现在的深度学习框架一般都是基于 Python 来实现,构建、训练、保存和调用模型都可以很容易地在 Python 下完成。但有时候,我们在实际应用这些模型的时候可能需要在其他编程语言下进行,本文将通过 C/C++ 间接调用 Python 的方式来实现在 C/C++ 程序中调用 TensorFlow 预训练好的模型。
1. 环境配置
-
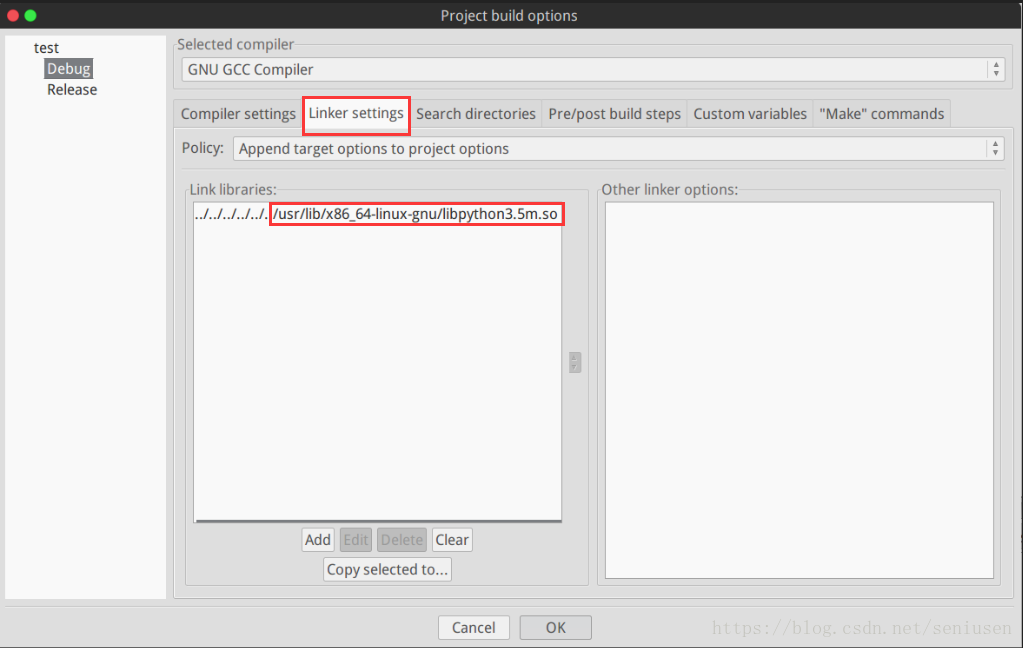
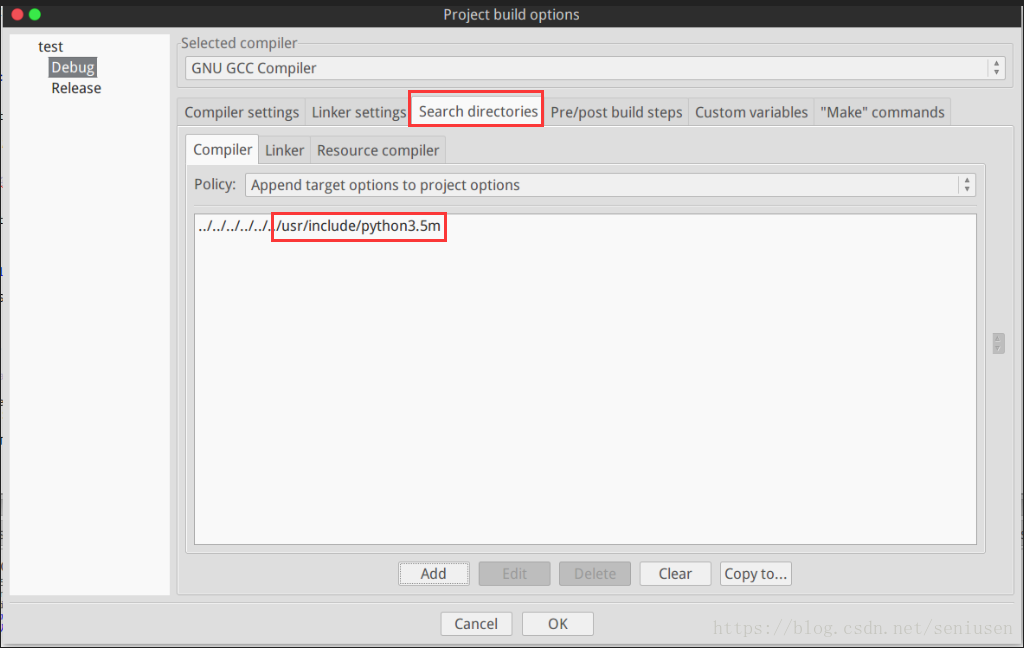
为了能在 C/C++ 中调用 Python,我们需要配置一下头文件和库的路径,本文以 Code::Blocks 为例介绍。
-
在 Build -> Project options 添加链接库 libpython3.5m.so 和头文件 Python.h 所在的路径,不同 Python 版本可以自己根据情况调整。
2. 初始化并导入 Python 模块及相关函数
void Initialize()
{
Py_Initialize();
if ( !Py_IsInitialized() )
{
printf("Initialize failed!");
}
// Path of the python file. 需要更改为 python 文件所在路径
PyRun_SimpleString("import sys");
PyRun_SimpleString("sys.path.append('/home/senius/python/c_python/test/')");
const char* modulName = "forward"; // Module name of python file.
