不影响客户端的情况下动态地重新 组织链和分配责任。
从击鼓传花谈起
击鼓传花是一种热闹而又紧张的饮酒游戏。在酒宴上宾客依次坐定位置,由一人击鼓,击鼓的地方与传花的地方是分开的,以示公正。开始击鼓时,花束就开始依次传递,鼓声一落,如果花束在某人手中,则该人就得饮酒。
击鼓传花便是责任链模式的应用。责任链可能是一条直线、一个环链或者一个树结构的一部分。
二、 责任链模式的结构
责任链模式涉及到的角色如下所示:
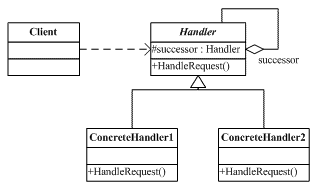
抽象处理者(Handler)角色:定义出一个处理请求的接口。如果需要,接口可以定义出一个方法,以设定和返回对下家的引用。这个角色通常由一个抽象类或接口实现。
具体处理者(ConcreteHandler)角色:具体处理者接到请求后,可以选择将请求处理掉,或者将请求传给下家。由于具体处理者持有对下家的引用,因此,如果需要,具体处理者可以访问下家。
要实现Chain of Responsibility模式,需要满足该模式的基本要件:
1,对象链的组织。需要将某任务的所有职责执行对象以链的形式加以组织。
2,消息或请求的传递。将消息或请求沿着对象链传递,以让处于对象链中的对象得到处理机会。
3,处于对象链中的对象的职责分配。不同的对象完成不同的职责。
4,任务的完成。处于对象链的末尾的对象结束任务并停止消息或请求的继续传递。
优点:
1,责任的分担。每个类只需要处理自己该处理的工作(不该处理的传递给下一个对象完成),明确各类的责任范围,符合类的最小封装原则。
2,可以根据需要自由组合工作流程。如工作流程发生变化,可以通过重新分配对象链便可适应新的工作流程。
3,类与类之间可以以松耦合的形式加以组织。
缺点:
因为处理时以链的形式在对象间传递消息,根据实现方式不同,有可能会影响处理的速度。
例子:
{
using System;
abstract class Handler
{
protected Handler successorHandler;
abstract public void HandleRequest(Request request);
public void SetSuccessor(Handler sucessor)
{
successorHandler = sucessor;
}
}
class ConcreteHandler1 : Handler
{
override public void HandleRequest(Request request)
{
// determine if we can handle the request
if (request.RequestType == 1) // some complex decision making!
{
// request handling code goes here
Console.WriteLine("request handled in ConcreteHandler1");
}
else
{
// not handled here - pass on to next in the chain
if (successorHandler != null)
successorHandler.HandleRequest(request);
}
}
}
class ConcreteHandler2 : Handler
{
override public void HandleRequest(Request request)
{
// determine if we can handle the request
if (request.RequestType == 2) // some complex decision making!
{
// request handling code goes here
Console.WriteLine("request handled in ConcreteHandler2");
}
else
{
// not handled here - pass on to next in the chain
if (successorHandler != null)
successorHandler.HandleRequest(request);
}
}
}
class ConcreteHandler3 : Handler
{
override public void HandleRequest(Request request)
{
// determine if we can handle the request
if (request.RequestType == 3) // some complex decision making!
{
// request handling code goes here
Console.WriteLine("request handled in ConcreteHandler3");
}
else
{
// not handled here - pass on to next in the chain
if (successorHandler != null)
successorHandler.HandleRequest(request);
}
}
}
class Request
{
private int iRequestType;
private string strRequestParameters;
public Request(int requestType, string requestParameters)
{
iRequestType = requestType;
strRequestParameters = requestParameters;
}
public int RequestType
{
get
{
return iRequestType;
}
set
{
iRequestType = value;
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Summary description for Client.
/// </summary>
public class Client
{
public static int Main(string[] args)
{
// Set up chain (usually one need to be done once)
Handler firstHandler = new ConcreteHandler1();
Handler secondHandler = new ConcreteHandler2();
Handler thirdHandler = new ConcreteHandler3();
firstHandler.SetSuccessor(secondHandler);
secondHandler.SetSuccessor(thirdHandler);
// After setting up the chain of responsibility, we can
// now generate requests and pass then off to the
// chain to be handled
// generate and fire request
Request newRequest = new Request(2,"This are the request parameters");
firstHandler.HandleRequest(newRequest);
return 0;
}
}
}