题目如下:
We run a preorder depth first search on the
rootof a binary tree.At each node in this traversal, we output
Ddashes (whereDis the depth of this node), then we output the value of this node. (If the depth of a node isD, the depth of its immediate child isD+1. The depth of the root node is0.)If a node has only one child, that child is guaranteed to be the left child.
Given the output
Sof this traversal, recover the tree and return itsroot.Example 1:
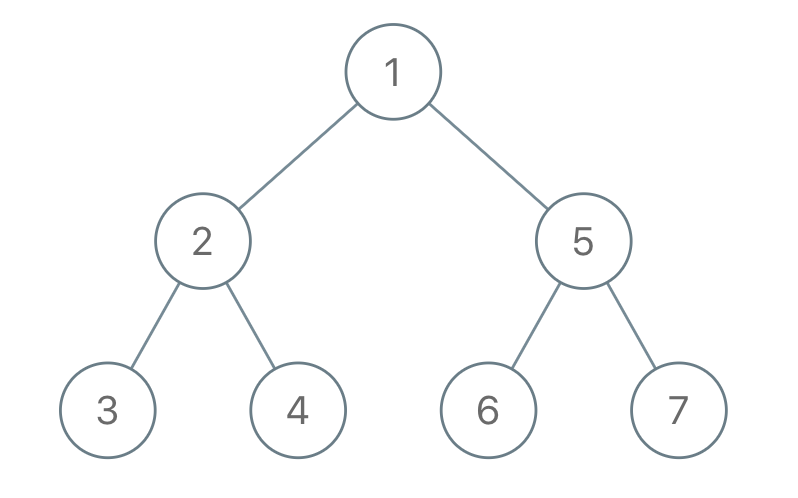
Input: "1-2--3--4-5--6--7" Output: [1,2,5,3,4,6,7]Example 2:
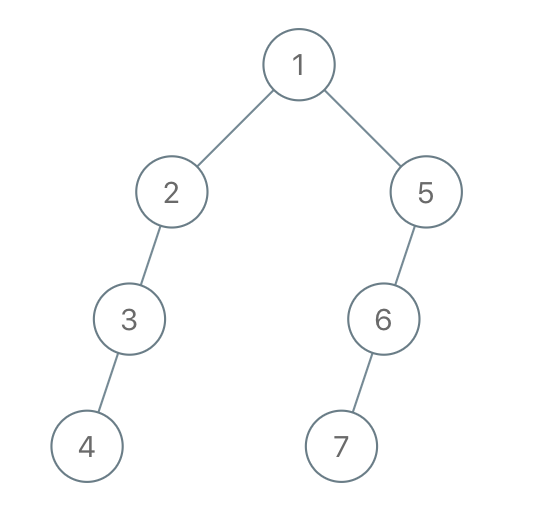
Input: "1-2--3---4-5--6---7" Output: [1,2,5,3,null,6,null,4,null,7]Example 3:
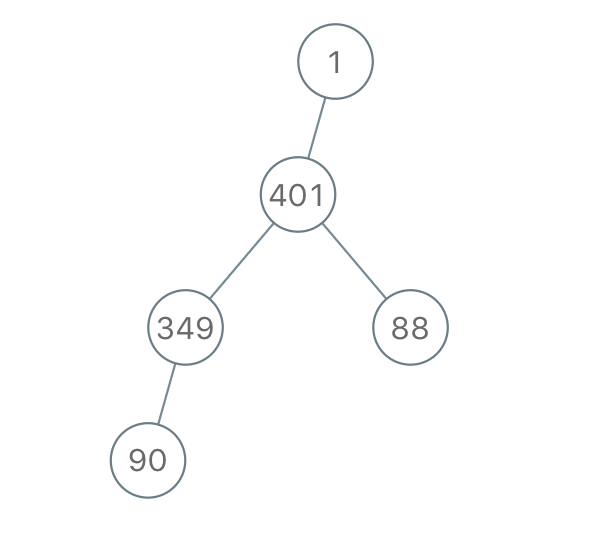
Input: "1-401--349---90--88" Output: [1,401,null,349,88,90]Note:
- The number of nodes in the original tree is between
1and1000.- Each node will have a value between
1and10^9.
解题思路:本题就是DFS的思想。首先解析Input,得到每个数值所对应的层级,接下来把Input中每个元素创建成树的节点,并且依次存入stack中。每次从Input新取出一个元素,判断其层级是否是stack中最后一个元素的层级加1,如果是表示这个节点是stack中最后一个元素的左子节点;如果是stack中倒数第二个元素的层级加1,如果是表示这个节点是stack中倒数第二个元素的右子节点;如果都不满足,stack中最后一个元素出栈,再继续做如上判断,直到找出其父节点为止。
代码如下:
# Definition for a binary tree node. # class TreeNode(object): # def __init__(self, x): # self.val = x # self.left = None # self.right = None class Solution(object): def recoverFromPreorder(self, S): """ :type S: str :rtype: TreeNode """ queue = [[0]] dashCount = 0 val = '' for i in S: if i == '-': if len(val) > 0: queue[-1].insert(0,val) val = '' dashCount += 1 else: if dashCount > 0: queue.append([dashCount]) dashCount = 0 val += i queue[-1].insert(0, val) #print queue item = queue.pop(0) root = TreeNode(int(item[0])) nodeList = [[root,item[1]]] while len(queue) > 0: val,level = queue.pop(0) while len(nodeList) > 0: if level == nodeList[-1][1] + 1: node = TreeNode(int(val)) nodeList[-1][0].left = node nodeList.append([node,level]) break elif len(nodeList) >= 2 and level == nodeList[-2][1] + 1: node = TreeNode(int(val)) nodeList[-2][0].right = node nodeList.append([node, level]) break else: nodeList.pop() return root