一。线程同步概念

二。互斥量(互斥锁)

1.pthread_mutex_init

2.pthread_mutex_destroy

3.pthread_mutex_lock(阻塞)
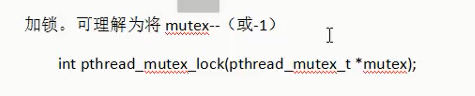
4.pthread_mutex_unlock

5.pthread_mutex_trylock(轮询尝试加锁 不阻塞)

6.互斥量示例
#include<pthread.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<string.h>
pthread_mutex_t mutex; //定义互斥量
void *thread_func(void *arg)
{
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); //子线程加锁
printf("hello ");
sleep(rand()%3);
printf("world
");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); //子线程解锁
sleep(rand()%3);
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL); //初始化mutex=1
pthread_t thid;
srand(time(NULL));
pthread_create(&thid,NULL,thread_func,NULL);
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); //主线程加锁
printf("HELLO");
sleep(rand()%3);
printf("WORLD
");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); //解锁
sleep(rand()%3);
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
三。死锁

#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<string.h>
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_mutex_t mutex1;
void *thread_func(void *arg)
{
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
printf("child pthread...
");
sleep(3);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex1);
printf("child pthread...
");
sleep(3);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex1);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(rand()%3);
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex1,NULL);
pthread_t thid;
srand(time(NULL));
pthread_create(&thid,NULL,thread_func,NULL);
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex1);
sleep(3);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
sleep(3);
printf("main pthread...");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex1);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(rand()%3);
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex1);
return 0;
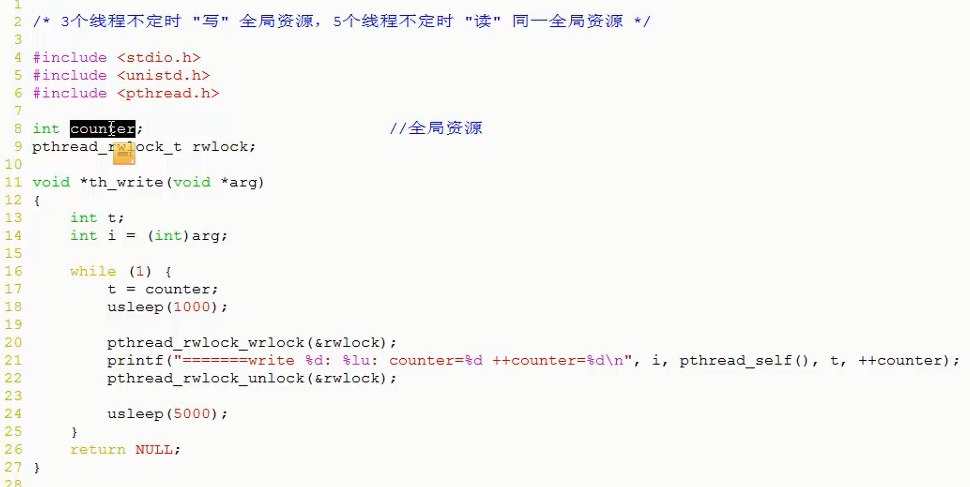
四。读写锁

写锁优先级高

1.pthread_rwlock_ini
2.pthread_rwlock_destroy
3.pthread_rwlock_rdlock
4.pthread_rwlock_wrlock
5.pthread_rwlock_unlock
6.读写锁示例


五。条件变量
1.条件变量基本概念


2.pthread_cond_wait

3.pthread_cond_timedwait


4.pthread_cond_signal
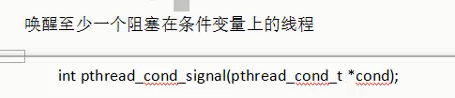
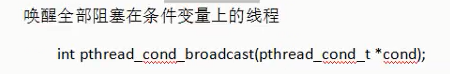
5.pthread_cond_broadcast
6.生产者消费者模型
#include<stdio.h> #include<pthread.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<stdlib.h>
//静态初始化 条件变量和互斥量 pthread_mutex_t mutex=PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; pthread_cond_t has_product=PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER; typedef struct node{ int data; struct node* next; }Linklist; Linklist* head=NULL; Linklist* mp=NULL; void* producter(void *arg) { while(1) { mp=(Linklist*)malloc(sizeof(Linklist)); mp->data=rand()%100+1; printf("product--------%d ",mp->data); pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); //得到互斥锁 mp->next=head; //生产 放入 共享池 head=mp; pthread_cond_signal(&has_product); //唤醒一个阻塞的线程 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); sleep(rand()%3); } return 0; } void* consumer(void *arg) { while(1) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); while(head==NULL) //若空,说明没有商品 { pthread_cond_wait(&has_product,&mutex); // 阻塞等待条件变量 ,释放互斥锁 } mp=head; //消费 head=head->next; pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); printf("consumer---------%d ",mp->data); free(mp); mp=NULL; sleep(rand()%3); } return 0; } int main() { pthread_t ptid,pcid; srand(time(NULL)); pthread_create(&ptid,NULL,producter,NULL); pthread_create(&pcid,NULL,consumer,NULL); pthread_join(ptid,NULL); pthread_join(pcid,NULL); return 0; }
7.条件变量优点

六。信号量
1.信号量基本概念



2.sem_init

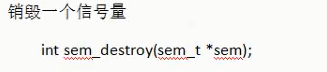
3.sem_destroy
4.sem_wait

5.sem_post

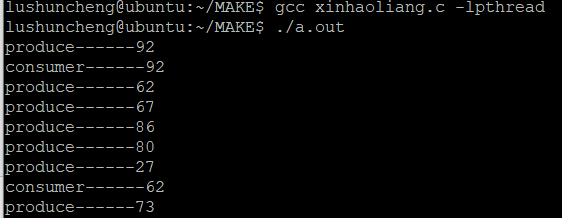
6.信号量模拟生产者消费者模型
#include<stdio.h>
#define NUM 5 //缓冲区个数
#include<pthread.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<semaphore.h>
sem_t buff; //信号量缓冲区
sem_t product; //信号量产品数
int data[NUM]; //临界区
void* producter(void *arg)
{
int i=0;
while(1)
{
sem_wait(&buff); //缓冲区个数--
data[i]=rand()%100+1; //生产
printf("produce------%d
",data[i]);
sem_post(&product); //产品数++
i=(i+1)%NUM;
sleep(rand()%4);
}
return 0;
}
void* consumer(void *arg)
{
int i=0;
while(1)
{
sem_wait(&product); //产品数--
printf("consumer------%d
",data[i]);
data[i]=0; //消费产品
sem_post(&buff); //缓冲区++
i=(i+1)%NUM;
sleep(20); //延迟20s
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t ptid,pcid;
srand(time(NULL));
sem_init(&buff,0,NUM); //初始化信号量buff为5
sem_init(&product,0,0); //初始化信号量product为0
pthread_create(&ptid,NULL,producter,NULL);
pthread_create(&pcid,NULL,consumer,NULL);
pthread_join(ptid,NULL);
pthread_join(pcid,NULL);
sem_destroy(&buff);
sem_destroy(&product);
return 0;
}
//缓冲区最多放5个产品,只有消费之后才能继续生产