benchmark函数以benchmark开头
benchmark的case一般会跑b.N次,且每次执行都如此
在执行过程中会根据实际case的执行时间是否稳定会增加b.N的次数以达到稳态。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"testing"
)
func TestPrint(t *testing.T) {
res := Print1to20()
fmt.Println("hey")
if res != 210 {
t.Errorf("wrong result of Print1to20")
}
}
func TestPrint1(t *testing.T) {
res := Print1to20()
res++
if res != 211 {
t.Errorf("wrong result of Print1to20")
}
}
func TestMain(m *testing.M) {
fmt.Println("starting...")
m.Run()
}
func BenchmarkAll(b *testing.B) {
for n := 0; n < b.N; n++ {
Print1to20()
}
}
执行命令:
go test -bench=.
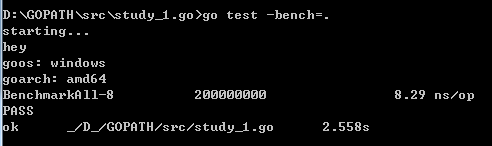
BenchmarkAll执行了200000000,每次执行耗时8.29ns
Benchmark函数首字母必须大写
Benchmark函数也是普通的test case之一,受TestMain限制
go test -benchmark -----只跑benchmark case
package main
import (
"fmt"
"testing"
)
func TestPrint(t *testing.T) {
res := Print1to20()
fmt.Println("hey")
if res != 210 {
t.Errorf("wrong result of Print1to20")
}
}
func TestPrint1(t *testing.T) {
res := Print1to20()
res++
if res != 211 {
t.Errorf("wrong result of Print1to20")
}
}
func aaa(n int) int {
return n
}
func TestMain(m *testing.M) {
fmt.Println("starting...")
m.Run()
}
func BenchmarkAll(b *testing.B) {
for n := 0; n < b.N; n++ {
aaa(n)
}
}
要注意benchmark函数执行能在一定时间内达到稳态,否则永远执行不完,没有结果