pMod = PyImport_ImportModule(modulName);
if(!pMod)
{
printf("Import Module failed!
");
}
const char* funcName = "load_model"; // Function name in the python file.
load_model = PyObject_GetAttrString(pMod, funcName);
if(!load_model)
{
printf("Import load_model Function failed!
");
}
funcName = "predict"; // Function name in the python file.
predict = PyObject_GetAttrString(pMod, funcName);
if(!predict)
{
printf("Import predict Function failed!
");
}
PyEval_CallObject(load_model, NULL); // 导入预训练的模型
pParm = PyTuple_New(1); // 新建一个元组,参数只能通过元组传入 Python 程序
}
- 通过 PyImport_ImportModule 我们可以导入需要调用的 Python 文件,然后再通过 PyObject_GetAttrString 得到模块里面的函数,最后导入预训练的模型并新建一个元组作为参数的传入。
3. 构建从 C 传入 Python 的参数
void Read_data()
{
const char* txtdata_path = "/home/senius/python/c_python/test/04t30t00.npy";
//Path of the TXT file. 需要更改为txt文件所在路径
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen(txtdata_path, "rb");
if(fp == NULL)
{
printf("Unable to open the file!");
}
fread(data, num*SIZE, sizeof(float), fp);
fclose(fp);
// copying the data to the list
int j = 0;
pArgs = PyList_New(num * SIZE); // 新建一个列表,并填入数据
while(j < num * SIZE)
{
PyList_SET_ITEM(pArgs, j, Py_BuildValue("f", data[j]));
j++;
}
}
- 读入测试数据,并将数据填入到一个列表。
4. 将列表传入元组,然后作为参数传入 Python 中,并解析返回值
void Test()
{
PyTuple_SetItem(pParm, 0, pArgs);
pRetVal = PyEval_CallObject(predict, pParm);
int list_len = PyList_Size(pRetVal);
PyObject *list_item = NULL;
PyObject *tuple_item = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < list_len; i++)
{
list_item = PyList_GetItem(pRetVal, i);
tuple_item = PyList_AsTuple(list_item);
PyArg_ParseTuple(tuple_item, "f", &iRetVal[i]);
}
}
- 传入元组到 Python 程序,调用 predict 函数得到返回值,然后进行解析。
5. 一些参数和主函数
#include <Python.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE 41*41*41*3
#define NUM 100
PyObject* pMod = NULL;
PyObject* load_model = NULL;
PyObject* predict = NULL;
PyObject* pParm = NULL;
PyObject* pArgs = NULL;
PyObject* pRetVal = NULL;
float iRetVal[NUM*3] = {0};
float data[NUM * SIZE] = {0};
int num = 1; //实际的样本数100
void Initialize();
void Read_data();
void Test();
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
Initialize(); // 初始化
Read_data(); // 读入数据
Test(); // 调用预测函数并解析返回值
int j = 0;
while(j < num*3)
{
printf("%f
", iRetVal[j]);
j++;
}
printf("Done!
");
Py_Finalize();
return 0;
}
获取更多精彩,请关注「seniusen」!